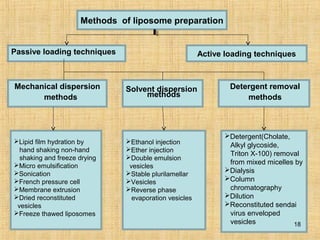
Liposomes are spherical vesicles composed of a lipid bilayer membrane enclosing an aqueous core. They can encapsulate both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs. Liposomes offer several advantages for drug delivery such as increased drug efficacy, reduced toxicity, and ability to target specific tissues. They are classified based on lamellarity and size. Common preparation methods include thin film hydration, reverse phase evaporation, and detergent removal. Key properties evaluated include particle size, surface charge, drug encapsulation efficiency, and drug release kinetics. Liposomes have applications as carriers for drugs, proteins, genes, and imaging agents.



















![4. Phase behavior
• At transition temperature liposomes undergo reversible phase
transition
• The transition temperature is the indication of stability
permeability and also indicates the region of drug entrapment
• Done by DSC
5. Drug Release Rate
The rate of drug release from the liposomes can be determined
by in vivo assays which helps to predict the pharmacokinetics
and bioavailability of the drug. However in vivo studies are
found to be more complete.
Liposome encapsulating the tracer [ H] insulin are employed forᵌ
the study. This [ H] insulin is preferred, as it is released onlyᵌ
in the ECF and undergoes rapid renal excretion of the face
tracer coupled to the degradation rate constant o the tracer
released from the liposomes. 22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/liposomes-150507145537-lva1-app6891/85/Liposomes-22-320.jpg)

