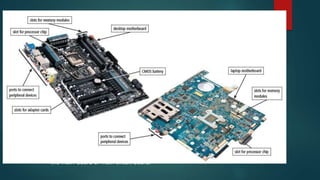
This document discusses microprocessors and motherboards. It begins by defining a microprocessor as an electronic chip that takes input, processes it, and provides output. It then describes single-core and dual-core microprocessor designs. A dual-core processor has two microprocessors on one chip that can execute instructions simultaneously for improved efficiency. The document notes benefits of dual-core processors for tasks like gaming or data transfers. It also distinguishes dual-core processors from Core 2 Duo and multi-processor systems. Finally, it briefly discusses quad-core processors and the role of the motherboard in connecting computer components like the CPU, memory, and I/O devices.