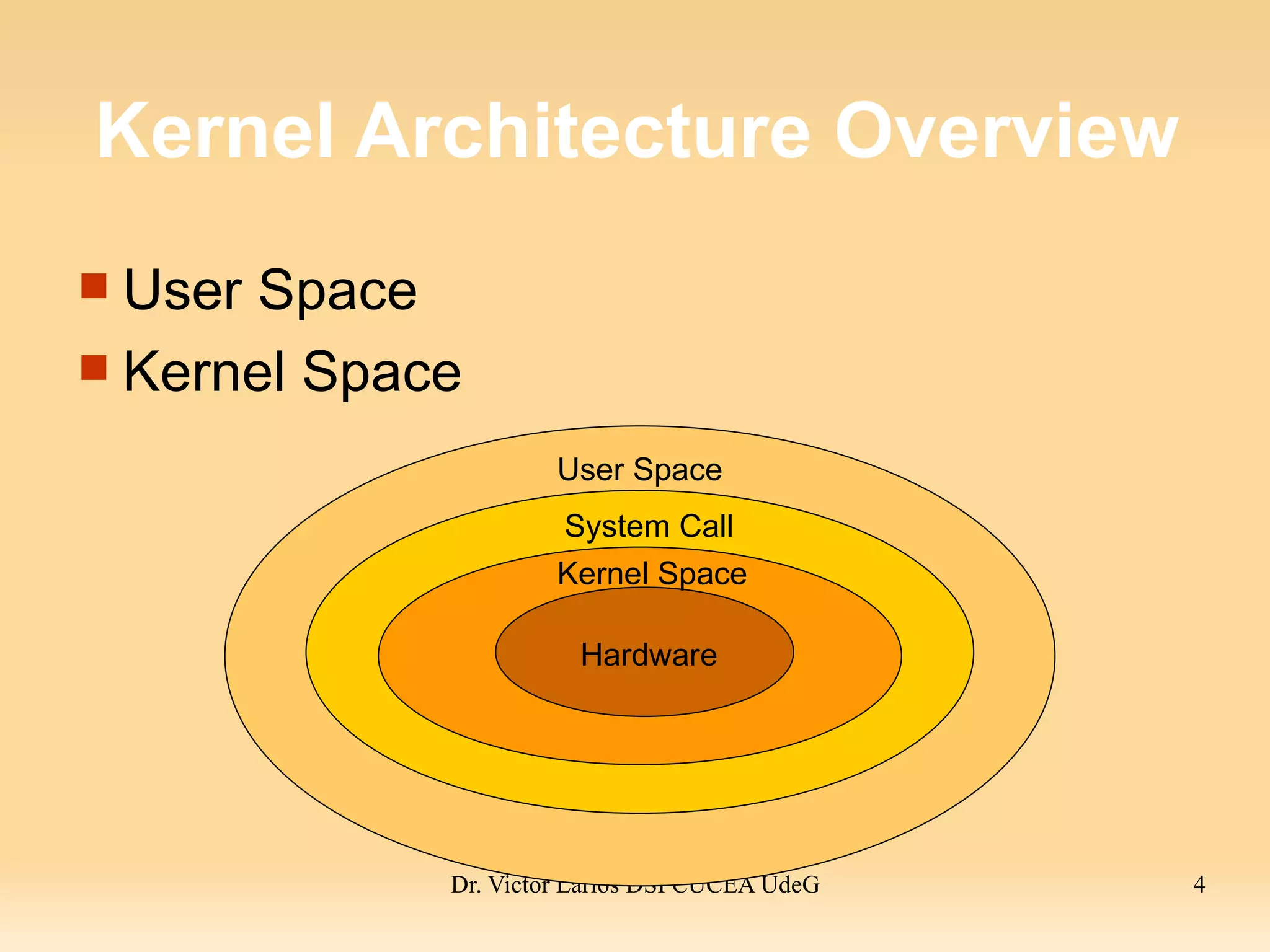
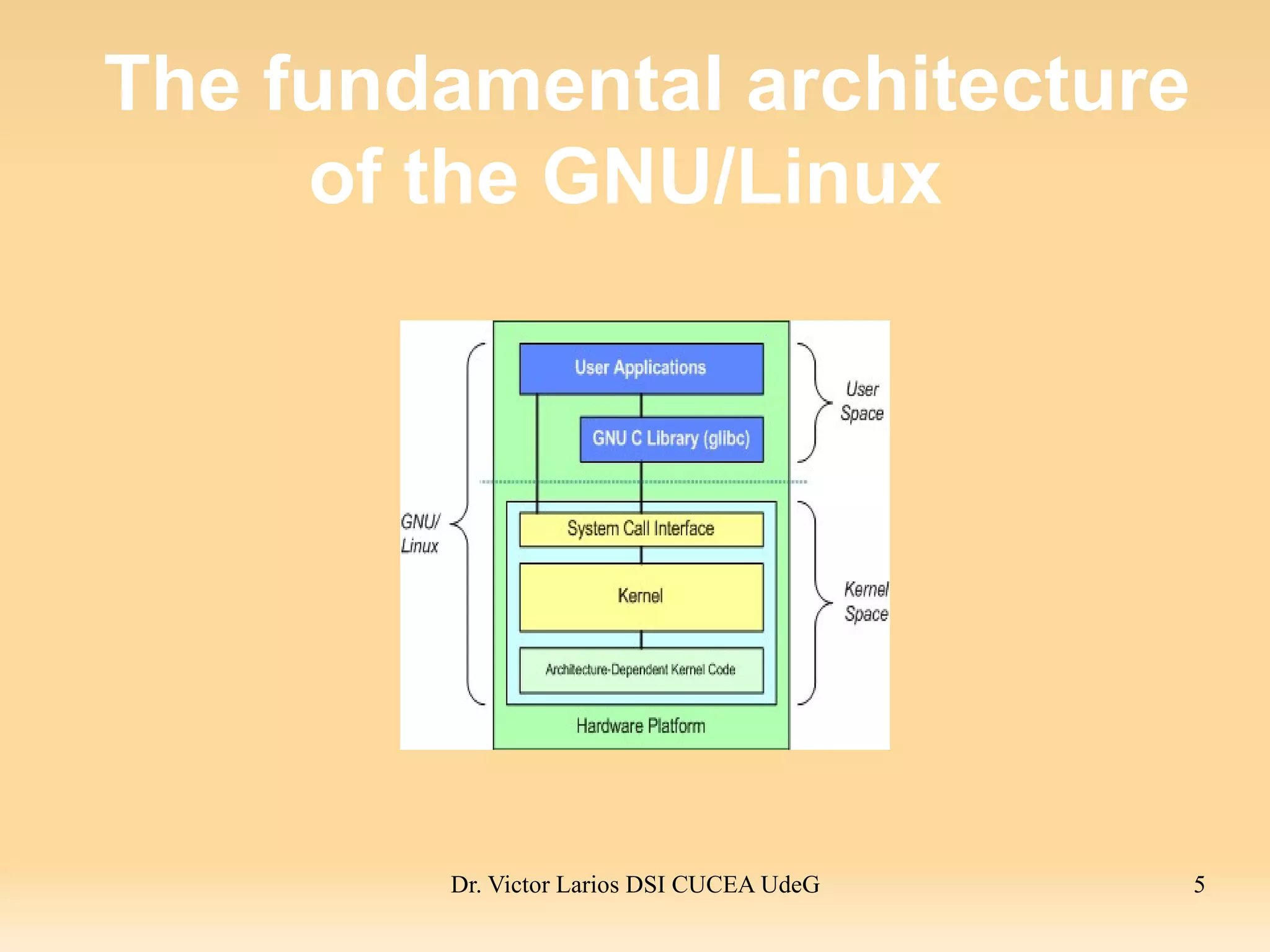
The document discusses the Linux kernel architecture. The kernel manages resources and arbitrates access between users and applications. It includes functions like file systems, process management, device drivers, memory management, and networking. The kernel space runs kernel processes while the user space runs user applications, which interact with the kernel through system calls. The kernel presents a consistent view of data stored on devices using a virtual file system.