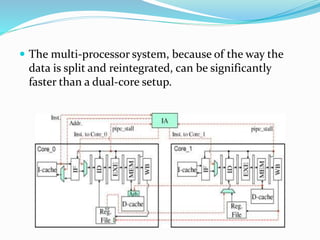
A dual core processor contains two separate processing units called cores contained within a single integrated circuit chip. Each core has its own cache and controller, allowing it to function similarly to an individual processor. By having two cores, dual core processors can perform some tasks twice as fast as a single core processor. Examples of dual core CPUs include the Intel Core Duo, AMD X2, and PowerPC G5. While dual core processors are faster than single core, software must be designed to take advantage of both cores for maximum performance gains.