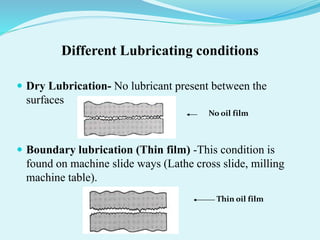
This presentation discusses lubricants, including their composition, properties, functions, and different types. Lubricants are substances that reduce friction between surfaces. They typically contain 90% base oil and less than 10% additives. Additives can improve properties like oxidation resistance. Lubrication reduces wear, friction, heat, noise, and corrosion. Different lubrication methods include oil cans, grease packing, and circulation systems. Lubricant types include solid, semi-solid, liquid, synthetic, animal, vegetable, and mineral oils. Properties like viscosity, stability, volatility, and thermal stability were also covered.