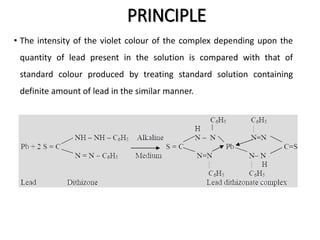
This document describes the limit test for lead using diphenylthiocarbazone (dithizone) which forms a violet colored lead-dithizonate complex in an alkaline medium. The method separates any lead impurity in a substance by extracting an alkaline solution with dithizone chloroform solution. The intensity of the violet color complex is then compared to a standard lead solution to determine the amount of lead present.