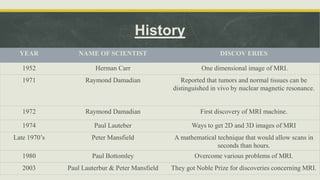
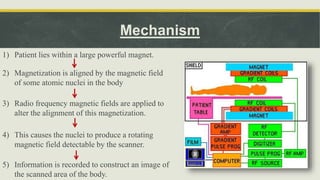
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique that uses nuclear magnetic resonance to visualize internal structures of the body. MRI works by aligning the magnetization of atomic nuclei when placed in a magnetic field and exposing them to radio frequencies, allowing for detailed images of tissues. The history of MRI involved early developments in one-dimensional imaging in the 1950s and the first MRI machine in the 1970s. MRI can be open or closed, and used for standing/sitting or lying down. Applications of MRI include detecting diseases, tumors, strokes and musculoskeletal and neurological conditions.