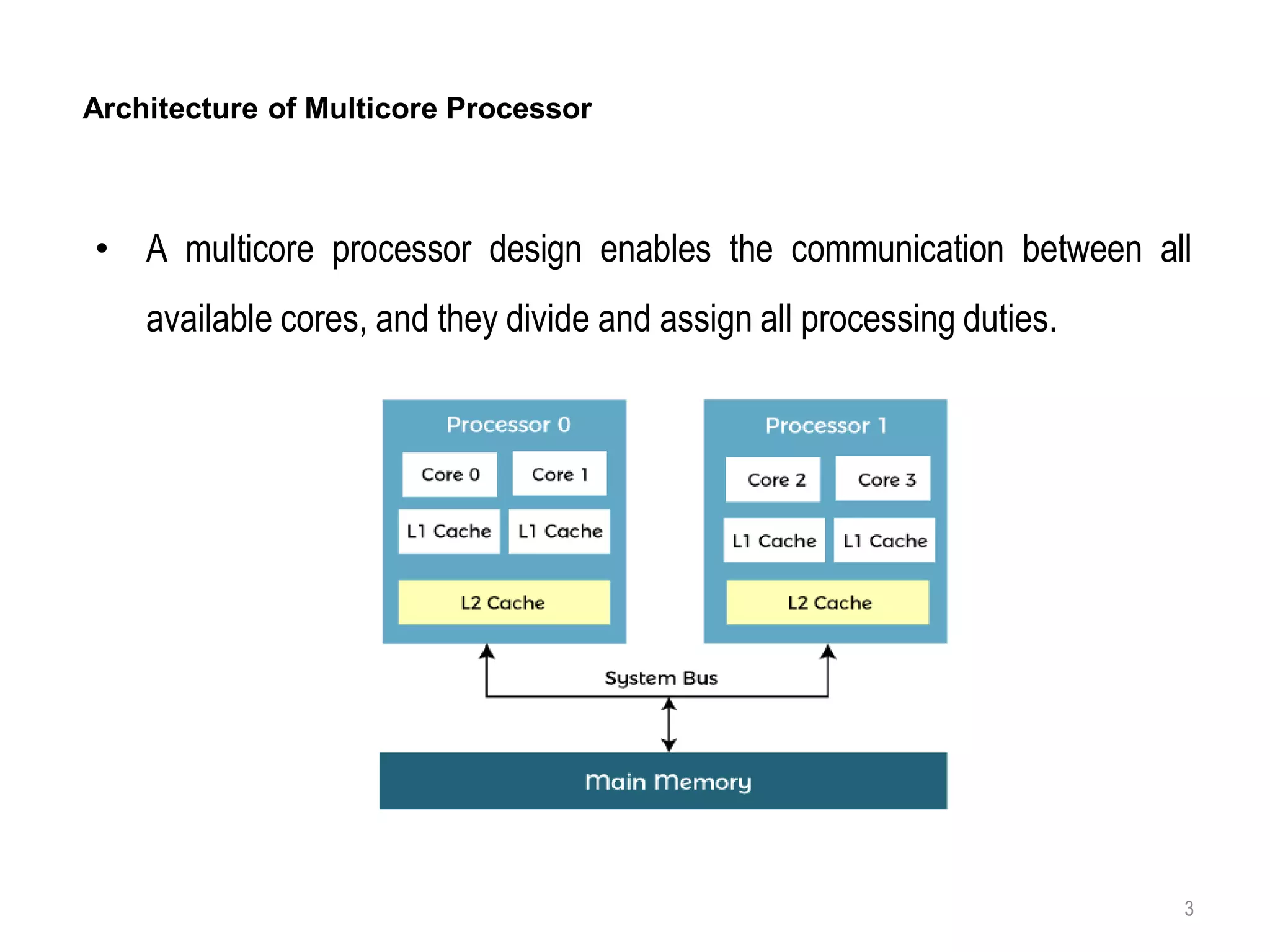
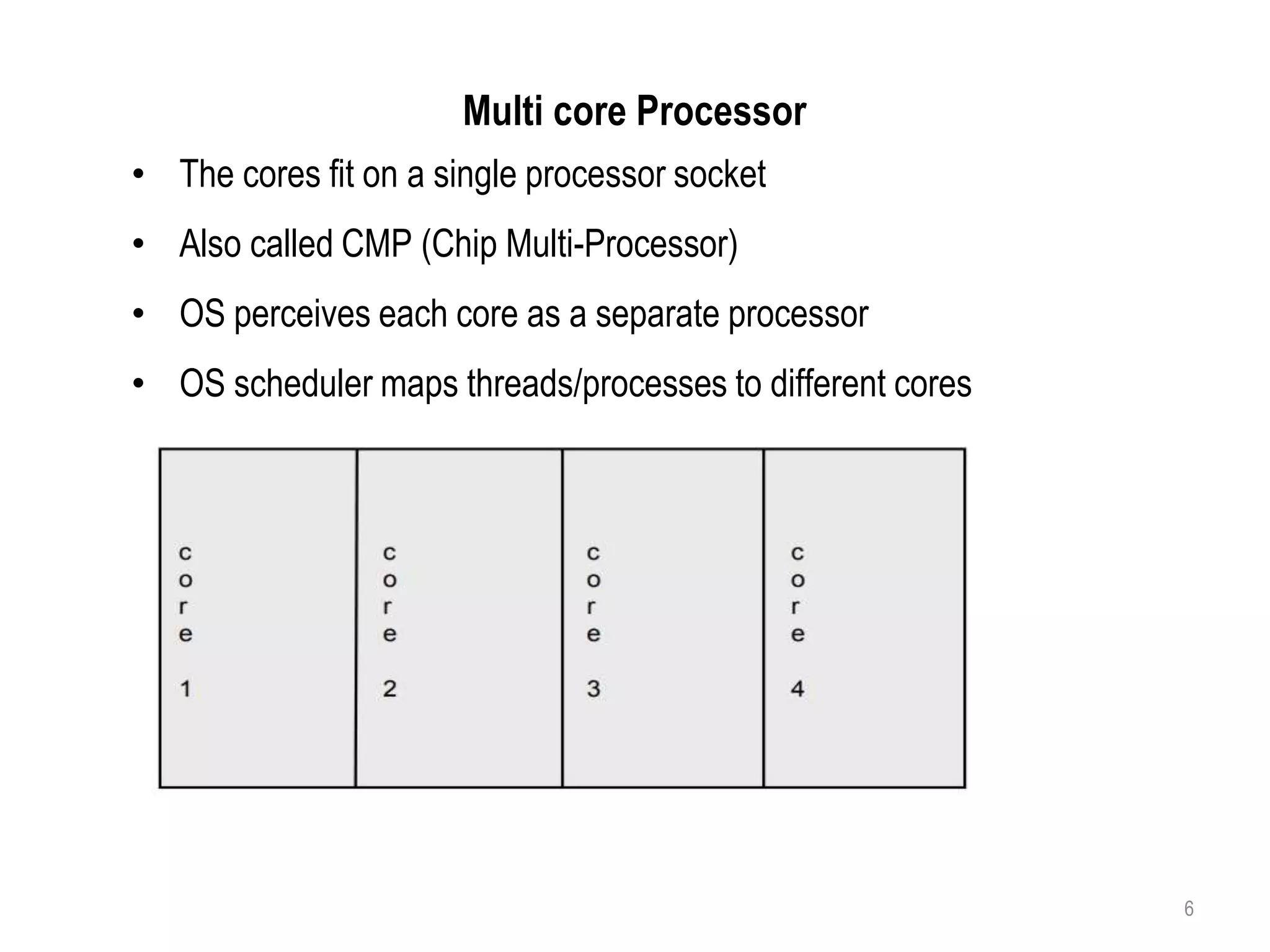
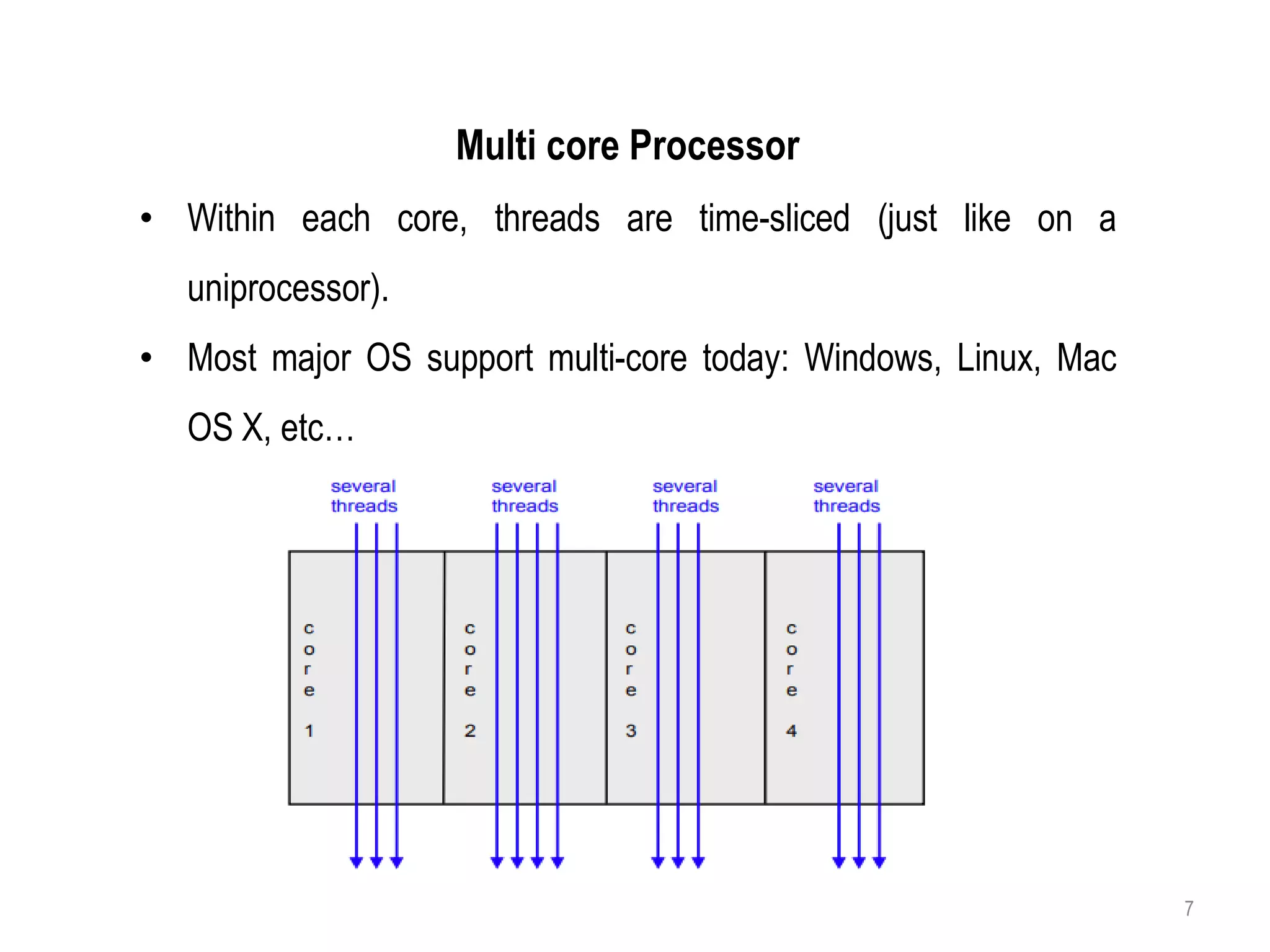
A multi-core processor contains two or more independent processing units called cores that can execute program instructions simultaneously. This allows multi-core processors to better perform multiple tasks at once, improve performance, reduce power consumption, and increase reliability compared to single-core processors. Each core on a multi-core processor can perform separate tasks, such as one core handling a movie while another handles a messaging app. The cores communicate through a shared pathway and the operating system distributes processes across the cores.