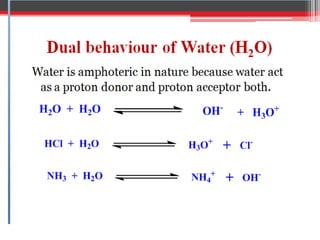
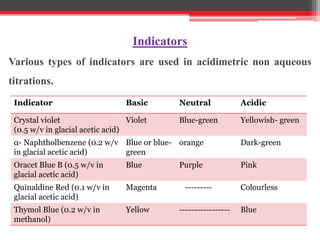
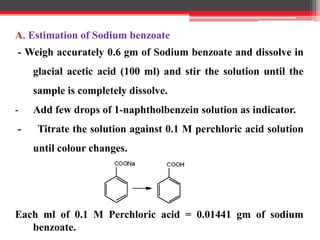
Non-aqueous titration is used when reactants are insoluble or reactive with water, or are very weak acids or bases that do not fully dissociate. Water is replaced by other solvents like perchloric acid. Non-aqueous titration can estimate weak acids and bases that cannot be easily titrated in water due to its amphoteric nature. Common types of non-aqueous titration include acidimetry, using acidic solvents and perchloric acid as the titrant to estimate weak bases, and alkalimetry, using basic solvents and sodium methoxide as the titrant to estimate weak acids.