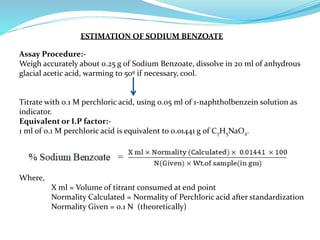
This document discusses non-aqueous titrations, which are used to analyze organic acids and bases that are insoluble or weakly reactive in water. It describes the principles, reasons for using non-aqueous titrations, common solvents like acetic acid, and provides examples of procedures to titrate drugs like ephedrine hydrochloride and sodium benzoate. The key steps involve dissolving the analyte in a non-aqueous solvent, titrating with an acid or base, and determining the endpoint using an indicator reaction.





![THEORY:-
According to Bronsted - Lowry theory the various reactions that take place
during many non-aqueous titrations.
Where, an acid is a proton donor and a base is a proton acceptor. Therefore,
when an acid [HA] undergoes dissociation it gives rise to a proton and the
conjugate base [A] of the acid:-
HA H+ + A-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nonaqueoustitration-210409143900/85/Non-aqueous-titration-6-320.jpg)