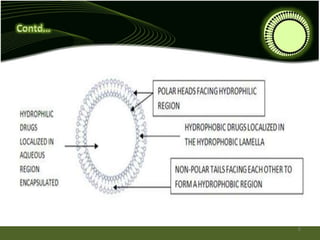
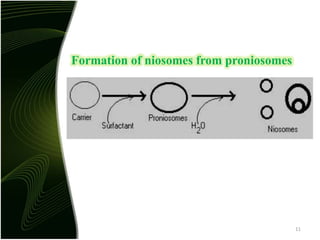
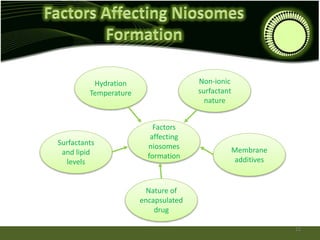
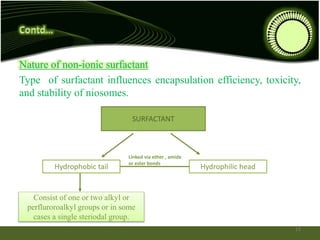
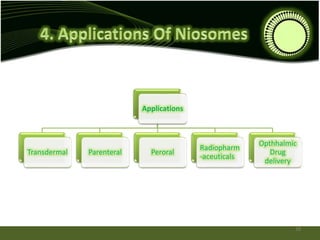
Niosomes are novel drug delivery systems composed of non-ionic surfactants and cholesterol. They can encapsulate both hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs. Niosomes are prepared using methods like ether injection, film hydration, sonication, and microfluidization. Key factors that affect niosome formation include the surfactant used, addition of cholesterol, and hydration temperature. Niosomes offer advantages over liposomes like improved stability and the ability to entrap both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs. Niosomes find applications in targeted drug delivery through routes like transdermal, parenteral, oral and for ophthalmic and radiopharmaceutical uses.