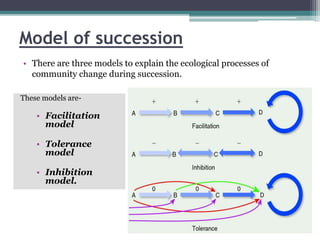
This document discusses ecological succession, which is the process of change in species composition of a community over time. It defines primary and secondary succession, and describes different types of succession including autogenic, allogenic, autotrophic, heterotrophic, progressive, and retrogressive succession. It also discusses Clements' model of succession involving nudation, invasion, ecesis, aggregation, competition, reaction, and stabilization. Finally, it outlines three major theories of climax communities - monoclimax, polyclimax, and climax pattern theory - and three models of succession - facilitation, tolerance, and inhibition.