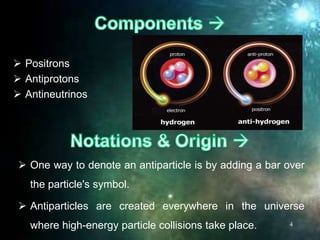
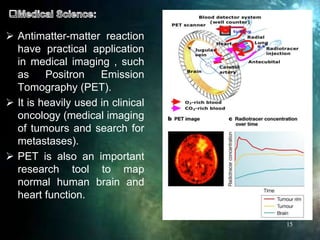
Antimatter consists of antiparticles, which mirror ordinary particles but possess opposite charge and magnetic properties, with implications for energy production and propulsion systems. Current research focuses on storage methods, such as the Penning trap, and the potential use of antimatter in medical imaging, particularly positron emission tomography (PET). Despite its immense energy potential, antimatter remains prohibitively expensive to produce, limiting its practical applications and advanced technologies for harnessing its power.