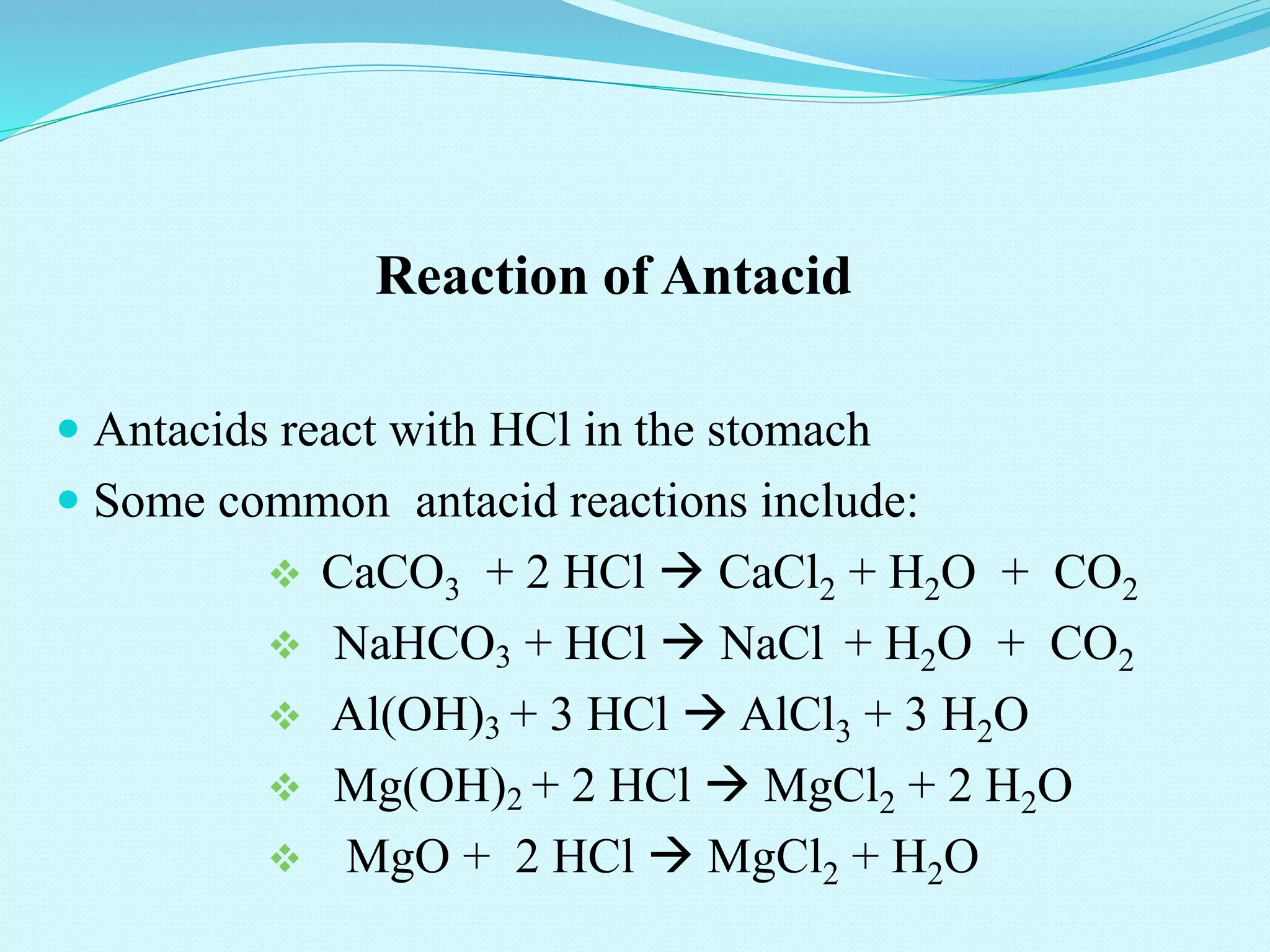
This document provides information about antacids. It defines antacids as weak bases that neutralize excess stomach acid through reactions in the stomach. Common antacid compounds include calcium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, aluminum hydroxide, and magnesium hydroxide. Antacids are available in capsule, tablet, powder, and liquid forms. They are used to relieve conditions caused by excess stomach acid like heartburn and ulcers. While helpful for acid reduction, antacids can cause side effects like diarrhea or constipation if taken long term.