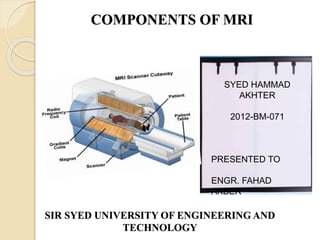
The document provides a detailed overview of the components and functioning of MRI systems, including superconducting magnets, permanent magnets, and resistive magnets. It explains the roles of gradient coils for imaging, shielding mechanisms, data acquisition, and the radio frequency (RF) system used for signal transmission and image reconstruction. Additionally, it describes the types of RF coils used for different anatomical areas and the process of generating and receiving RF energy from tissues.