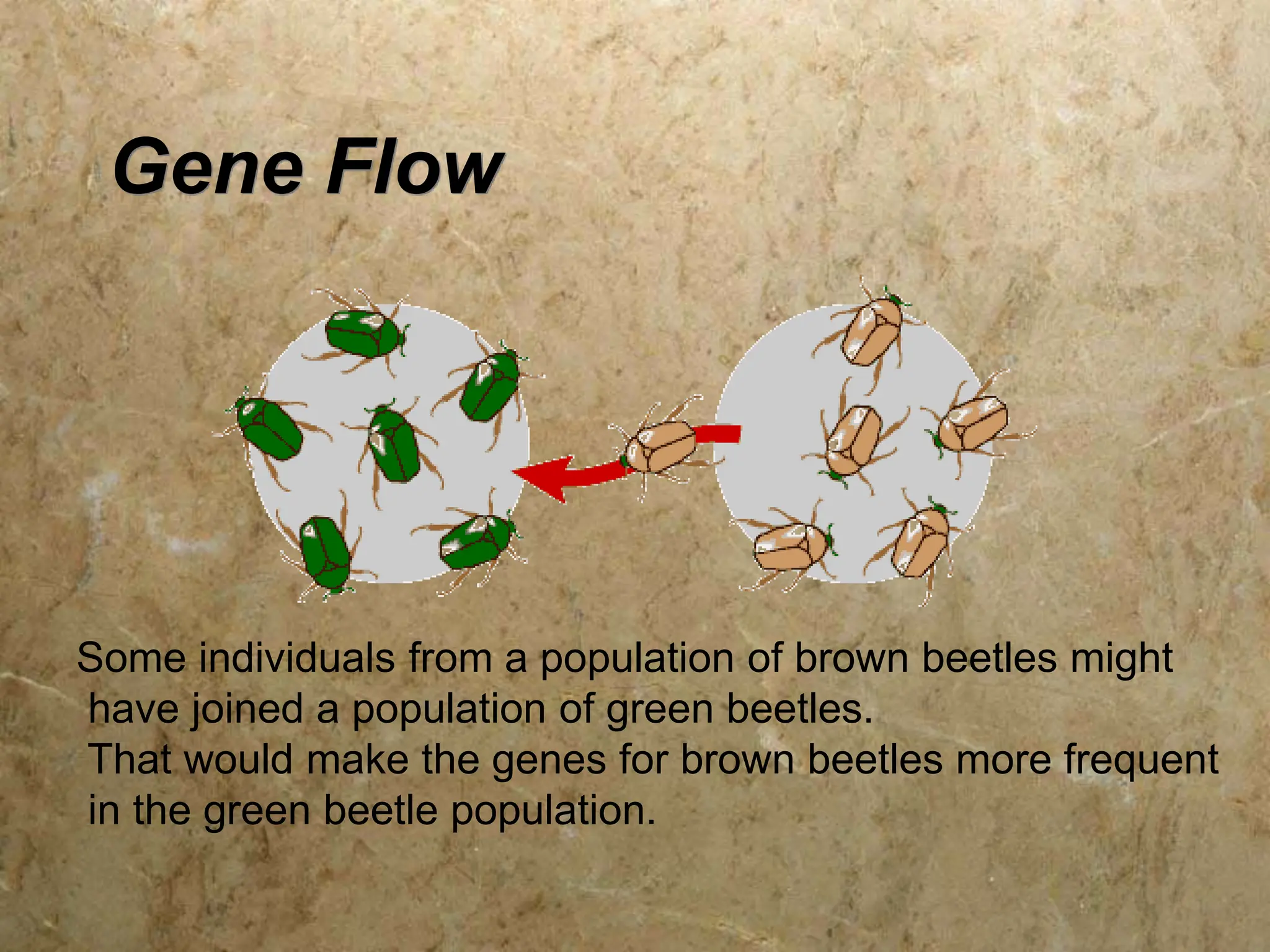
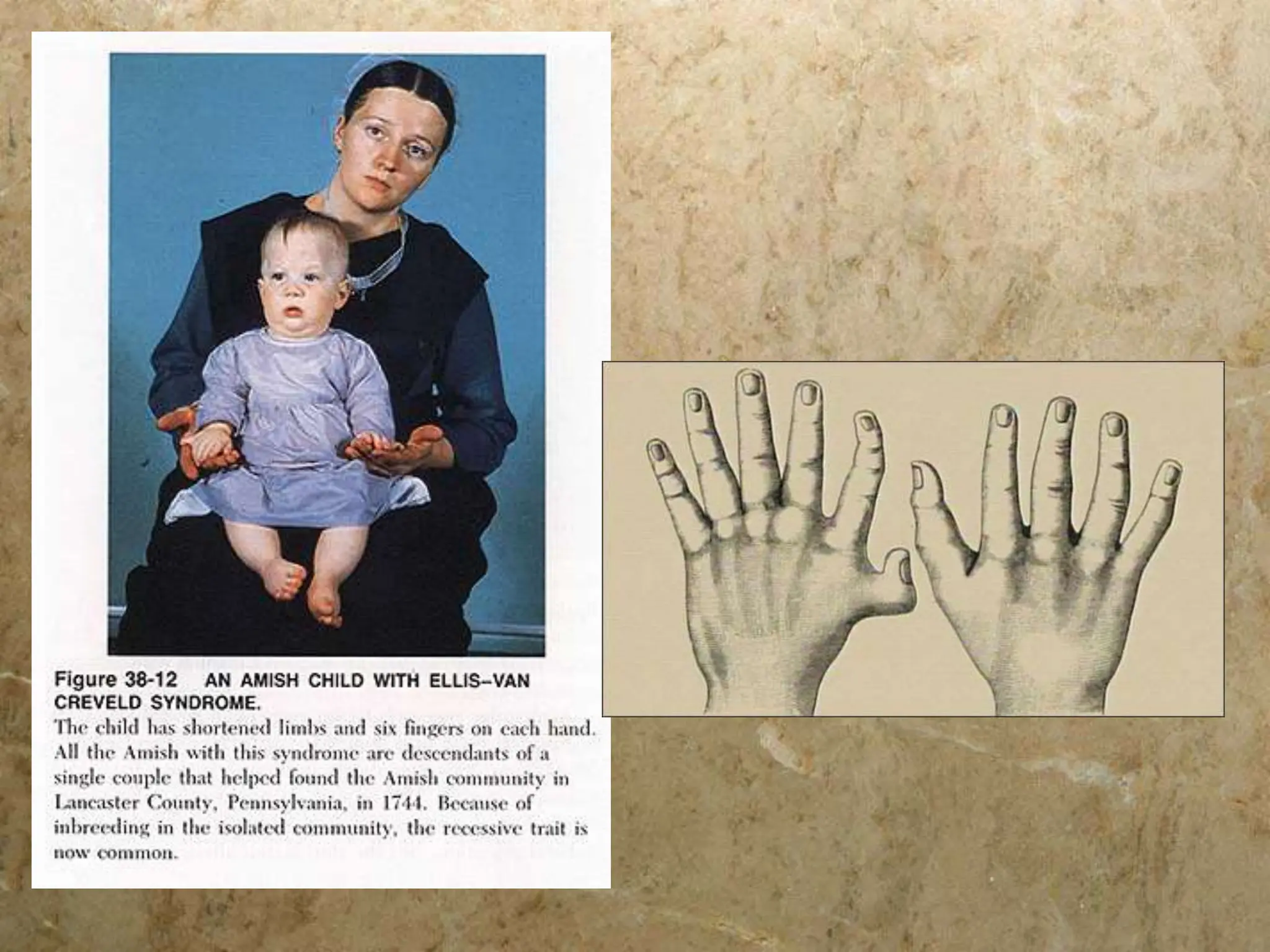
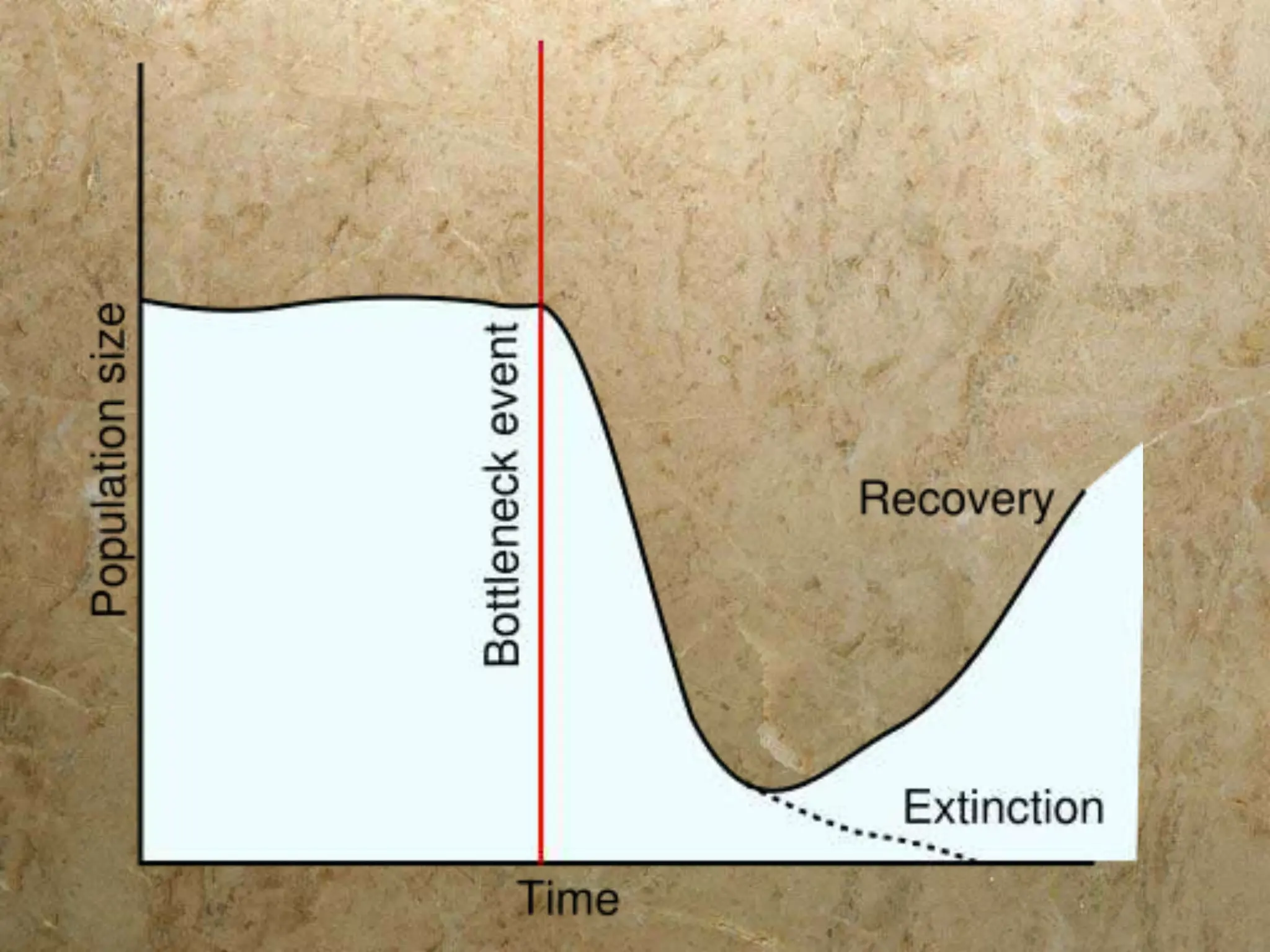
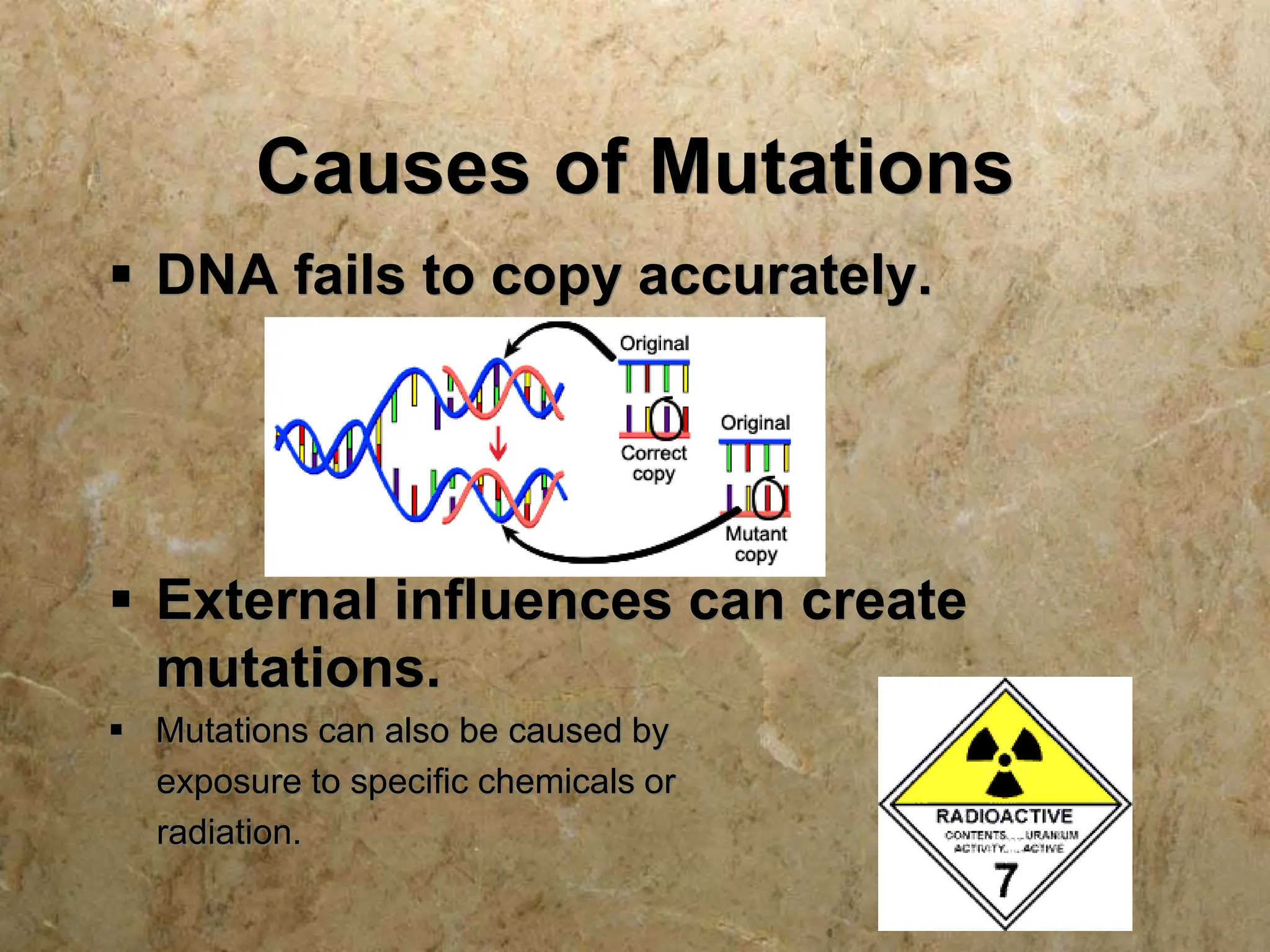
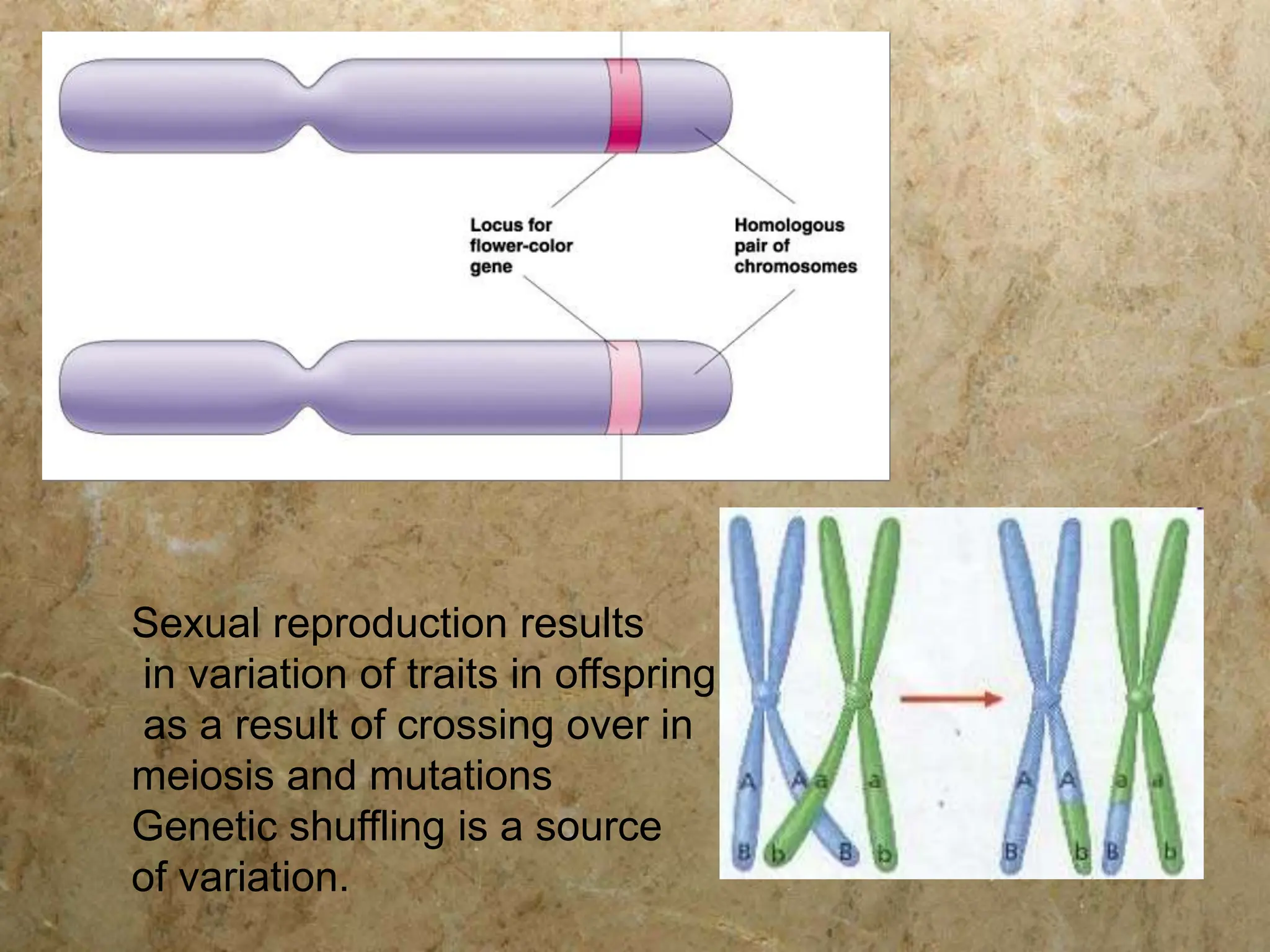
There are five main mechanisms of evolution: natural selection, gene flow, genetic drift, mutations, and non-random mating. Natural selection occurs as individuals with traits better suited to their environment tend to survive and pass on their genes more than others. Gene flow introduces new alleles as individuals migrate and breed with other populations. Genetic drift is the change in allele frequencies due to chance events in small populations. Mutations provide genetic variation for natural selection to act upon. Non-random mating, like sexual selection and inbreeding, can also change allele frequencies in a population over time.