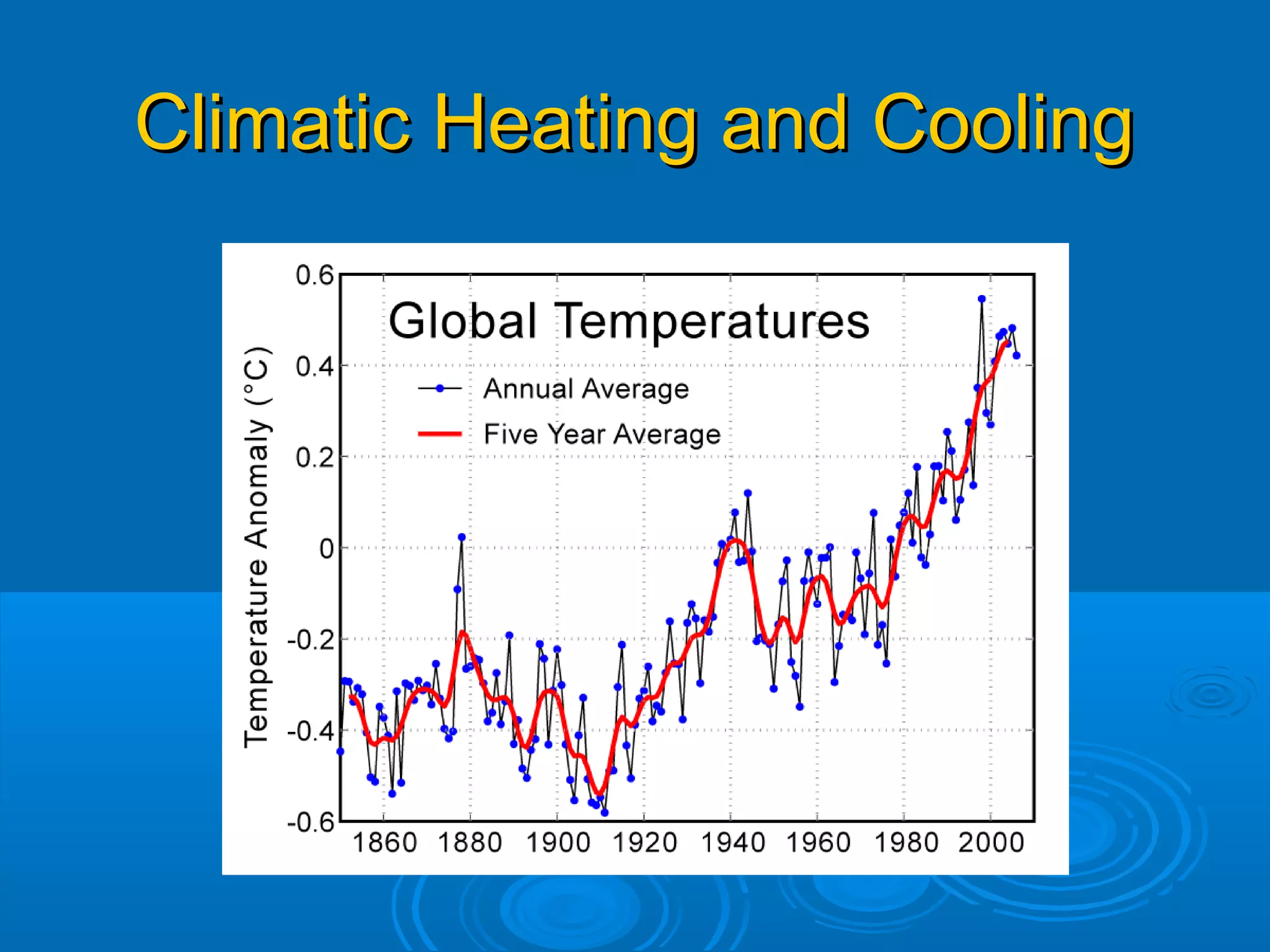
The document discusses extinction and biodiversity loss. It defines extinction as occurring when the last member of a species dies. The passenger pigeon is provided as an example, with the last one dying alone in a zoo in 1914 after the species was already functionally extinct in the wild. Major causes of extinction discussed include habitat degradation and destruction from human activities like pollution, climate change, and overpopulation. Statistics are given on current extinction rates from human impacts being 1500 times the natural rate, with many species projected to be lost in the coming centuries if trends continue. The major impacts of biodiversity loss on human concerns like medicine, agriculture, ecosystem services, and moral obligations are also briefly touched on.