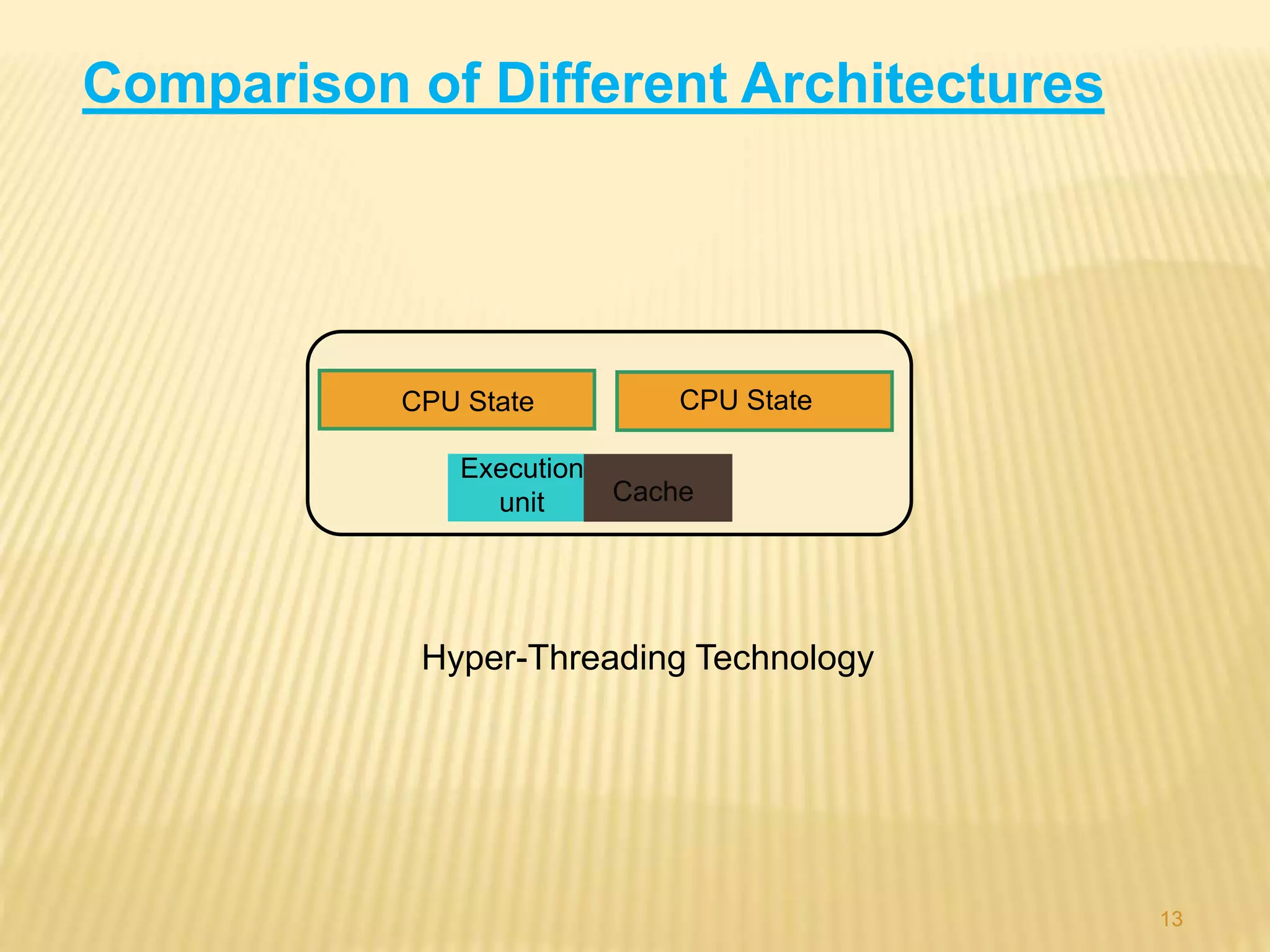
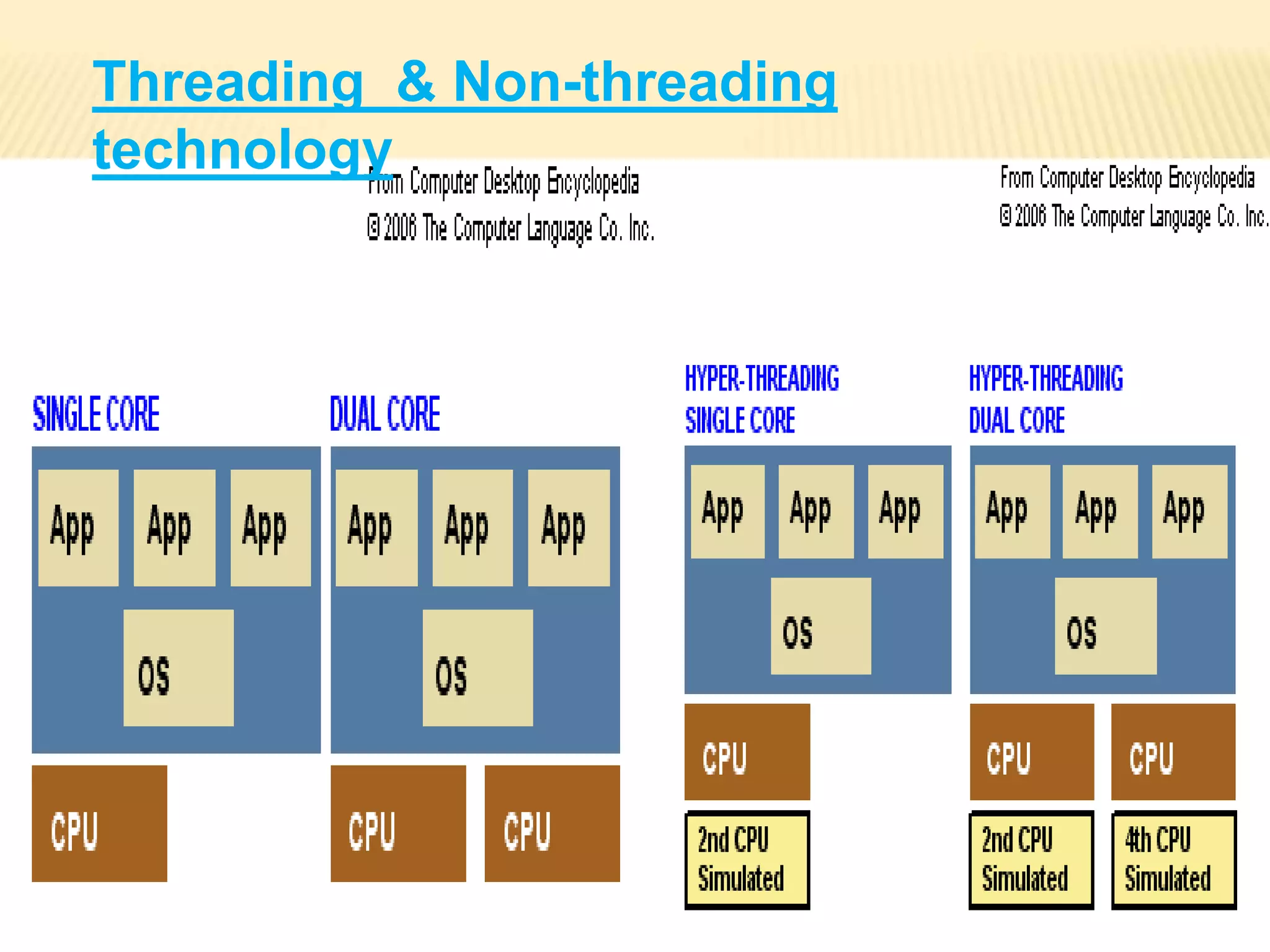
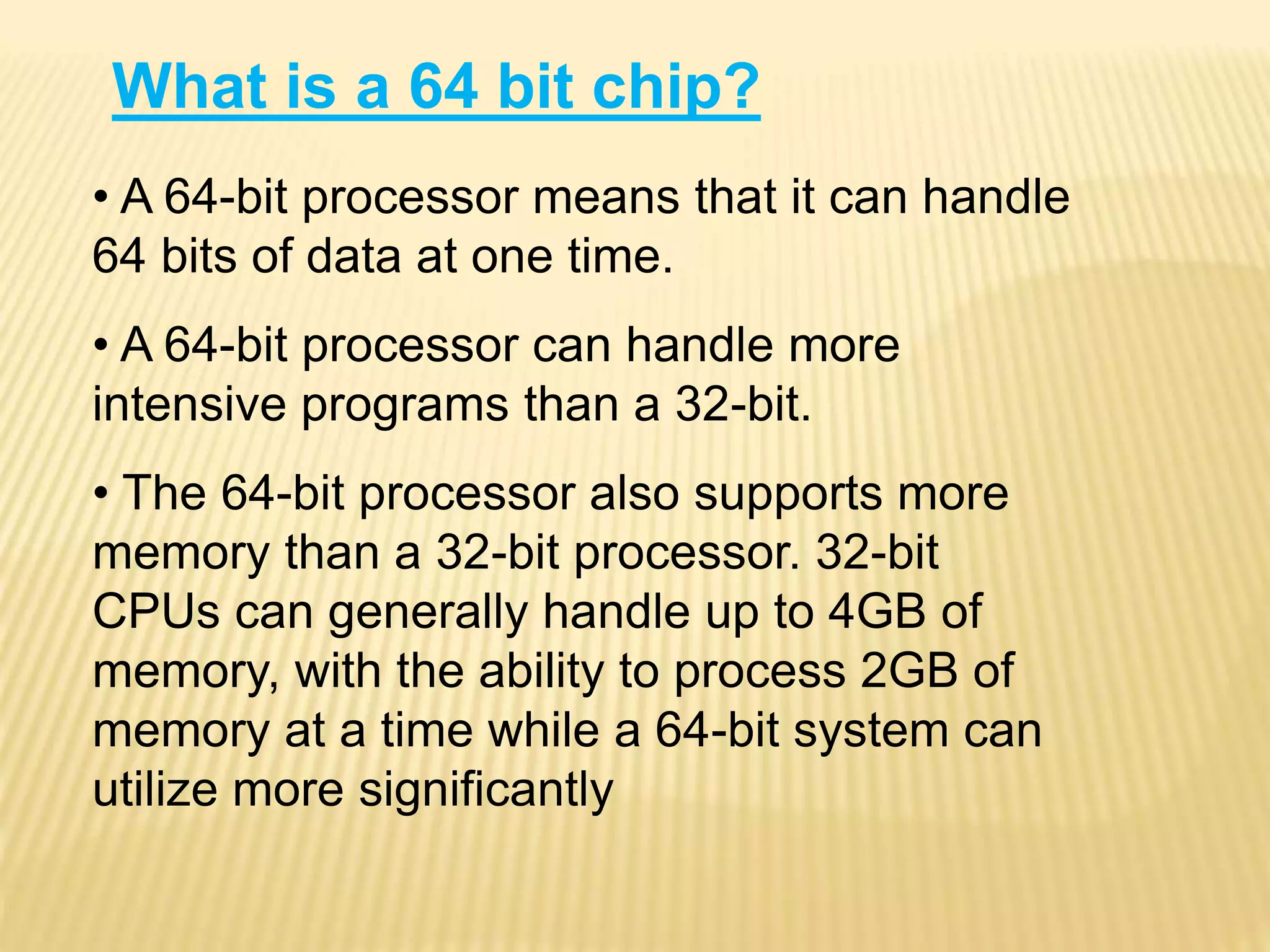
This document provides an overview of multi-core processors, including their history, architecture, advantages, disadvantages, applications and future aspects. It discusses how multi-core processors work with multiple independent processor cores on a single chip to improve performance over single-core processors. Some key points covered include the introduction of dual-core chips by IBM, Intel and AMD in the early 2000s; comparisons of single-core, multi-core and other architectures; advantages like improved multi-tasking and security; and challenges for software to fully utilize multi-core capabilities.



















![References
• R. Merritt, “CPU Designers Debate Multi-core Future”, EETimes Online, February
2008, http://www.eetimes.com/showArticle.jhtml?articleID=206105179
• R. Merritt, “Multicore Puts Screws to Parallel-Programming Models”, EETimes Online,
February 2008,
http://www.eetimes.com/news/latest/showArticle.jtml?articleID=206504466
• R. Merritt, “X86 Cuts to the Cores”, EETimes Online, September 2007,
http://www.eetimes.com/showArticle.jtml?articleID=202100022
• R. Merritt, “Multicore Goals Mesh at Hot Chips”, EETimes Online, August 2007,
http://www.eetimes.com/showArticle.jtml?articleID=201800925
• P. Frost Gorder, “Multicore Processors for Science and Engineering”, IEEE CS,
March/April 2007
• D. Geer, “Chip Makers Turn to Multicore Processors”, Computer, IEEE Computer
Society, May 2005 [5] L. Peng et al, “Memory Performance and
It has been taken from various sources](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multicoreprocessortechnology-150817172018-lva1-app6892/75/Multicore-Processor-Technology-27-2048.jpg)
