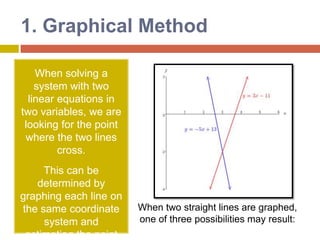
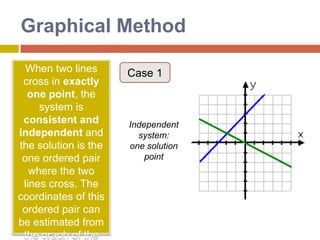
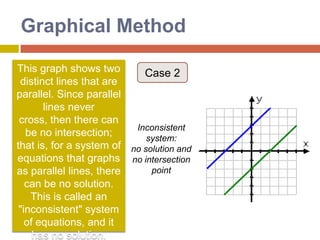
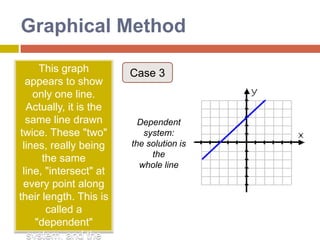
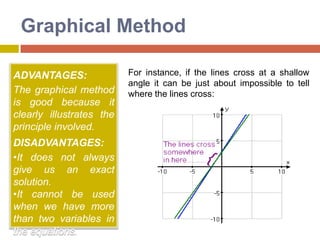
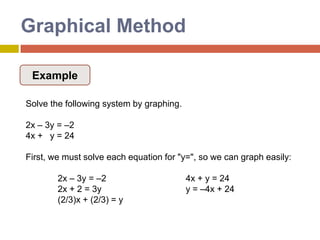
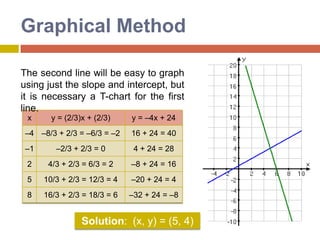
1) The graphical method involves graphing the lines represented by each equation on the same coordinate plane and finding the point where they intersect, which gives the solution.
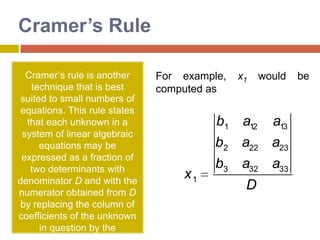
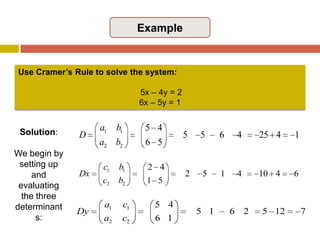
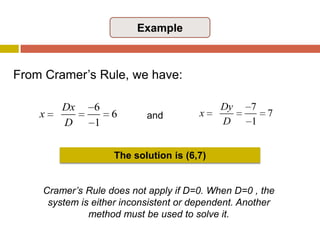
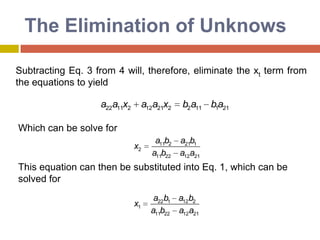
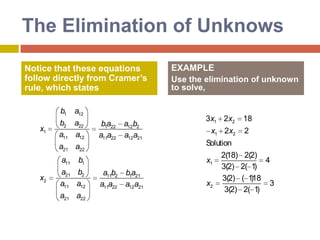
2) Cramer's rule expresses each unknown as a ratio of determinants, with the numerator being the determinant of the coefficient matrix with one column replaced by the constants.
3) Gaussian elimination transforms the coefficient matrix into upper triangular form using elementary row operations, then back substitution solves for the unknowns.


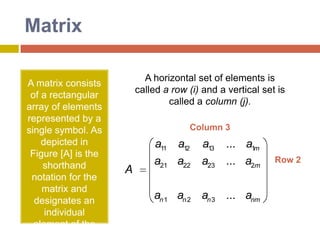

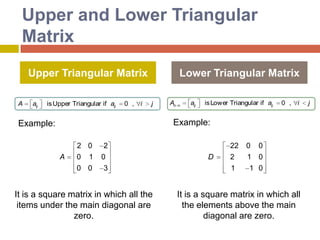
![MatrixA horizontal set of elements is called a row(i) and a vertical set is called a column (j). A matrix consists of a rectangular array of elements represented by a single symbol. As depicted in Figure [A] is the shorthand notation for the matrix and designates an individual element of the matrix.Column 3Row 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/directmethods-100727140401-phpapp01/85/Direct-methods-10-320.jpg)
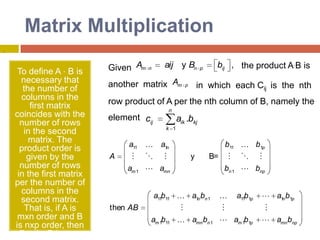
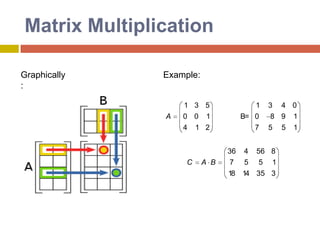










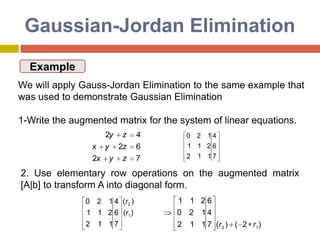

![GaussianEliminationThe general procedure for Gaussian Elimination can be summarized in the following steps: Write the augmented matrix for the system of linear equations. Use elementary row operations on the augmented matrix [A|b] to transform A into upper triangular form. If a zero is located on the diagonal, switch the rows until a nonzero is in that place. If you are unable to do so, stop; the system has either infinite or no solutions. Use back substitution to find the solution of the problem.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/directmethods-100727140401-phpapp01/85/Direct-methods-39-320.jpg)
![GaussianEliminationExample1. Write the augmented matrix for the system of linear equations.2.Use elementary row operations on theaugmented matrix [A|b] to transform A into upper triangular form.Change row 1 to row 2and vice versa](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/directmethods-100727140401-phpapp01/85/Direct-methods-40-320.jpg)

