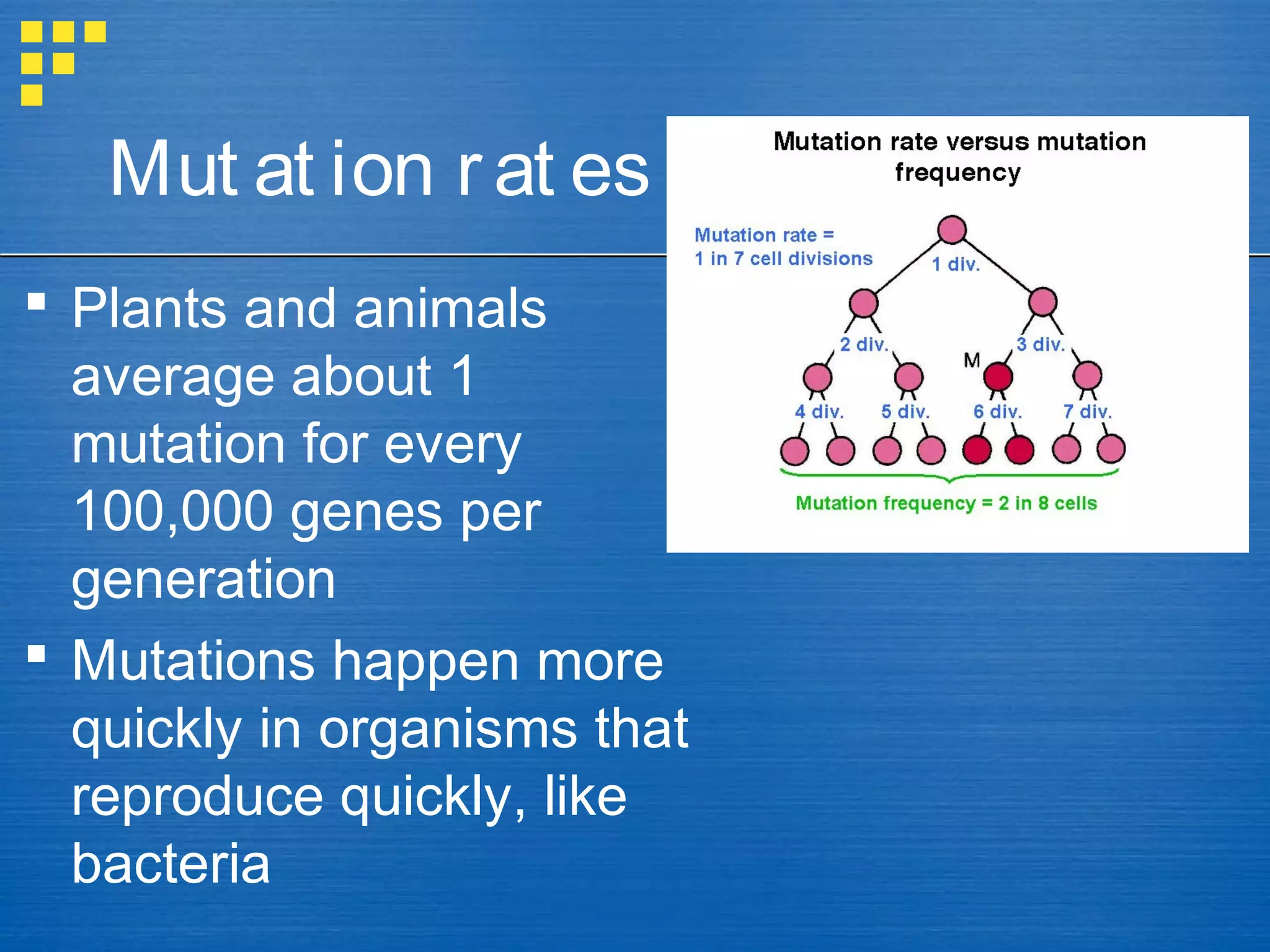
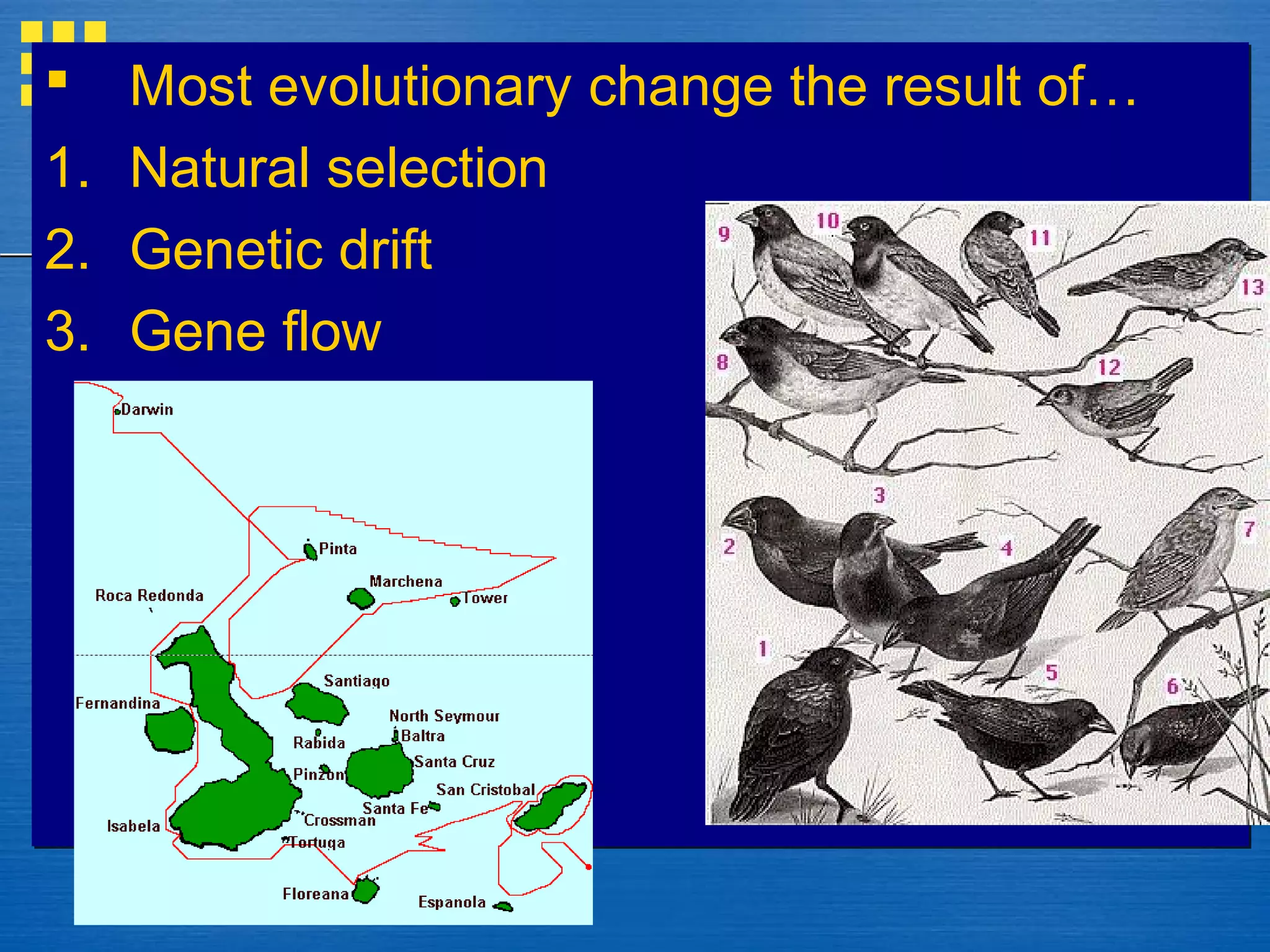
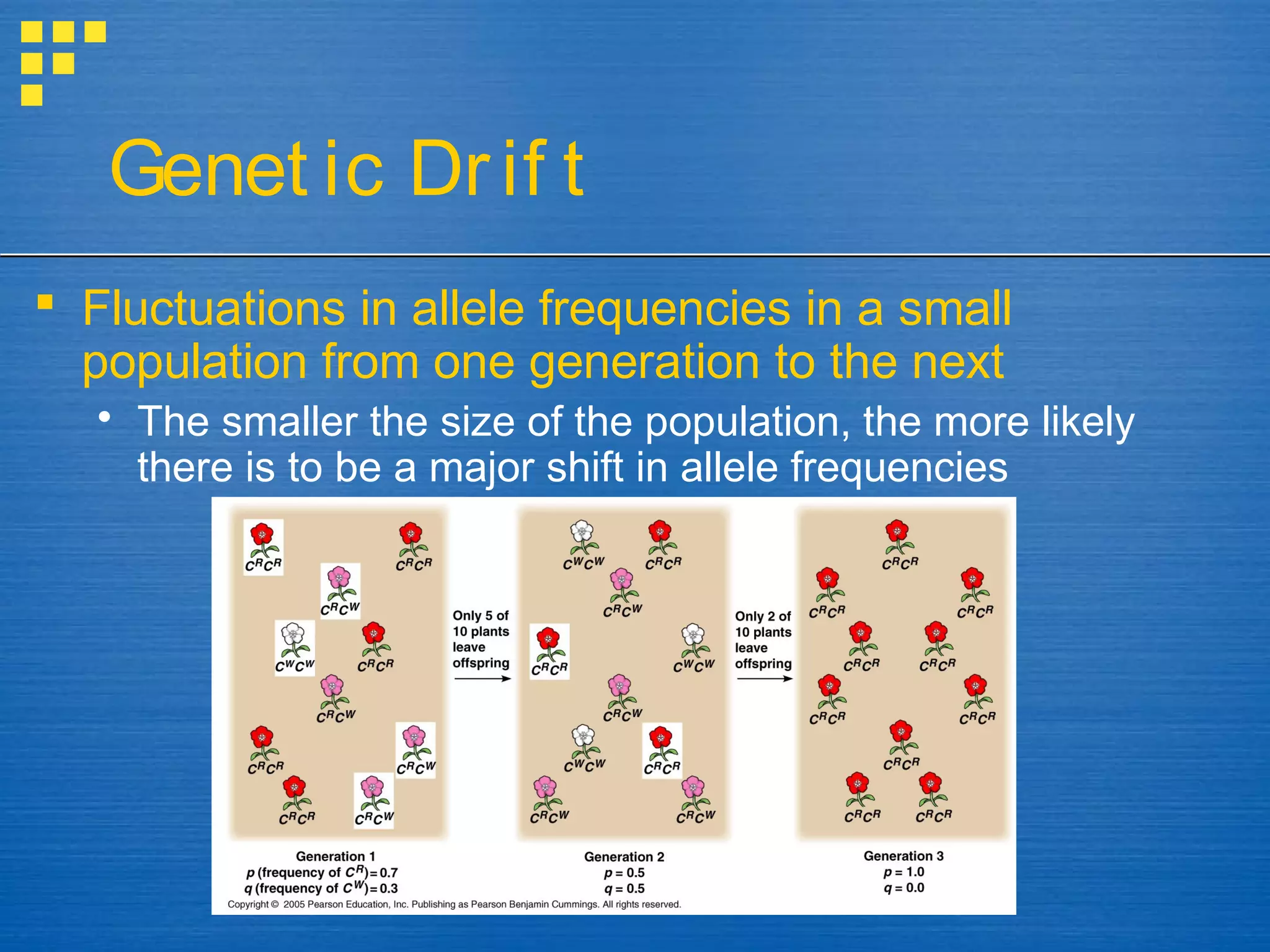
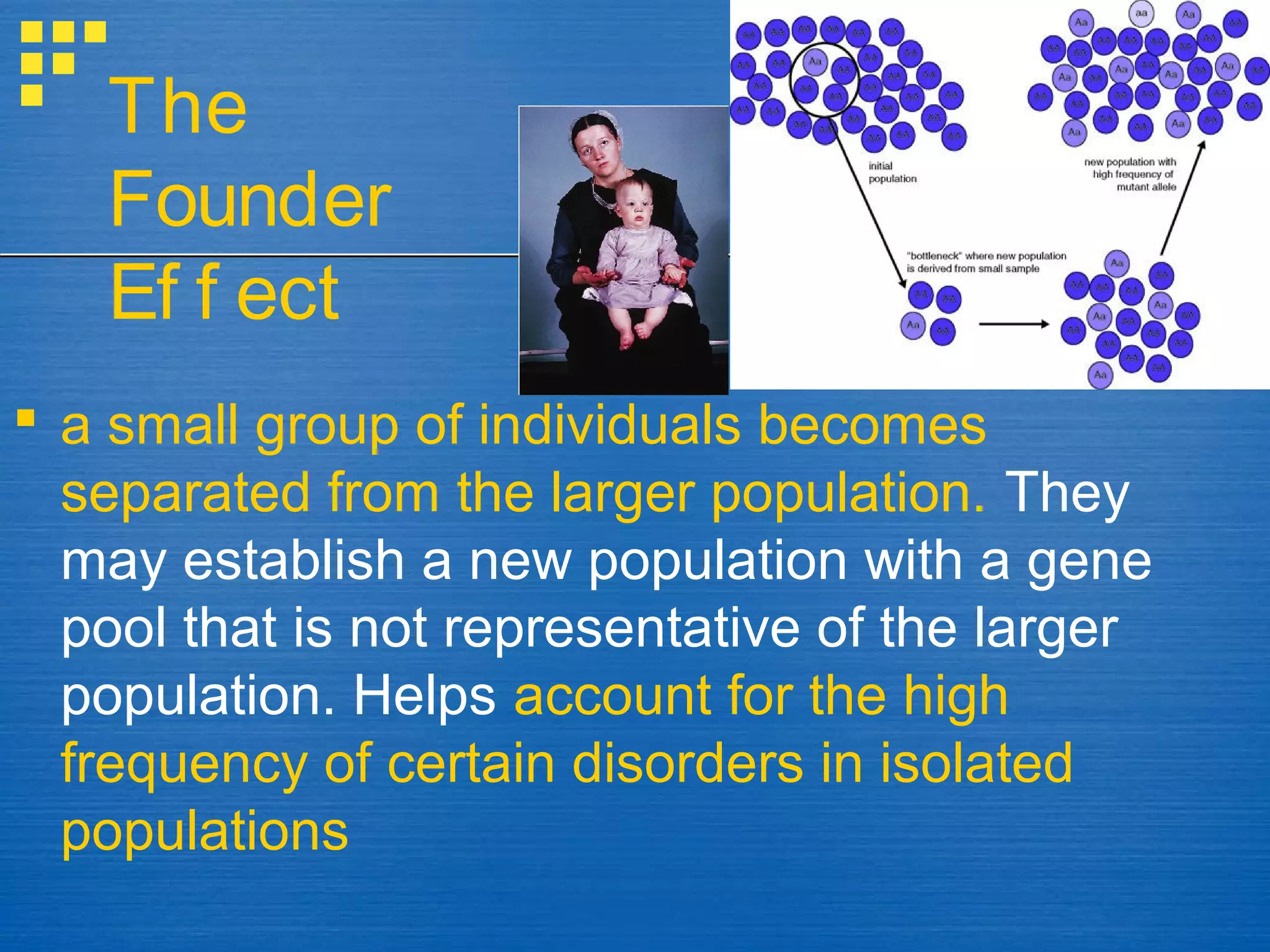
Mutations and genetic recombination introduce genetic variation within populations. Natural selection acts on this variation, favoring traits that increase reproductive success. Over generations, this leads to adaptation and evolution of populations as allele frequencies change. Genetic drift also causes random changes in allele frequencies, especially in small, isolated populations. Gene flow moves alleles between populations through migration.