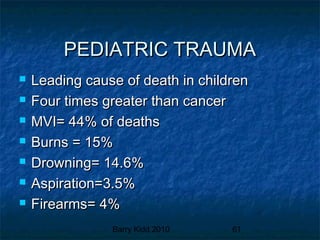
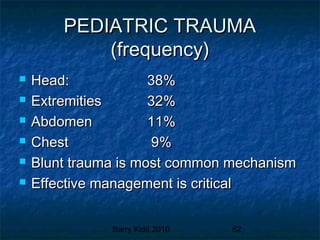
This document provides an overview of pediatric emergencies and assessments. It discusses pediatric development across different age groups and how that impacts examinations. Key points include how trauma is the leading cause of death for children, the importance of involving parents in assessments, and anatomical and physiological differences between children and adults that providers must consider. Proper communication and understanding a child's development level are essential for pediatric assessments.