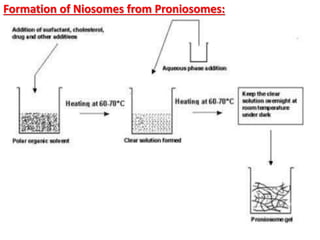
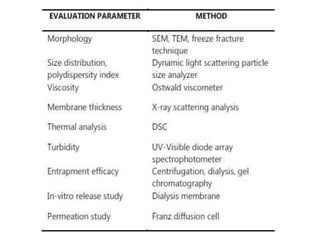
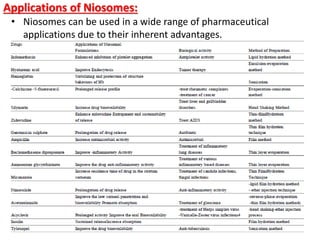
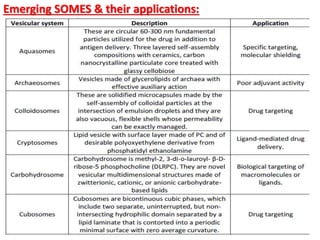
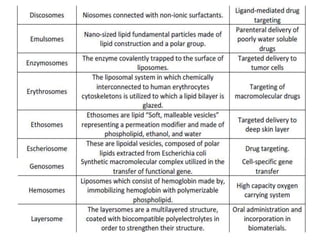
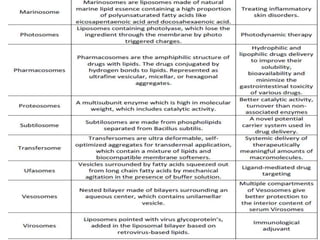
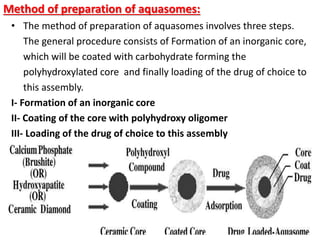
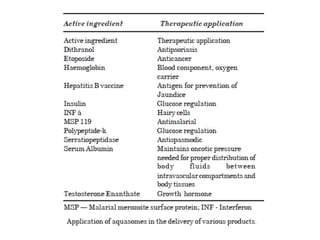
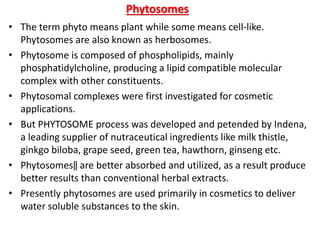
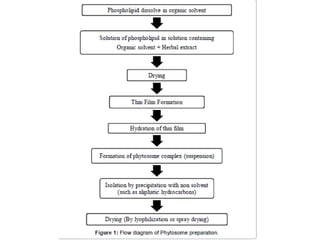
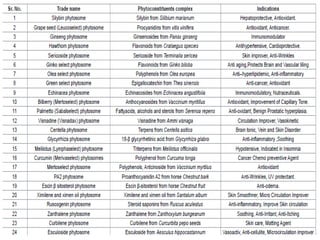
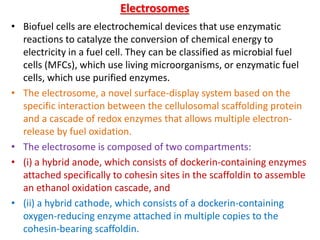
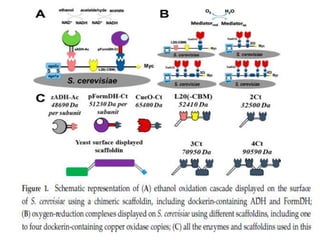
This document discusses niosomes, which are non-ionic surfactant vesicles that can be used as drug carriers. Niosomes are formed using cholesterol and nonionic surfactants through techniques like thin film hydration, sonication, microfluidization. They can encapsulate both hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs. Compared to liposomes, niosomes are more stable and less expensive to produce. Niosomes show potential for targeted drug delivery and sustained release, making them a promising drug delivery system.