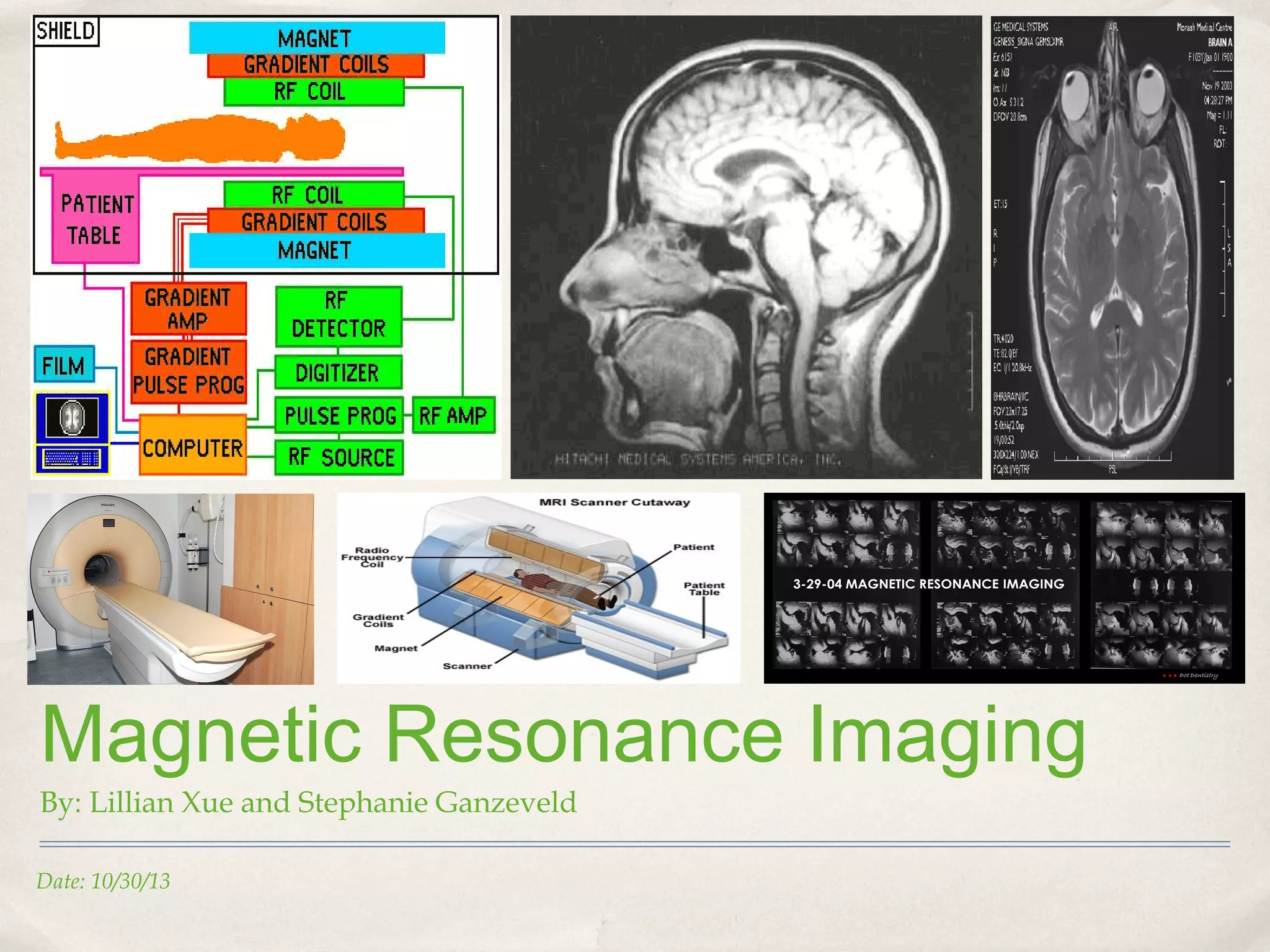
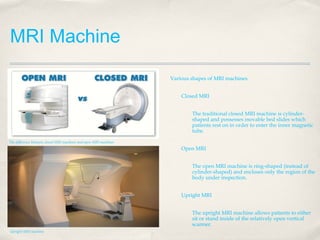
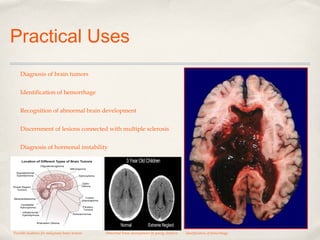
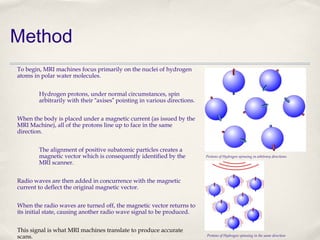
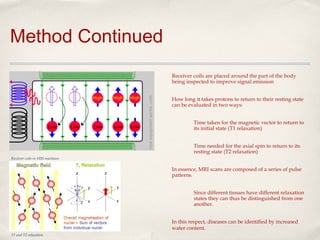
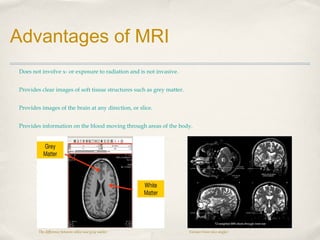
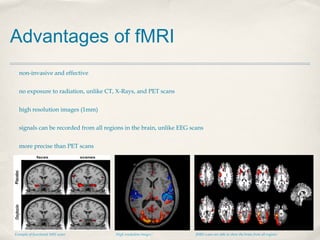
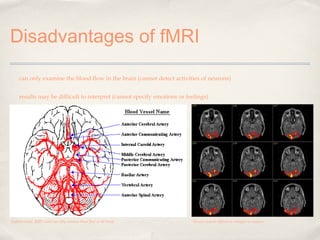
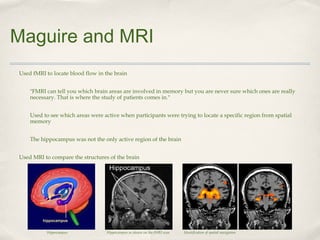
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique that uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the inside of the body. There are different types of MRI machines, including closed, open, and upright configurations. MRI is used to diagnose conditions such as brain tumors, hemorrhages, and multiple sclerosis. It works by aligning hydrogen atoms in the body using magnetism and radio waves, and analyzing the signals produced to form images of tissues and structures. Advantages include a lack of radiation and ability to image soft tissues, while disadvantages include cost and potential incompatibility with metallic implants.