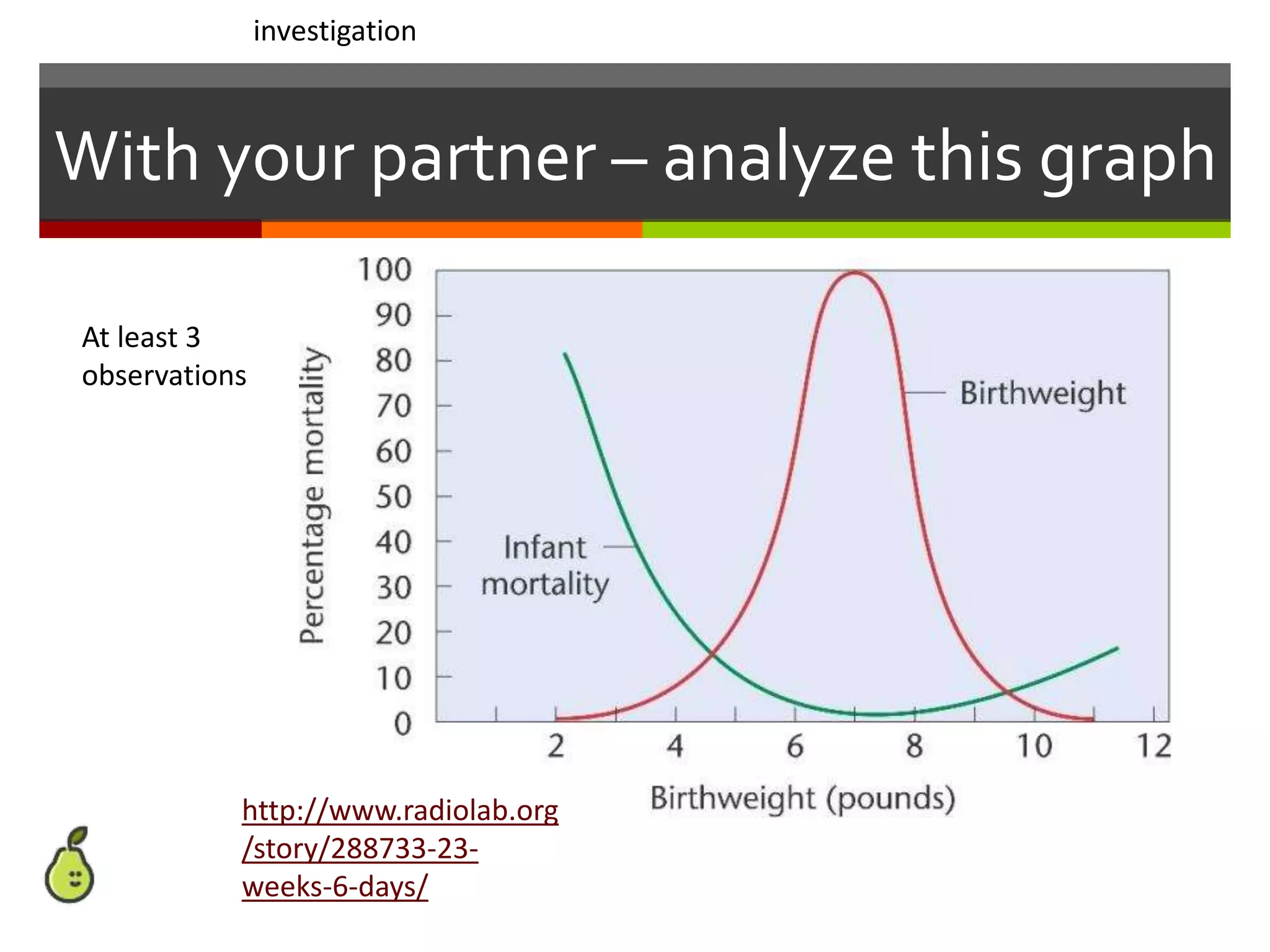
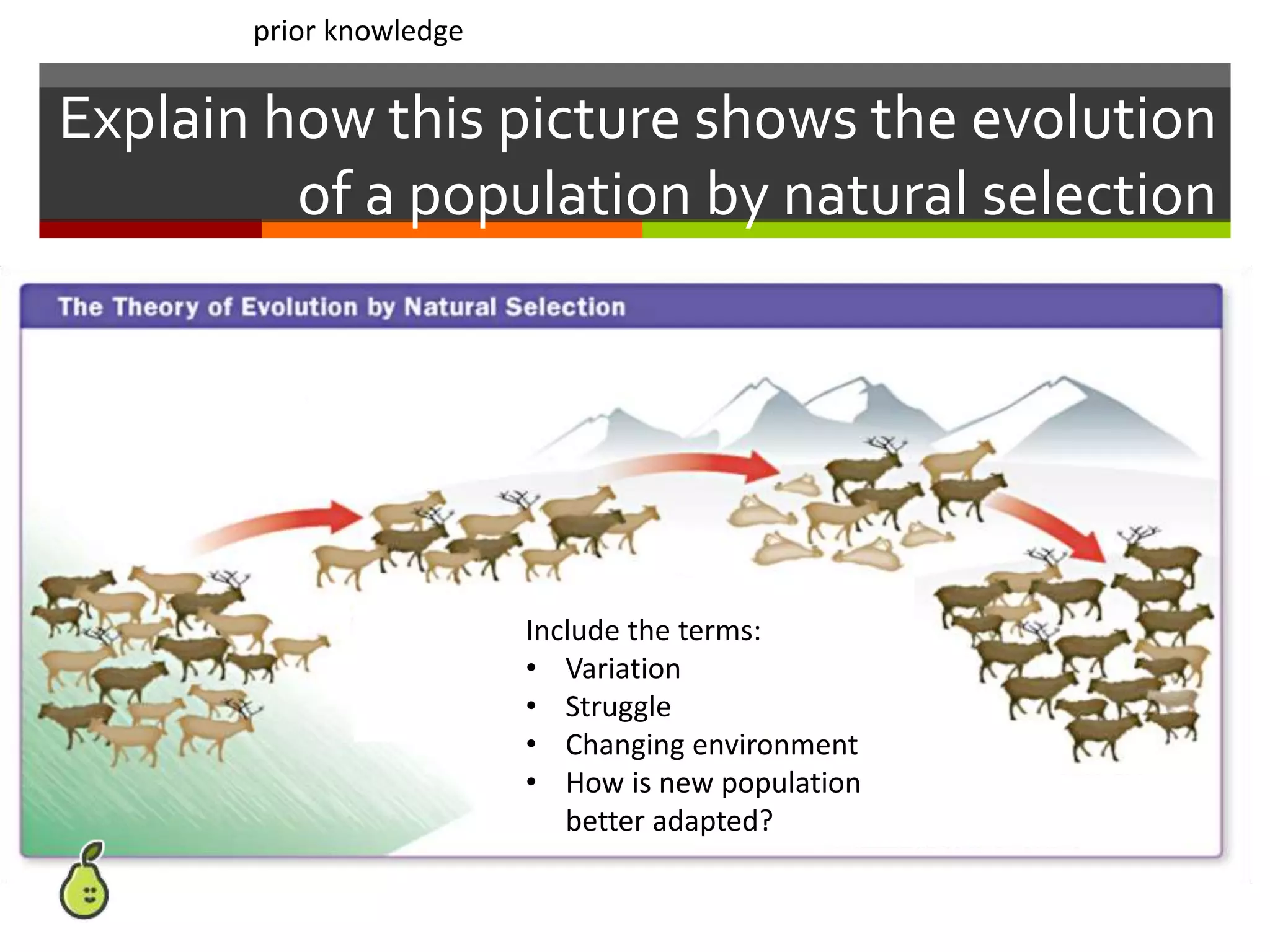
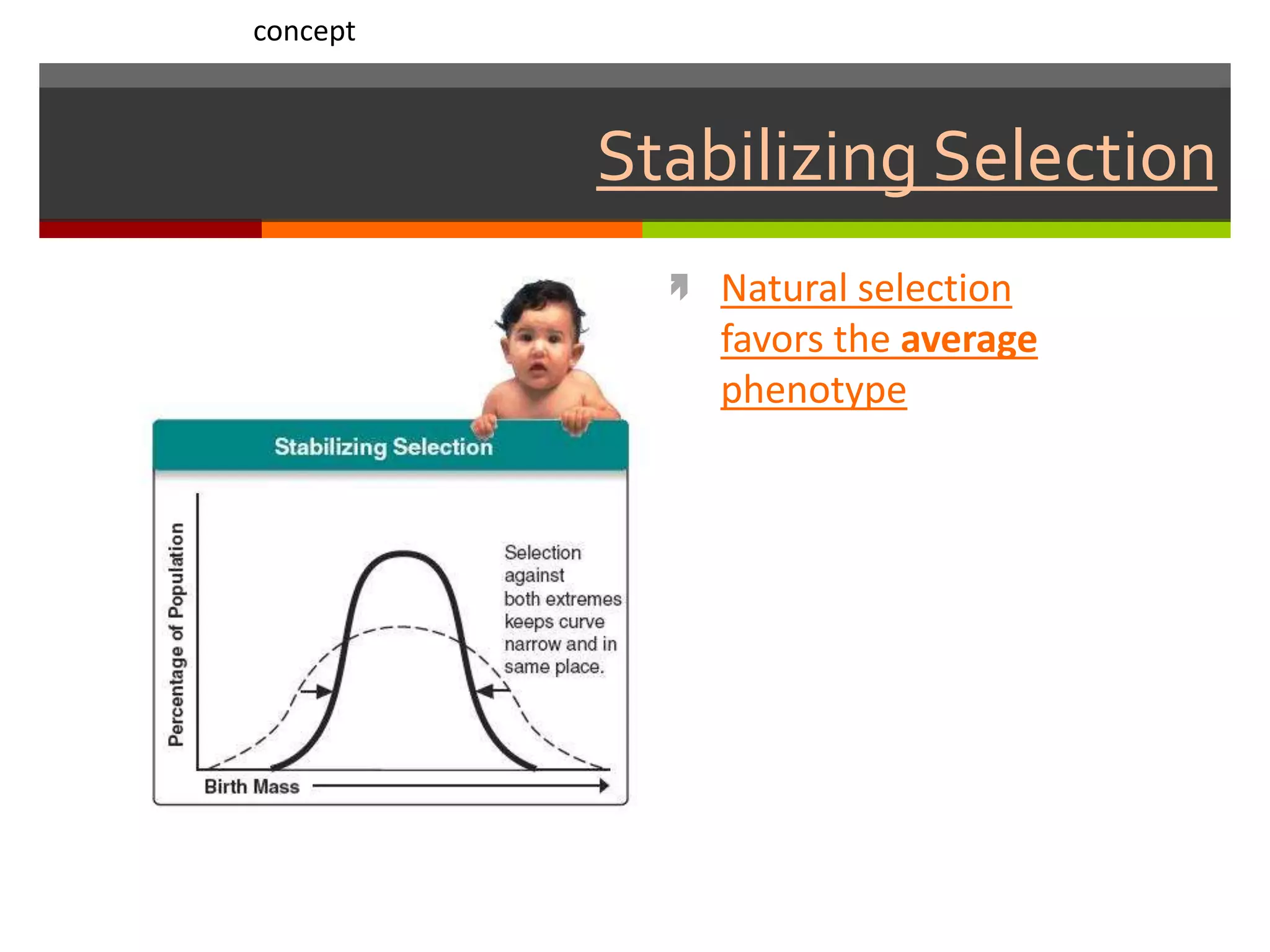
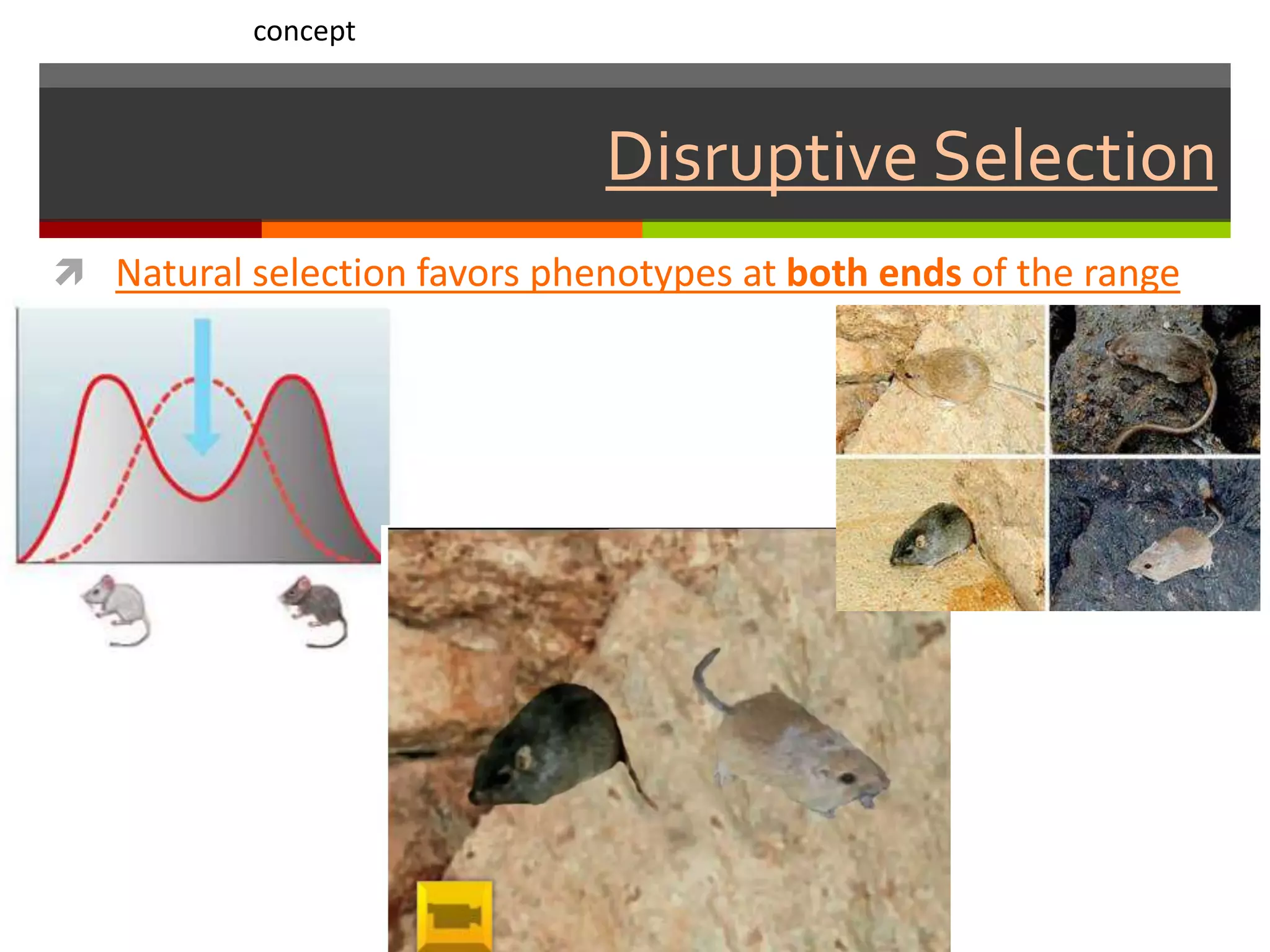
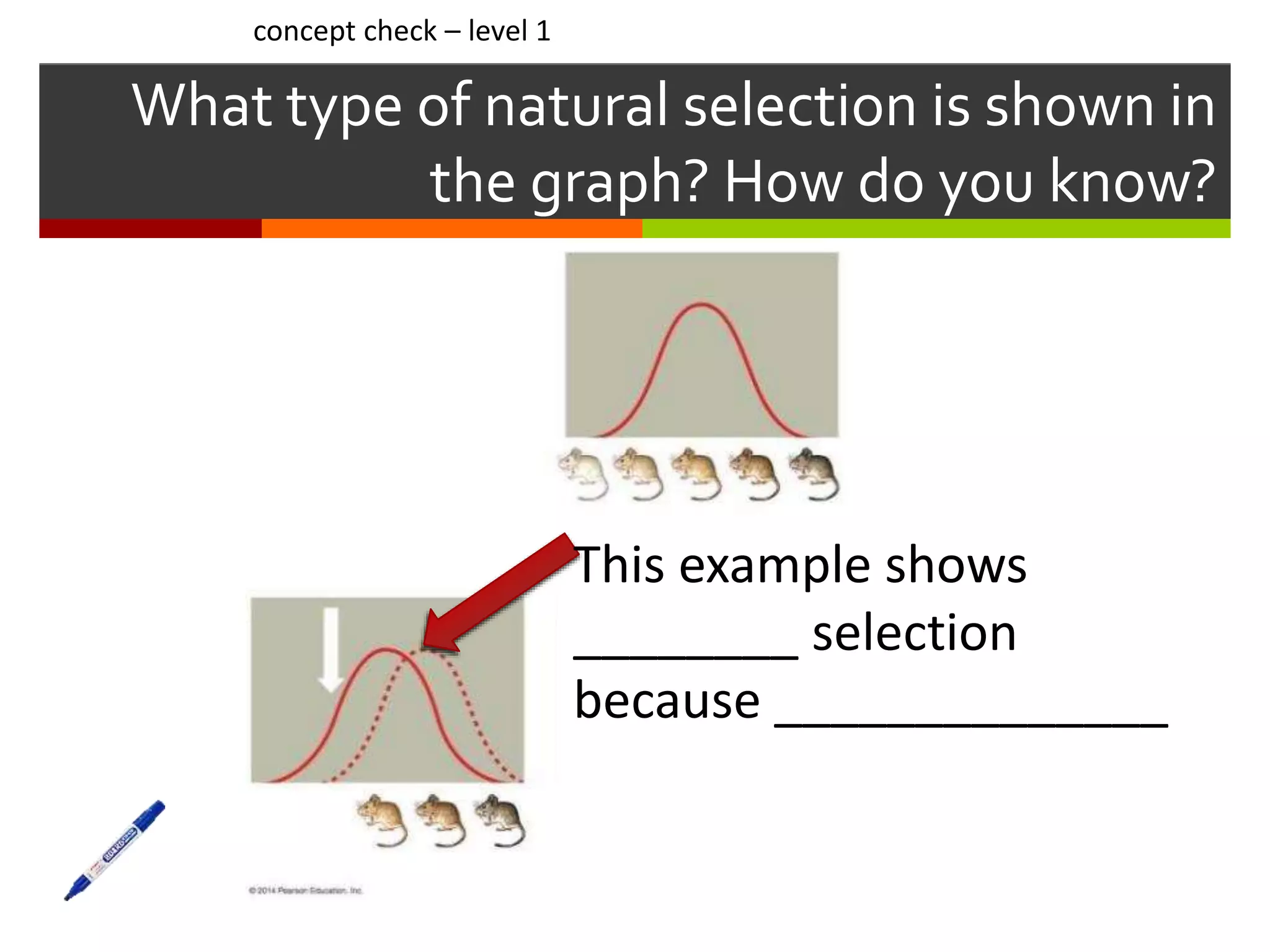
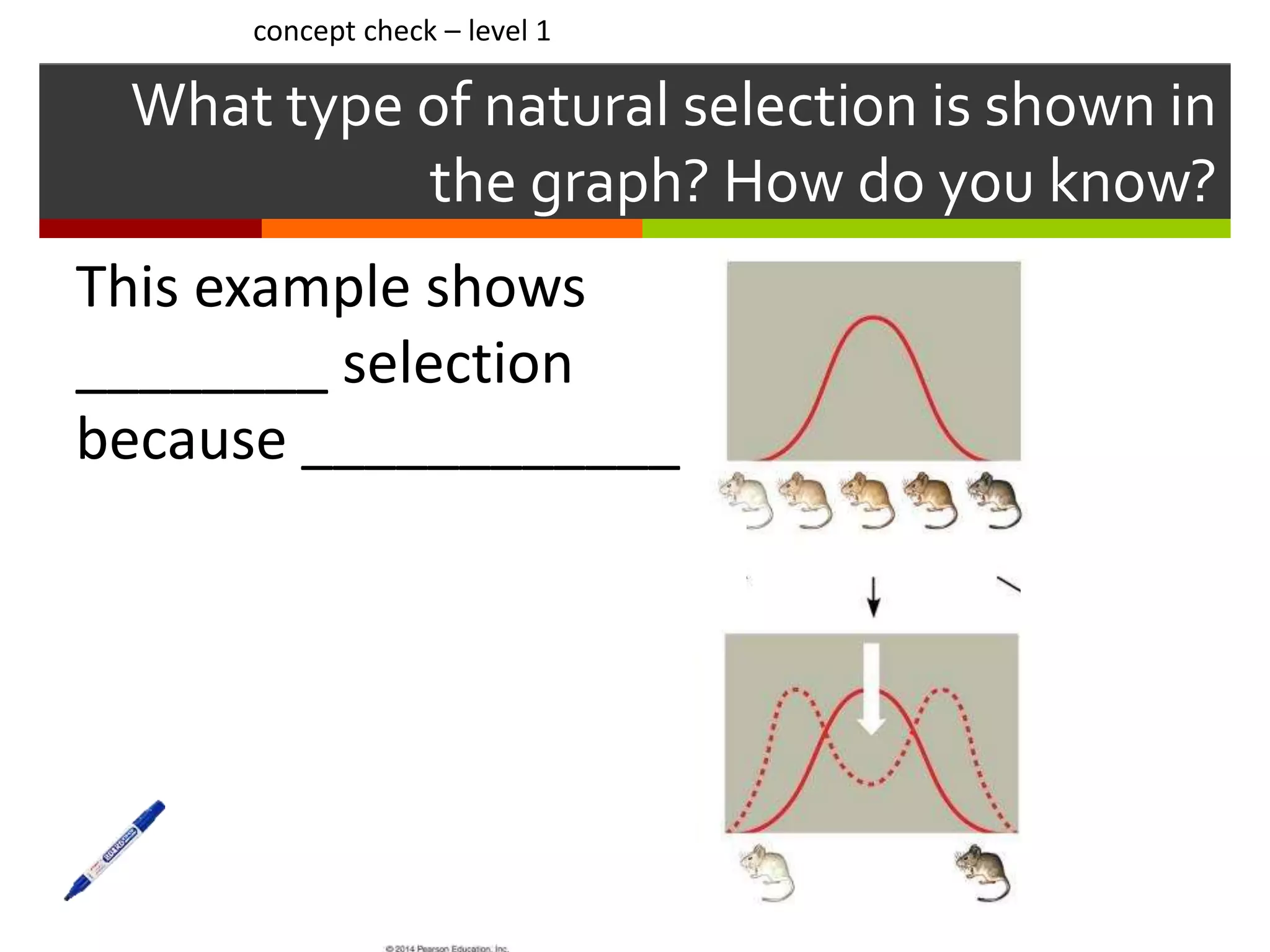
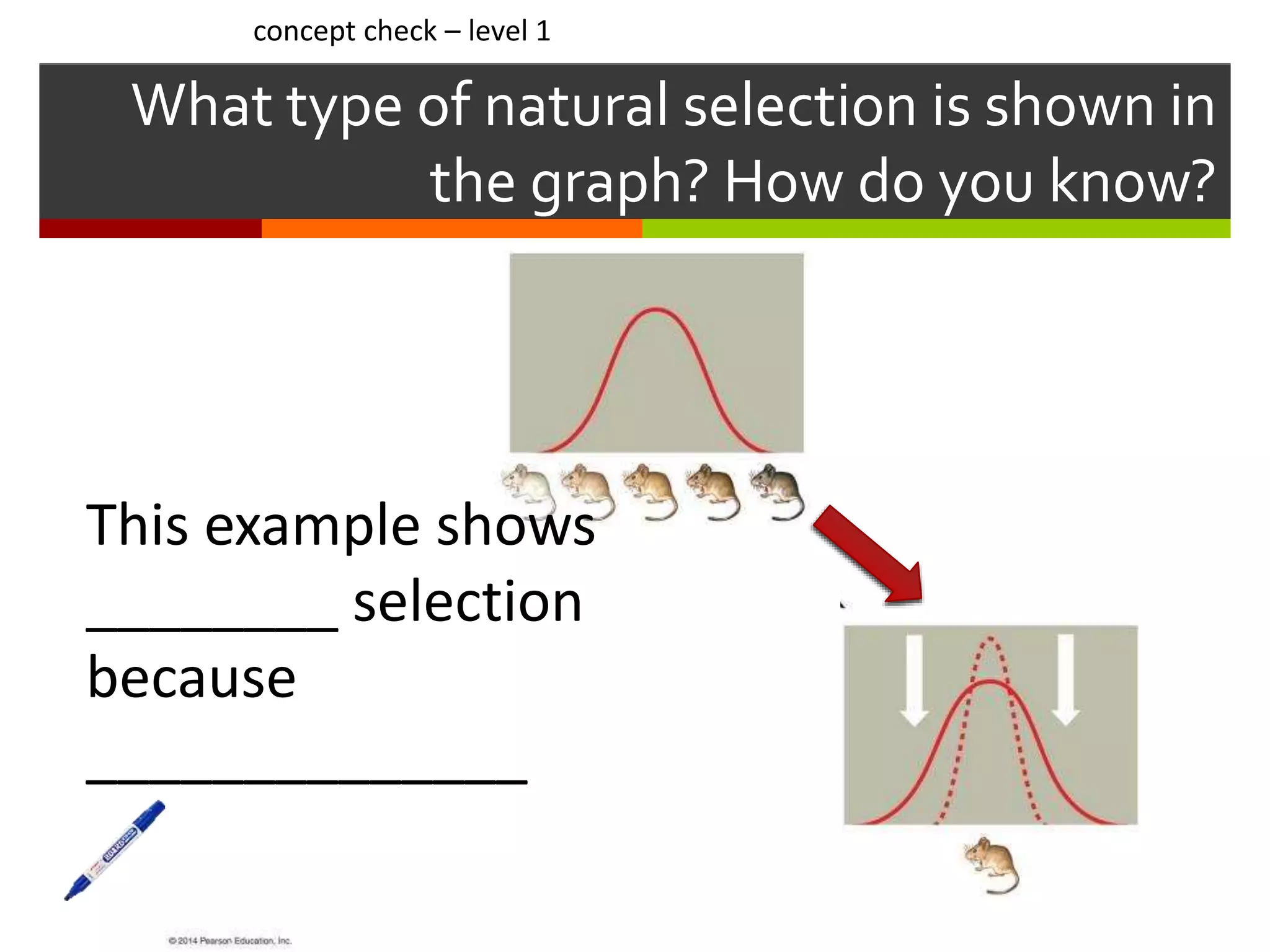
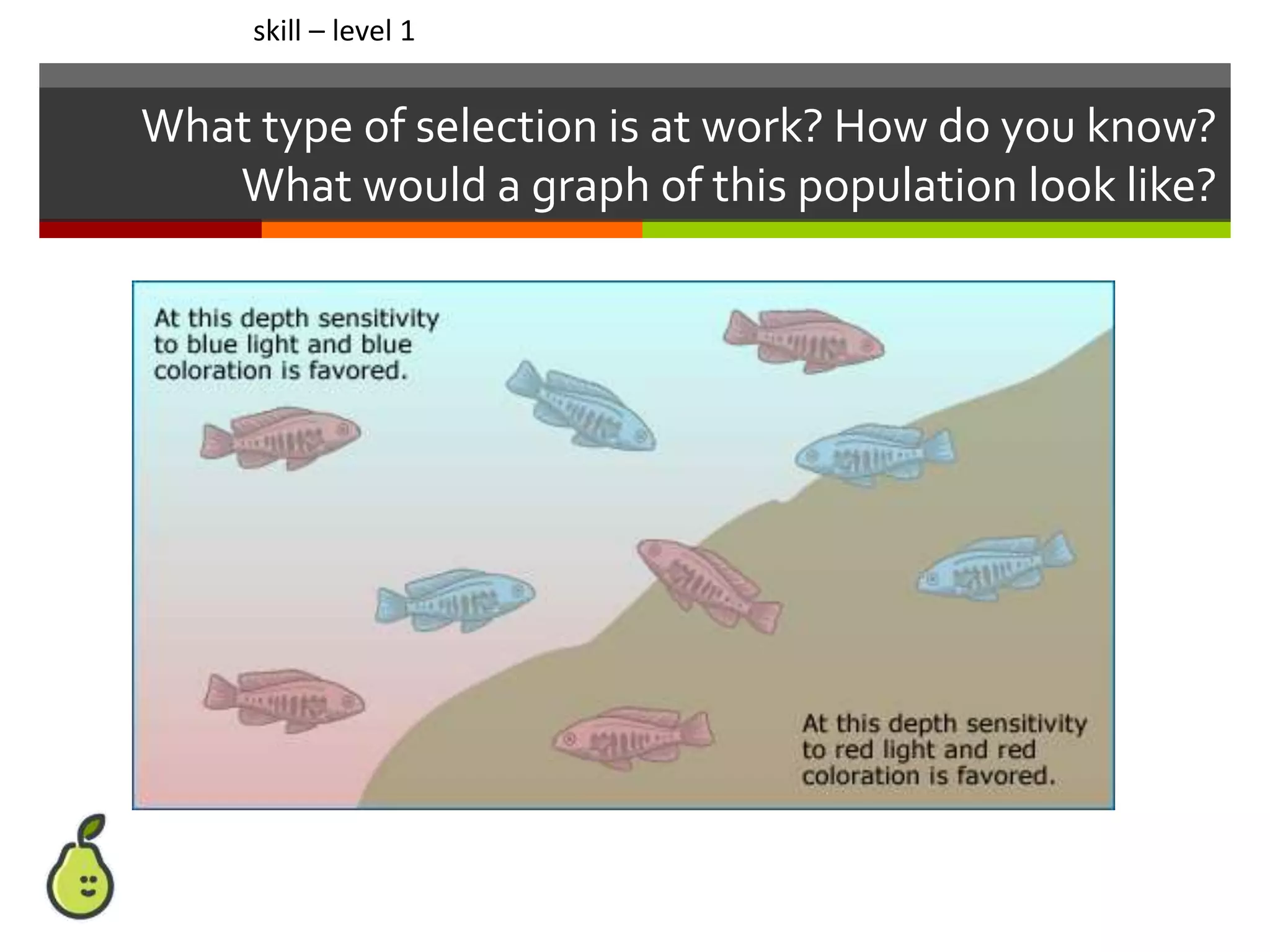
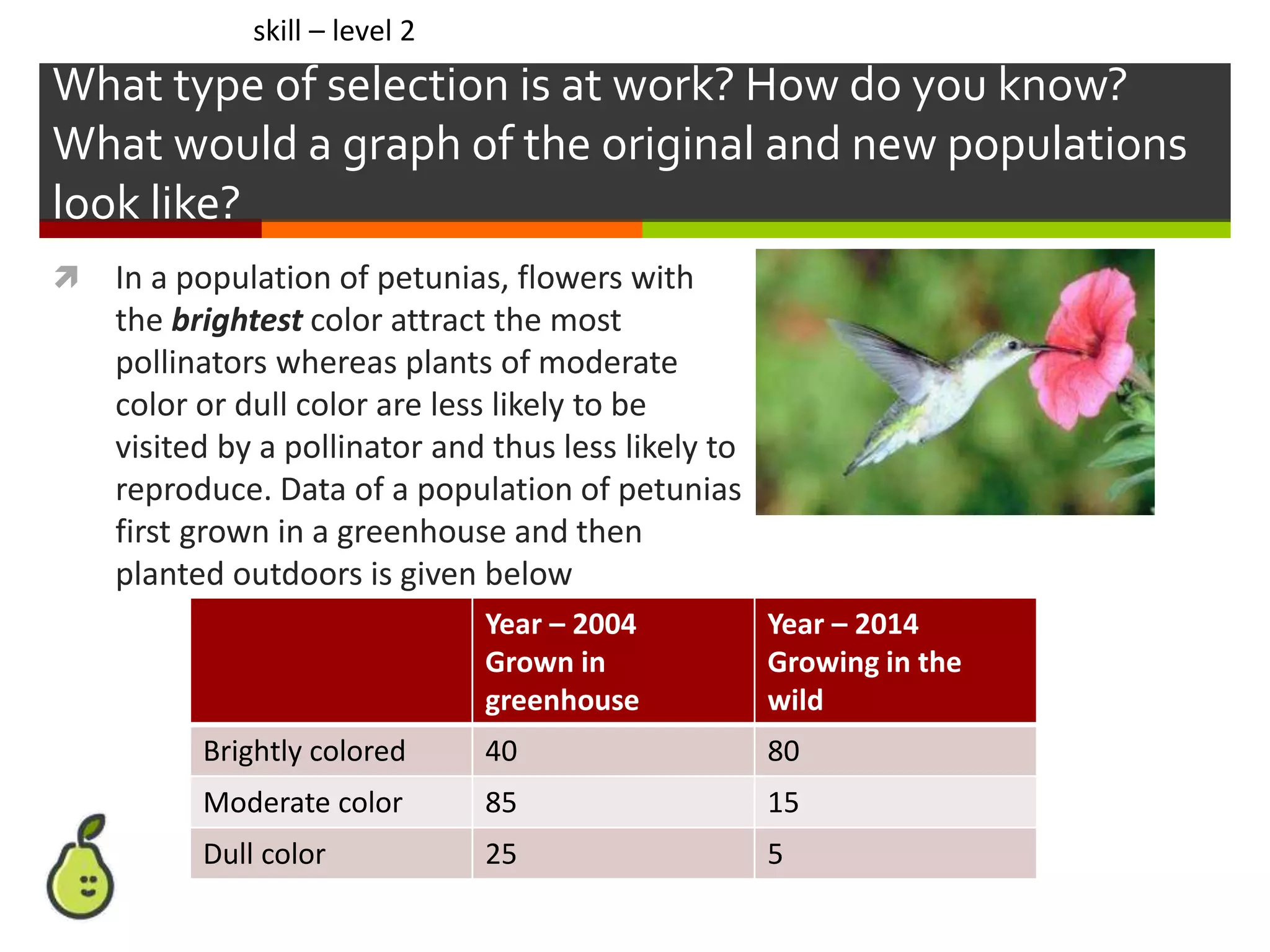
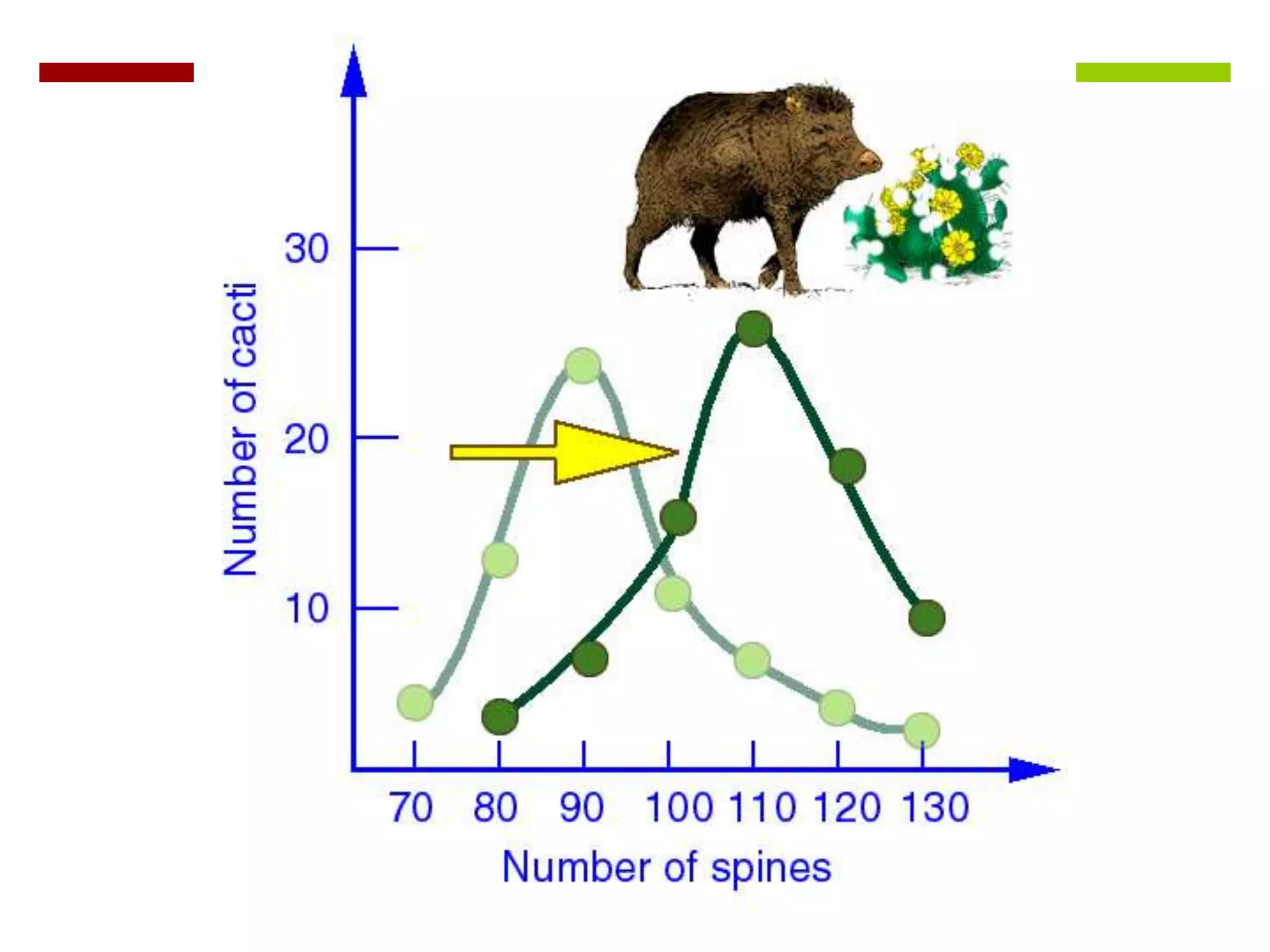
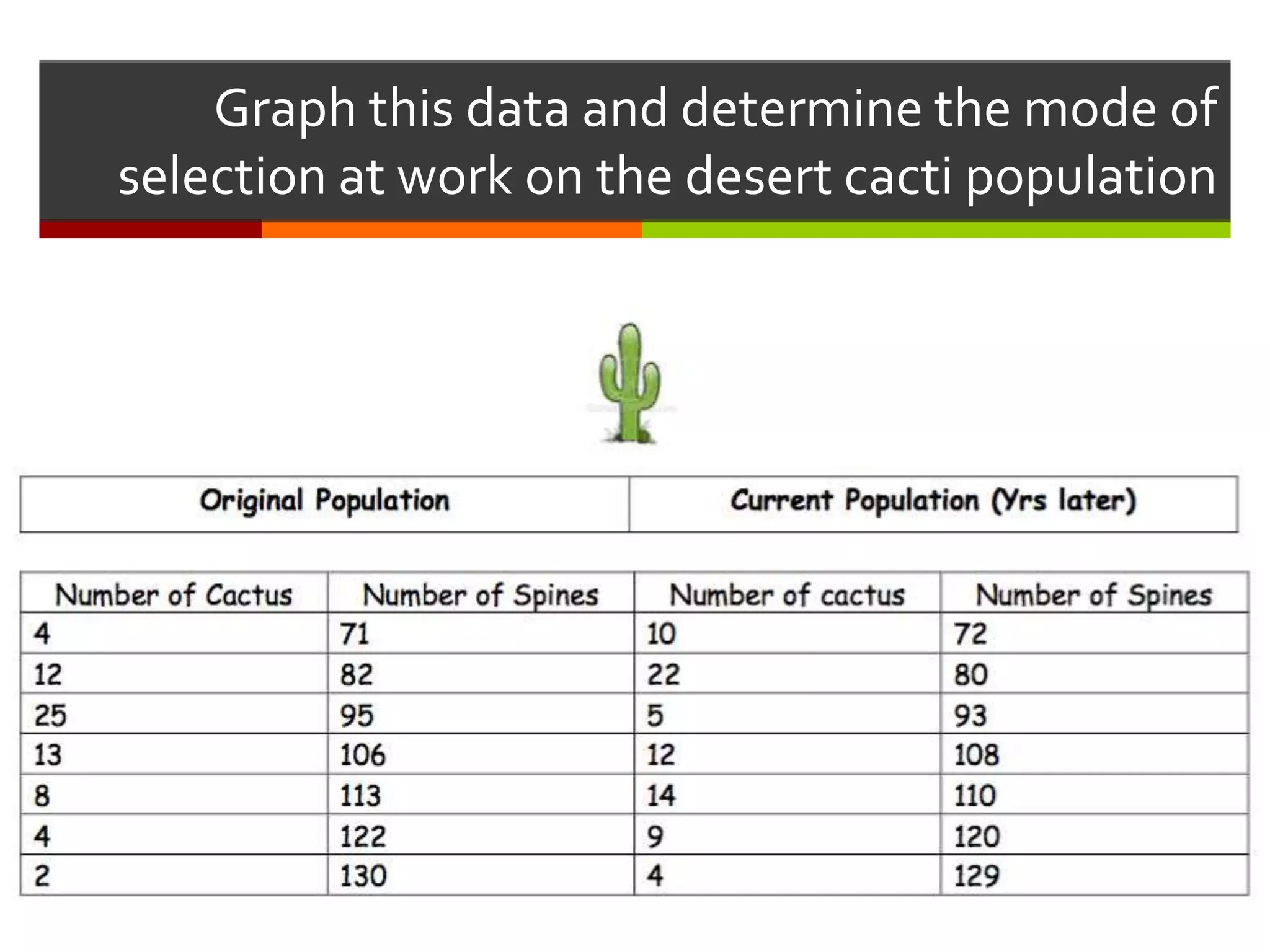
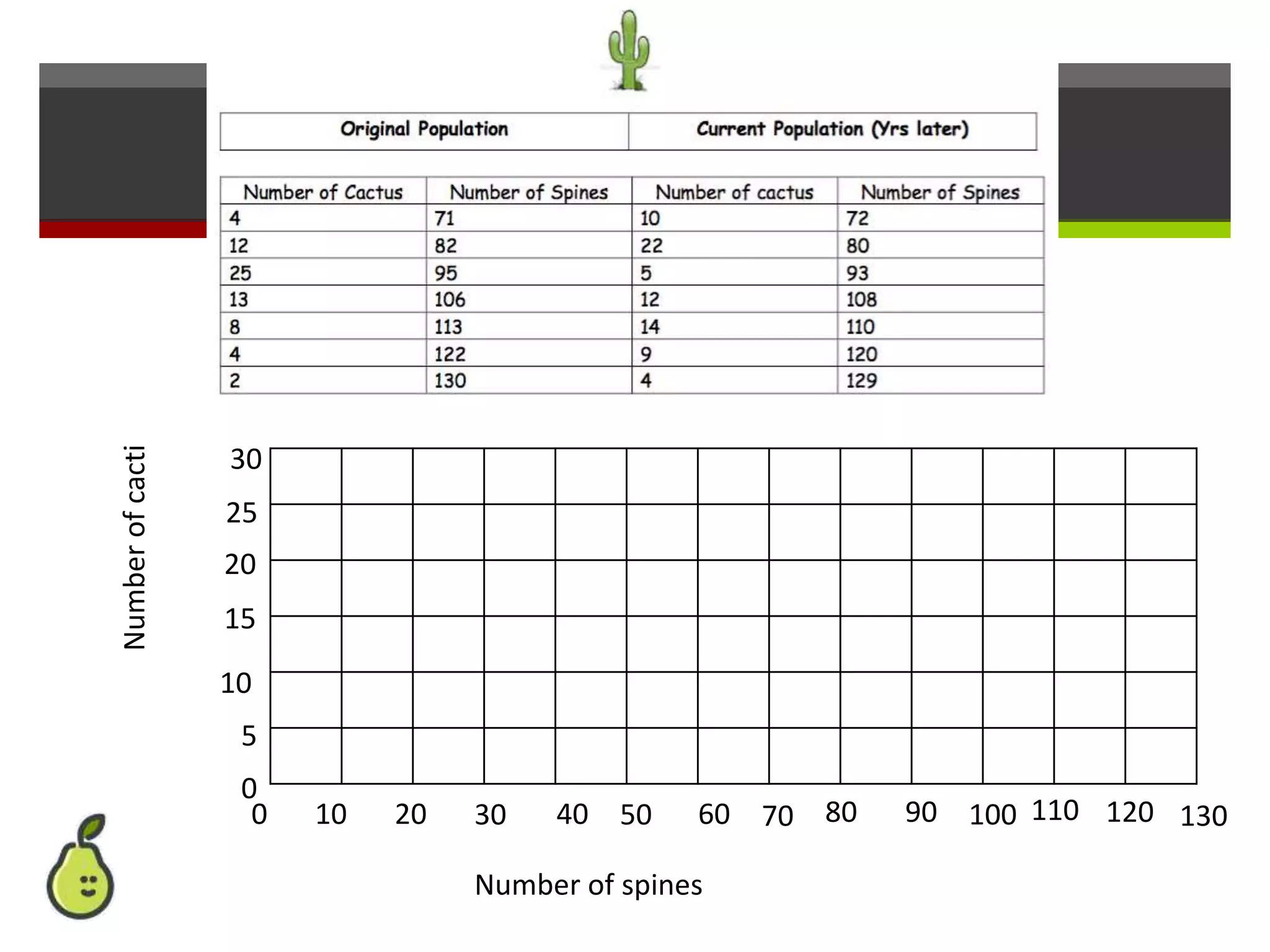
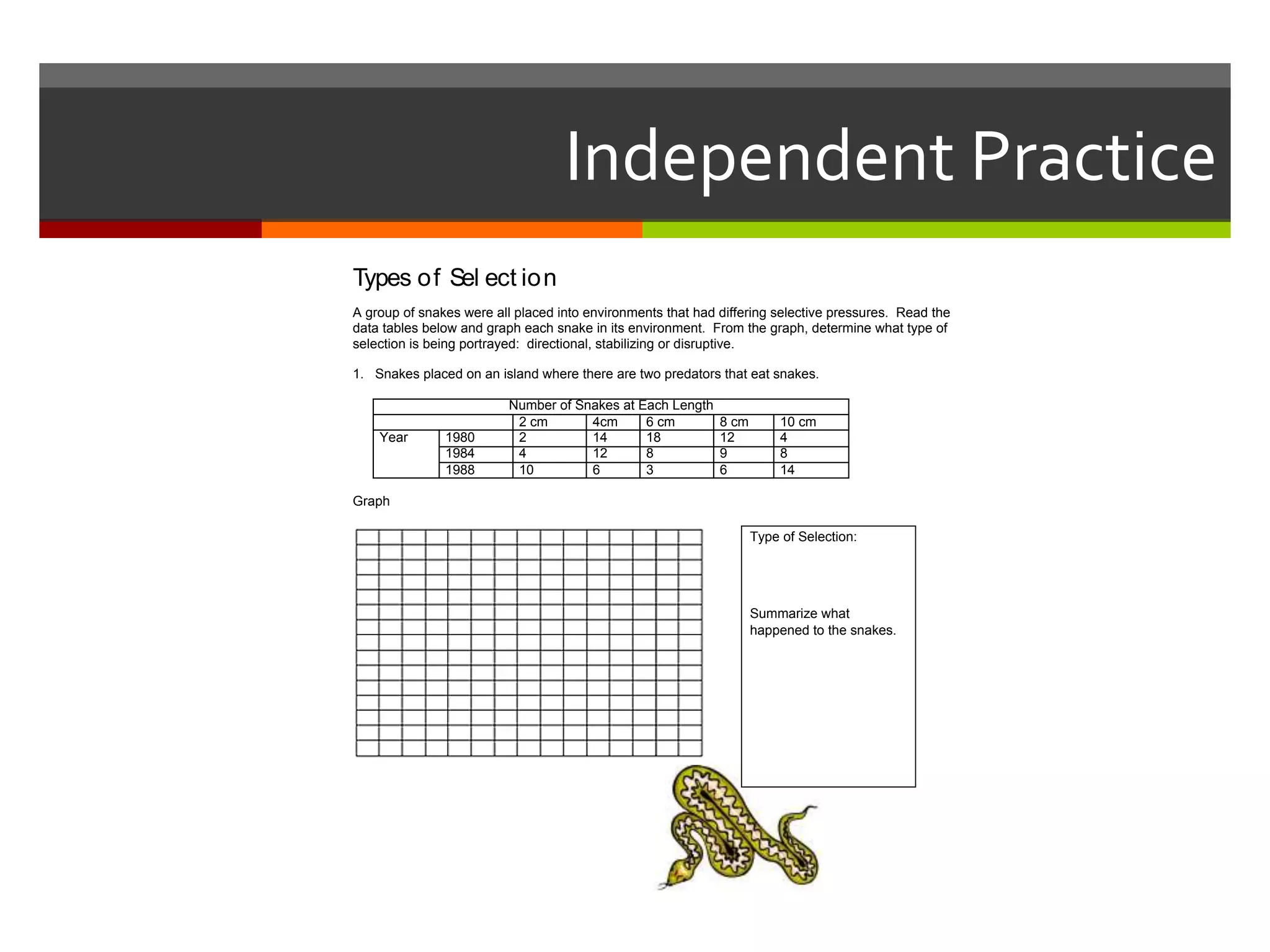
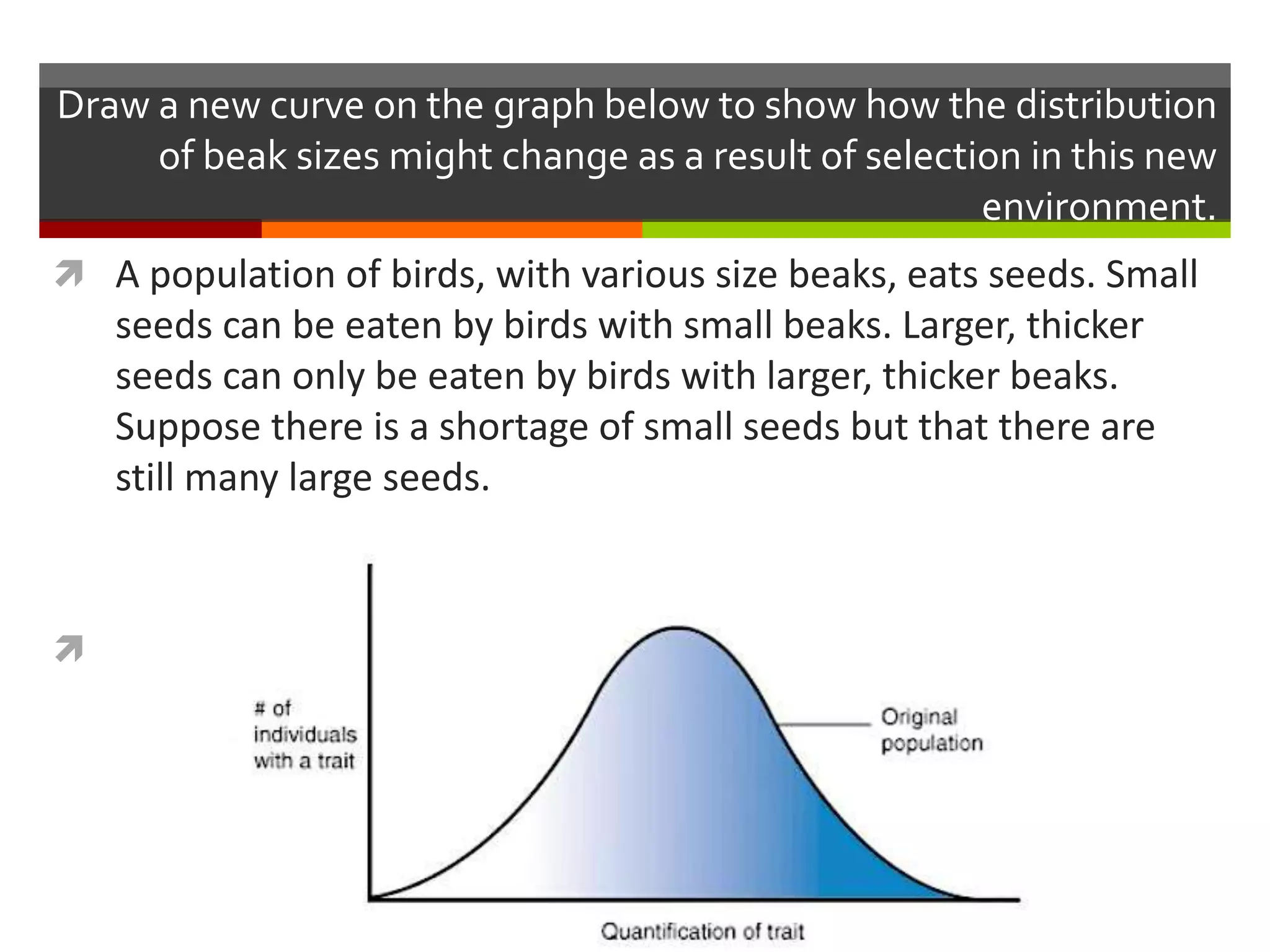
This document provides instruction on natural selection and different modes of selection. It begins with an overview of natural selection, noting it requires variation in a population, struggle for survival/competition, and a changing environment. It then defines and provides examples of three modes of selection: stabilizing selection, which favors the average phenotype; directional selection, which favors one end of the phenotypic range; and disruptive selection, which favors phenotypes at both ends of the range. Students are asked questions to analyze examples and identify the mode of selection occurring. The objective is for students to differentiate selection modes and use shifts in phenotypic distributions as evidence of evolution by natural selection.