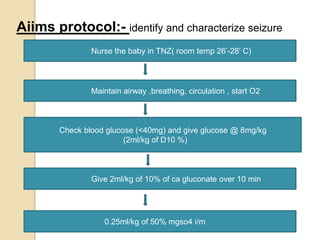
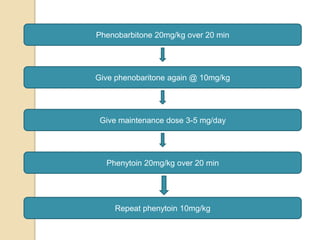
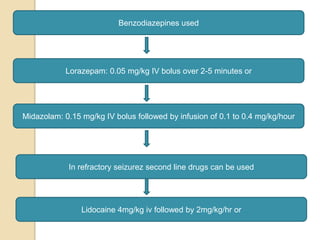
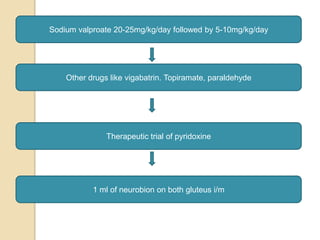
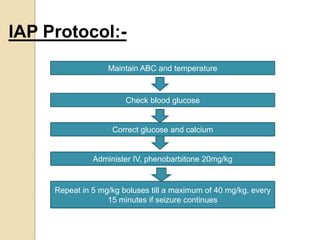
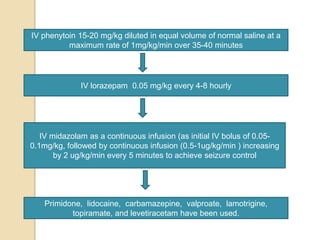
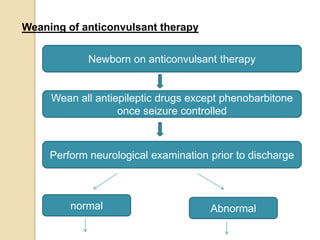
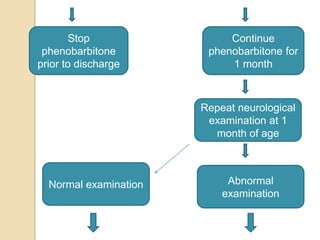
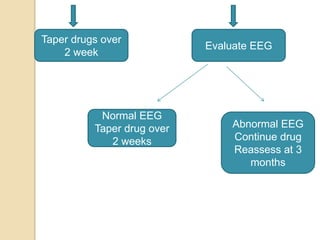
This document discusses protocols for treating neonatal seizures. It defines seizures and classifies them as epileptic, non-epileptic, or EEG-only seizures. It describes different types of seizures including subtle, clonic, tonic, and myoclonic seizures. It then outlines the AIIMS, IAP, and Nelson protocols for treating neonatal seizures, which involve maintaining vital signs, checking glucose, administering anti-seizure medications like phenobarbital and phenytoin, and in refractory cases using additional medications. It provides guidance on weaning anti-seizure medications and monitoring the infant neurologically before discharge.