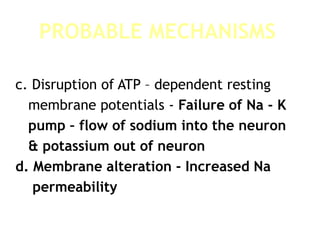
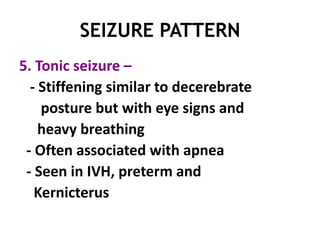
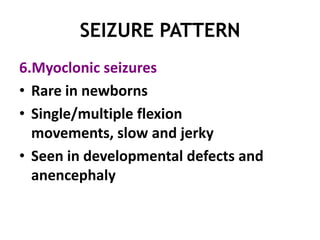
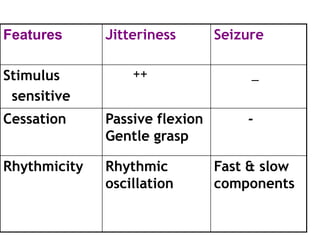
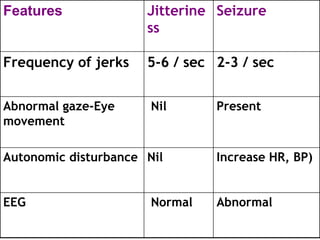
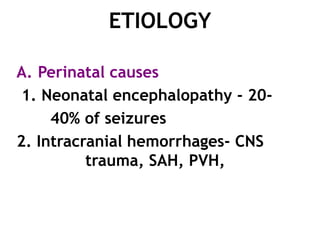
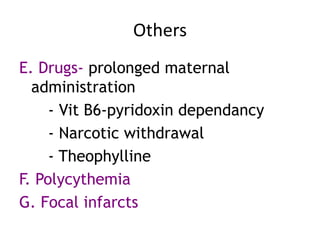
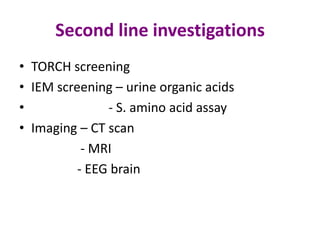
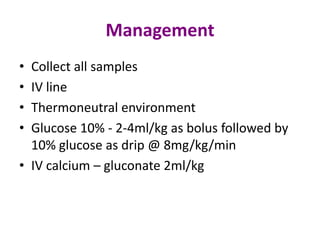
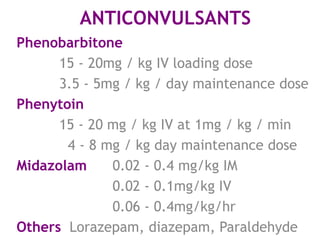
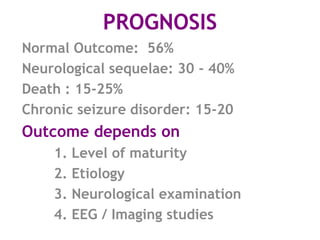
This document discusses neonatal seizures, beginning with an introduction stating they are not uncommon and often the first sign of neurological disorders. It then covers the pathophysiology, incidence, patterns, etiology, diagnosis, management, treatment including anticonvulsants, and prognosis of neonatal seizures over multiple pages with headings and subheadings. Key points include seizures occurring in 1 in 200 healthy newborns, various possible causes like hypoglycemia or infections, treatments involving anticonvulsants like phenobarbital or midazolam, and prognosis varying from normal outcome to neurological sequelae depending on factors like etiology and examination findings.
![Neonatal Seizures
Dr. Kalpana Malla
MD Pediatrics
Manipal Teaching Hospital
Download more documents and slide shows on The Medical Post [ www.themedicalpost.net ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newborn-neonatalseizures-120107084218-phpapp01/85/Neonatal-seizures-1-320.jpg)























![Thank you
Download more documents and slide shows on The
Medical Post [ www.themedicalpost.net ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newborn-neonatalseizures-120107084218-phpapp01/85/Neonatal-seizures-36-320.jpg)