Embed presentation
Downloaded 48 times
![Bloch Equations
dMz(t) = − [Mz(t) − M0]
dt T1
dMxy(t) = − Mxy(t)
dt T2
Mz
Mxy
Mz Mz
Mxy
Mxy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/o7sprchash6hppniv2kx-signature-32d797e46816d2f1ad04b19f9671fd9c01ddaa51c8250008594a8e918e443472-poli-160917224221/75/Mri-system-block-diagram-14-2048.jpg)
![T1 Relaxation
Mz(t) = M0 + {Mz(0) − M0}exp(-t/T1)
Mz Mz
t t
saturation–
recovery
inversion–recovery
dMz(t) = − [Mz(t) − M0]
dt T1
M0 M0
Mz(0) = 0 Mz(0) = −M0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/o7sprchash6hppniv2kx-signature-32d797e46816d2f1ad04b19f9671fd9c01ddaa51c8250008594a8e918e443472-poli-160917224221/75/Mri-system-block-diagram-15-2048.jpg)

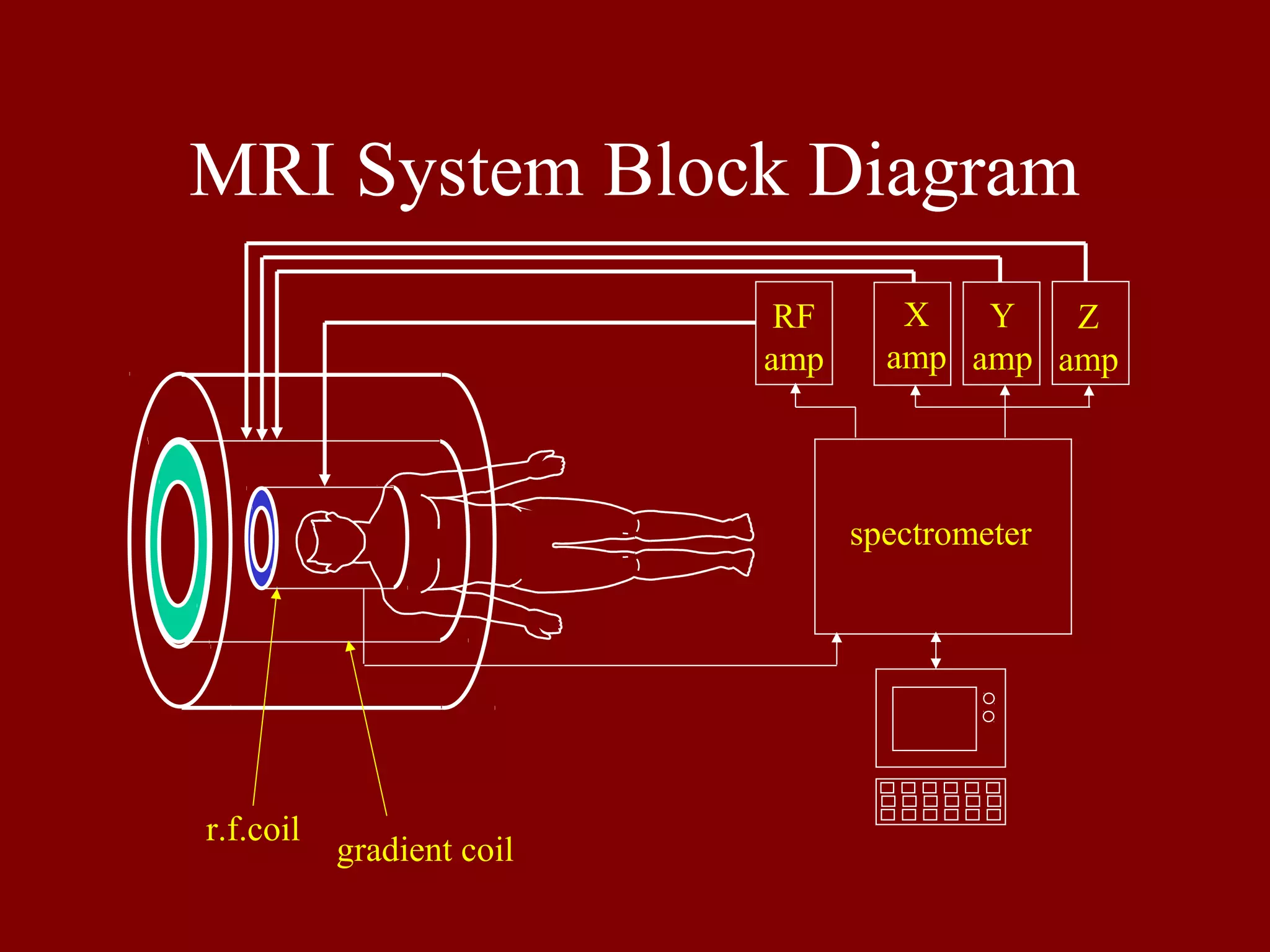
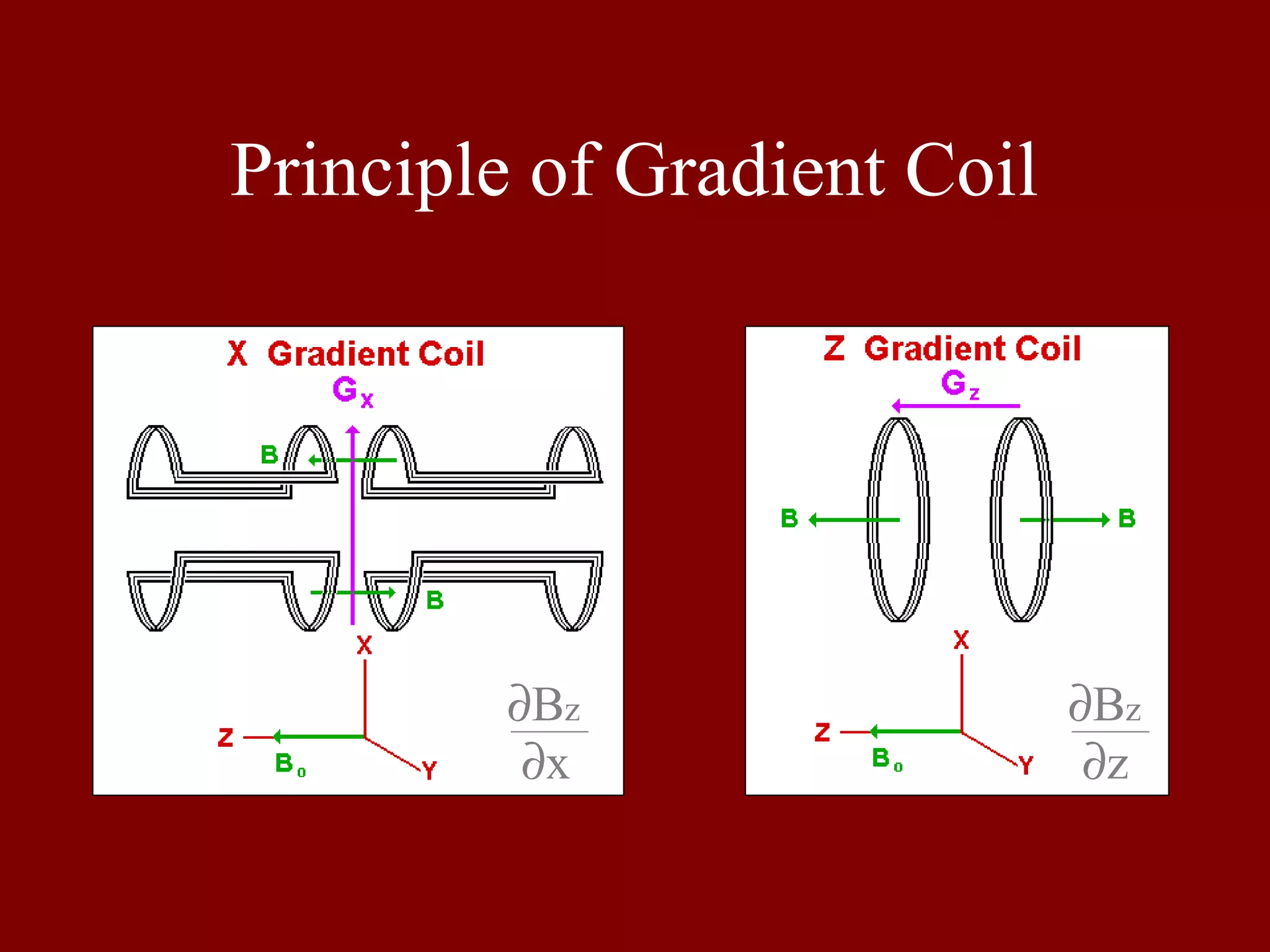
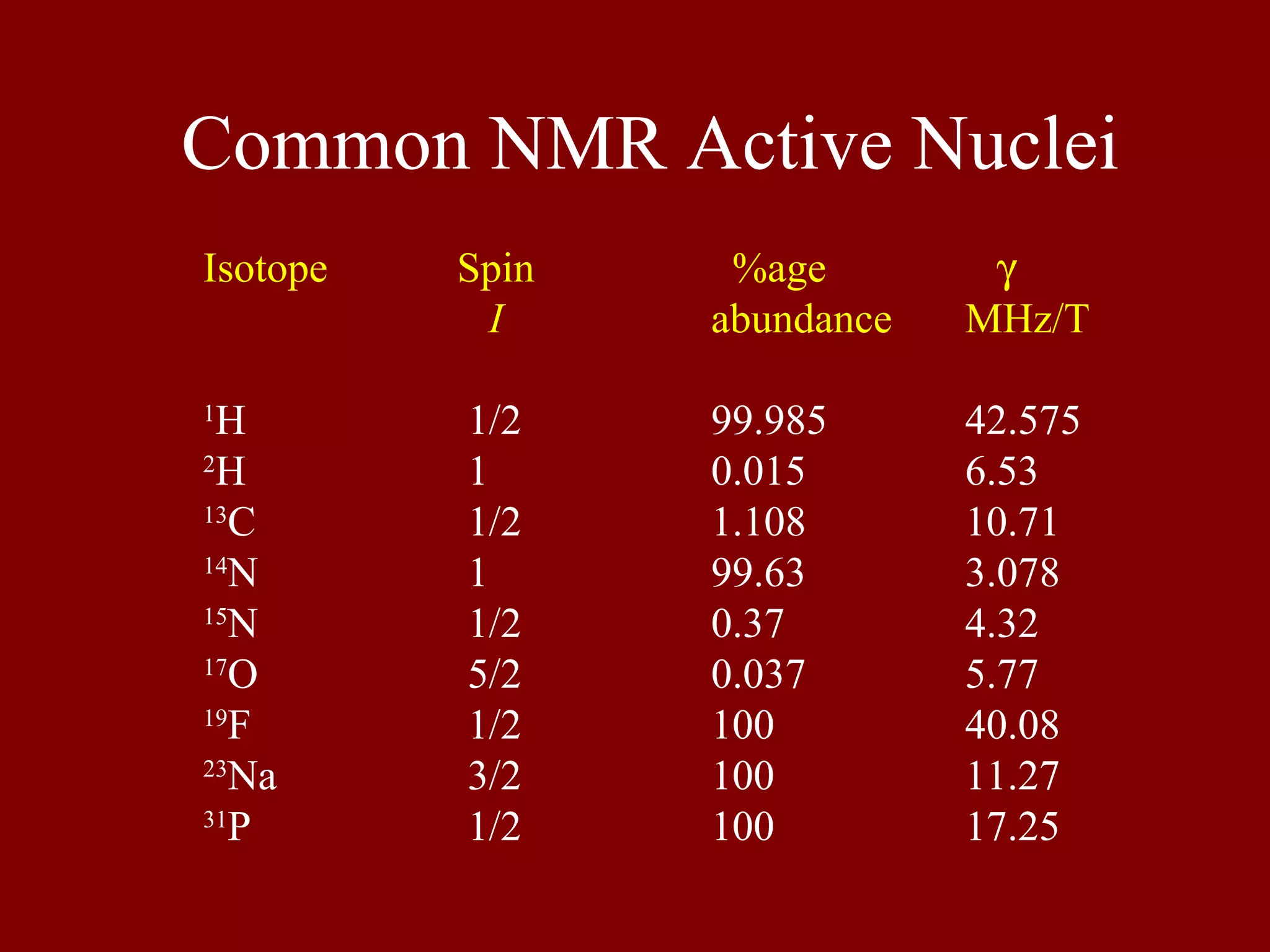
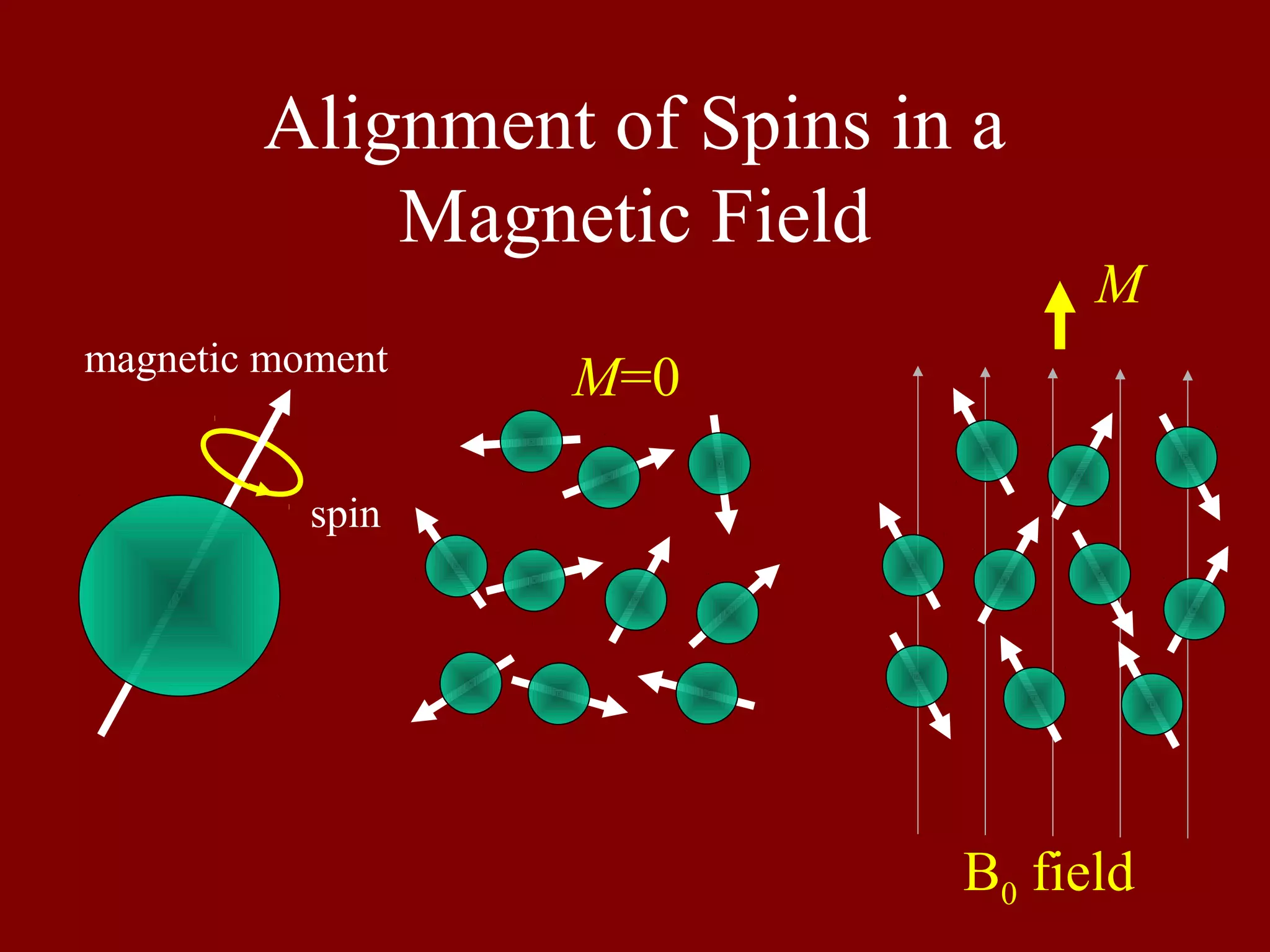
This document provides an overview of MRI system components and basic MRI physics concepts. It includes: 1) A diagram of the main components of an MRI system, including RF coils, gradient coils, and amplifiers. 2) Tables listing common NMR-active nuclei and their properties important for MRI. 3) Explanations of spin alignment in magnetic fields, Larmor frequency, spin excitation, free induction decay, Bloch equations, T1 and T2 relaxation, and slice selection techniques.













![Bloch Equations
dMz(t) = − [Mz(t) − M0]
dt T1
dMxy(t) = − Mxy(t)
dt T2
Mz
Mxy
Mz Mz
Mxy
Mxy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/o7sprchash6hppniv2kx-signature-32d797e46816d2f1ad04b19f9671fd9c01ddaa51c8250008594a8e918e443472-poli-160917224221/75/Mri-system-block-diagram-14-2048.jpg)
![T1 Relaxation
Mz(t) = M0 + {Mz(0) − M0}exp(-t/T1)
Mz Mz
t t
saturation–
recovery
inversion–recovery
dMz(t) = − [Mz(t) − M0]
dt T1
M0 M0
Mz(0) = 0 Mz(0) = −M0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/o7sprchash6hppniv2kx-signature-32d797e46816d2f1ad04b19f9671fd9c01ddaa51c8250008594a8e918e443472-poli-160917224221/75/Mri-system-block-diagram-15-2048.jpg)






Depicts a block diagram of an MRI system consisting of components such as RF amplitifiers, spectrometers, and gradient coils.
Explains the principle of gradient coils in MRI, focusing on magnetic field gradients and spatial encoding.
Lists common NMR active nuclei with their isotope spins, abundance percentages, and resonance frequencies.
Discusses the alignment of nuclear spins in a magnetic field and the corresponding magnetic moments.
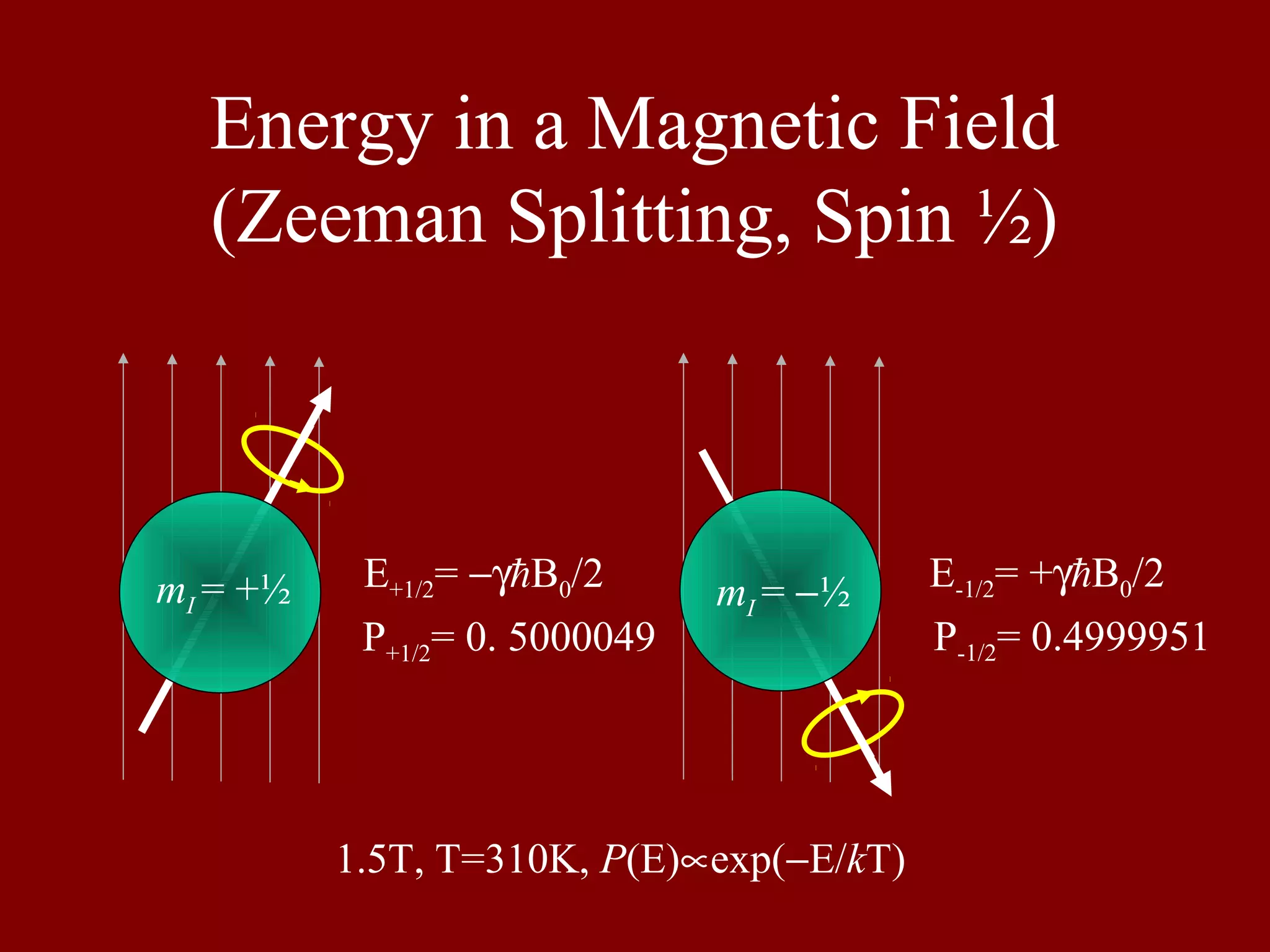
Details the Zeeman splitting energy levels for spin-1/2 particles in a magnetic field and their population ratios.
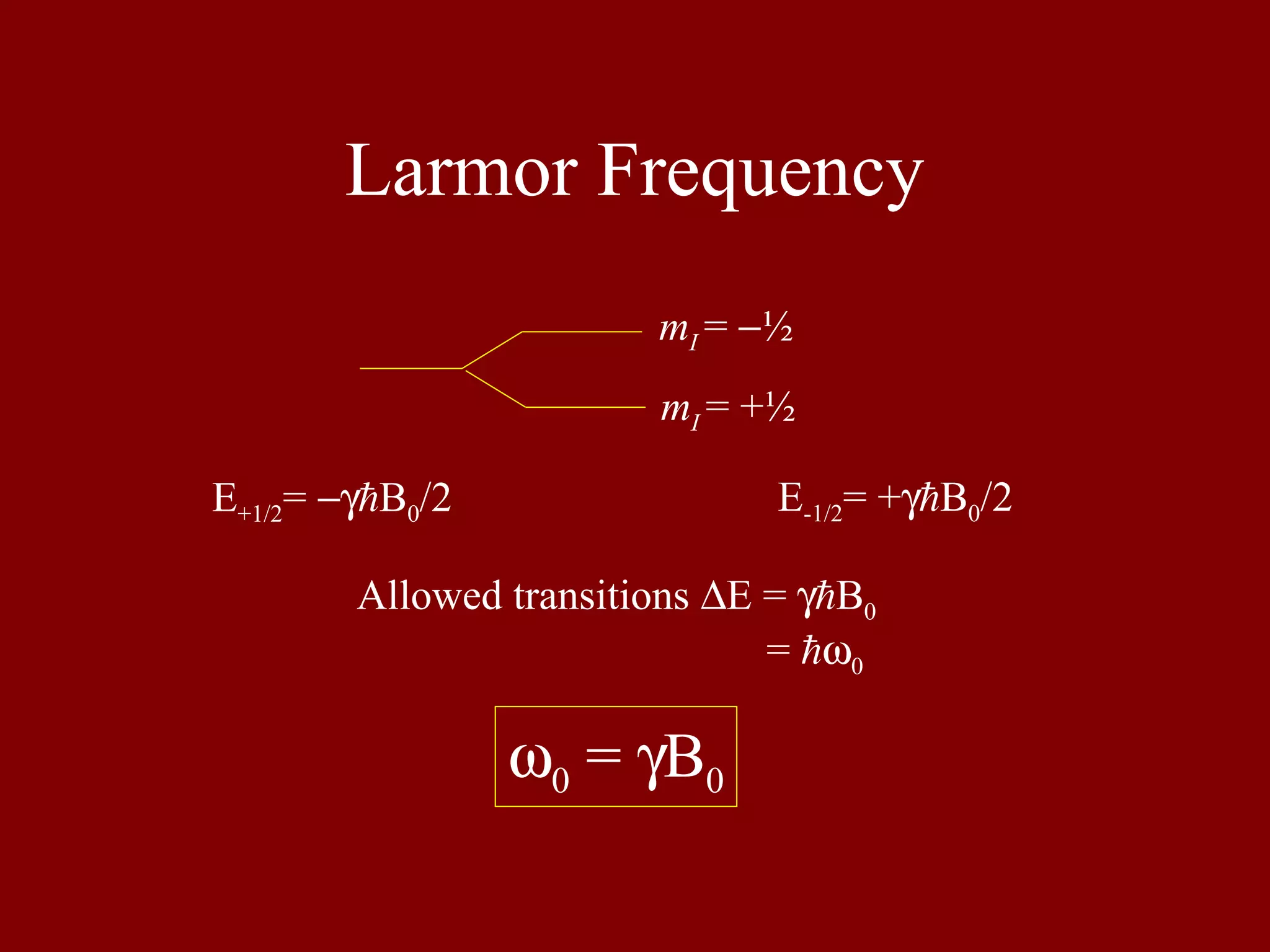
Describes the relationship between energy transitions and Larmor frequency in the context of spin-1/2 nuclei.
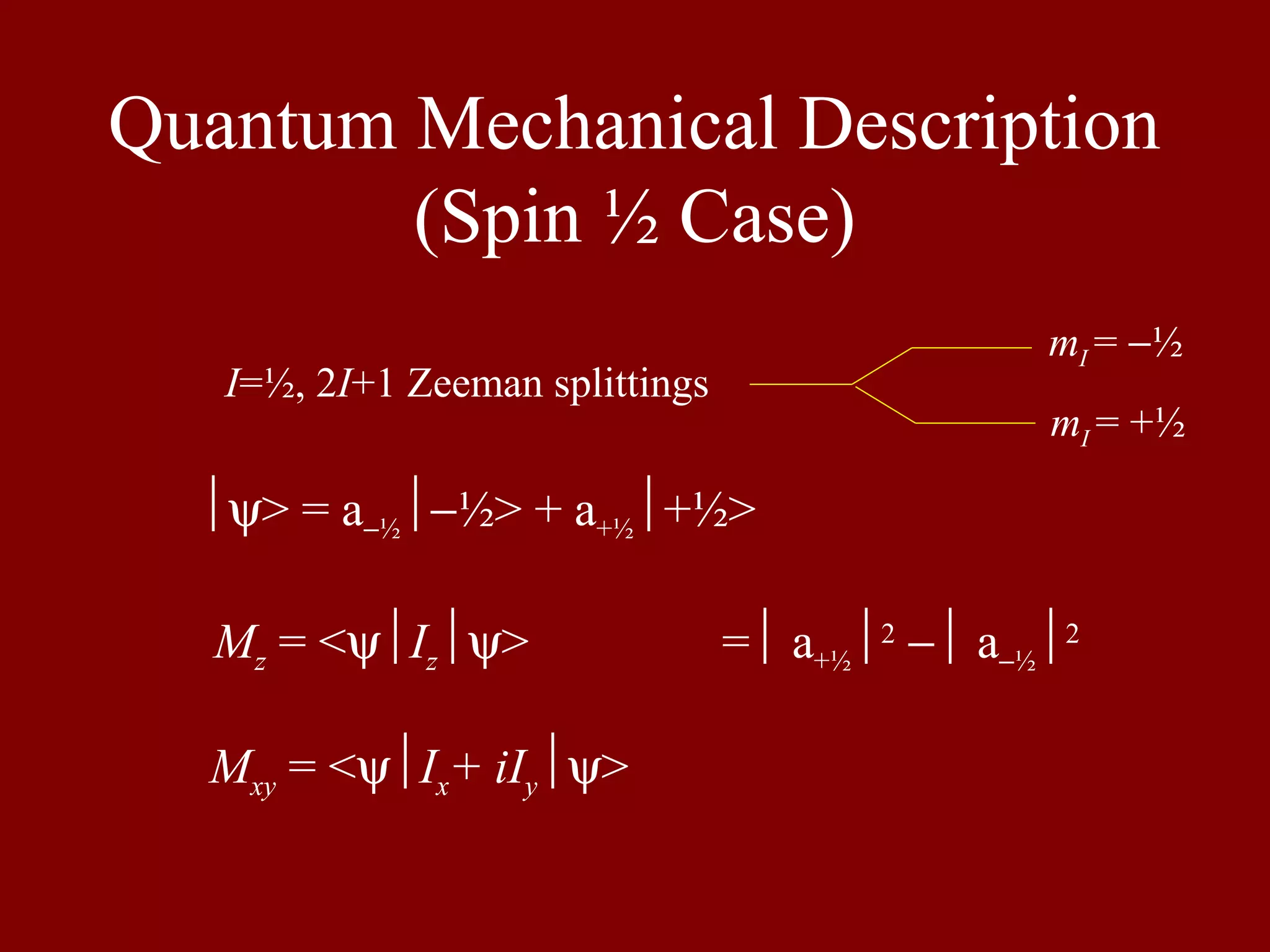
Presents the quantum mechanical description of spins in a Zeeman field, including mathematical expressions for spin states.
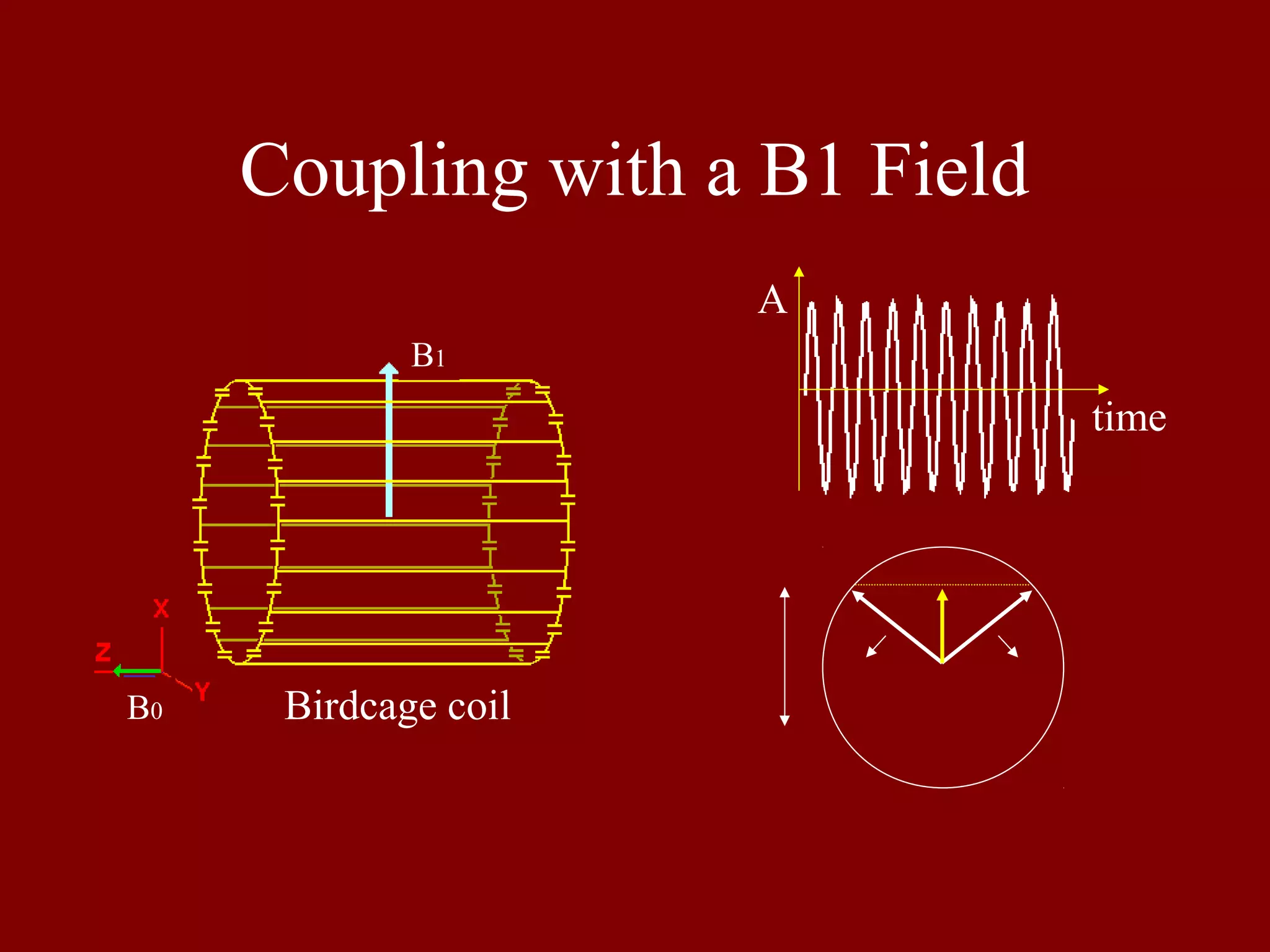
Illustrates the coupling of nuclear spins with the B1 RF field during excitation using a birdcage coil.
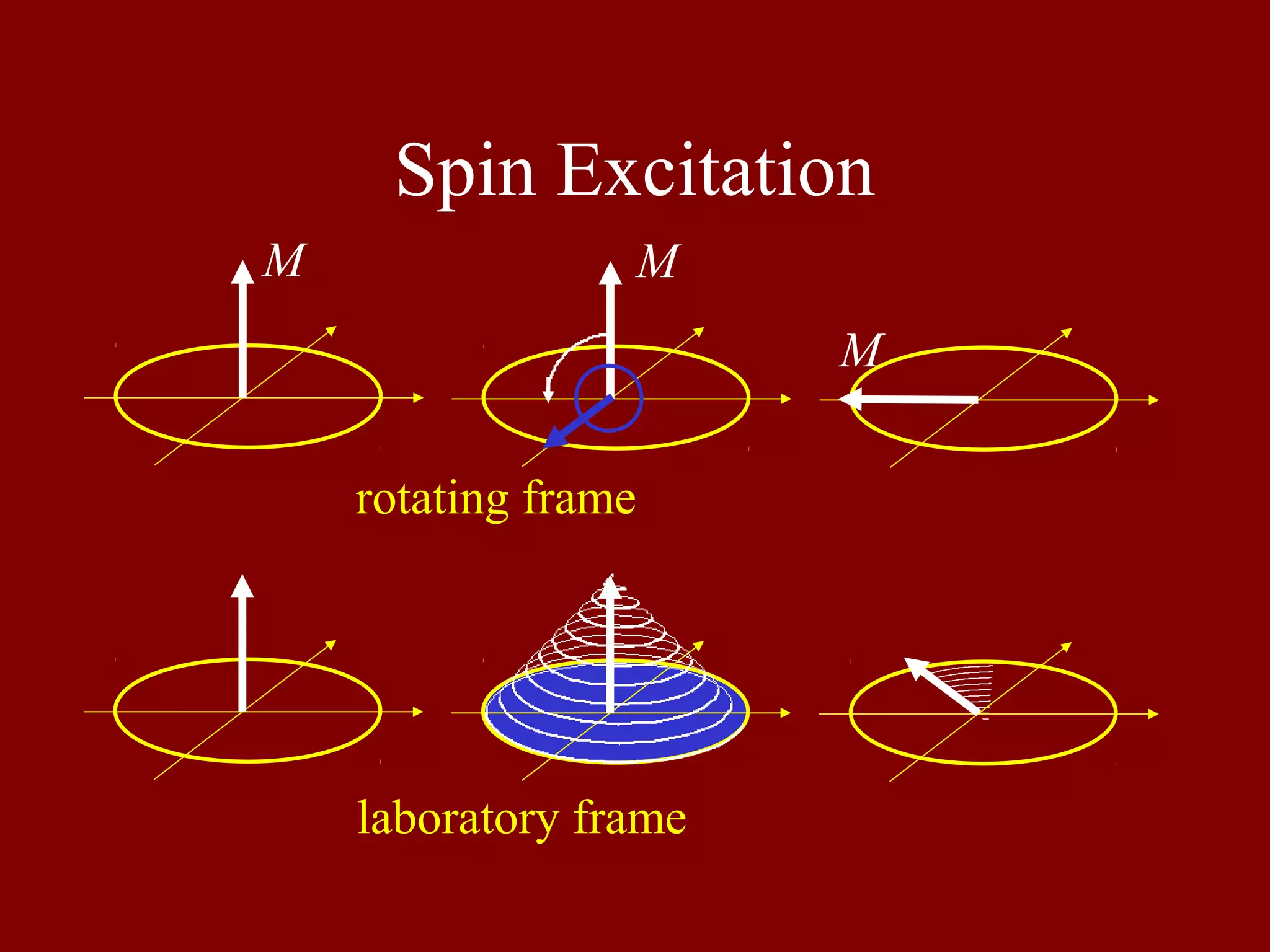
Describes the dynamics of spin excitation in both the rotating frame and the laboratory frame.
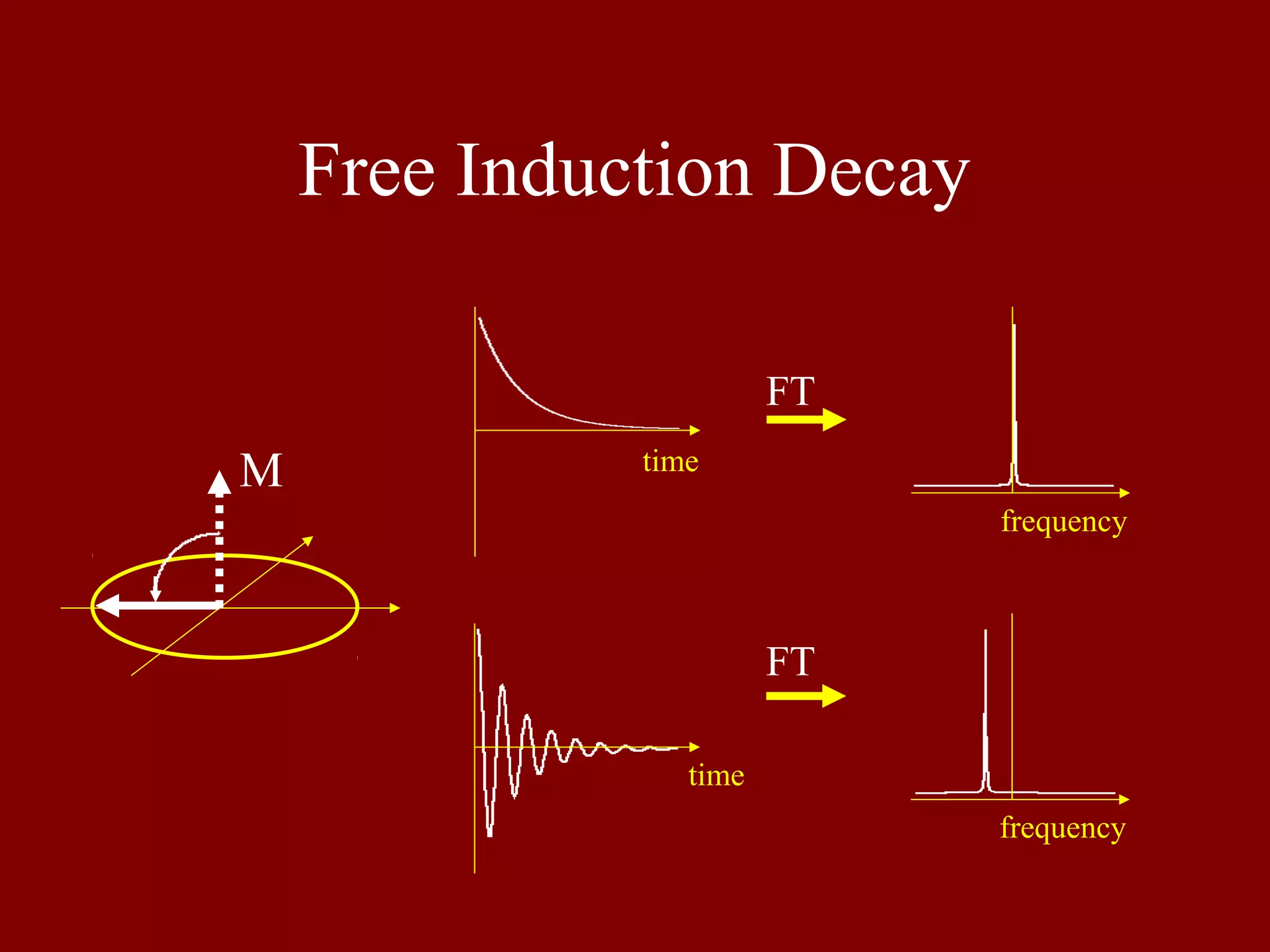
Explains the concept of Free Induction Decay (FID) in nuclear magnetic resonance.
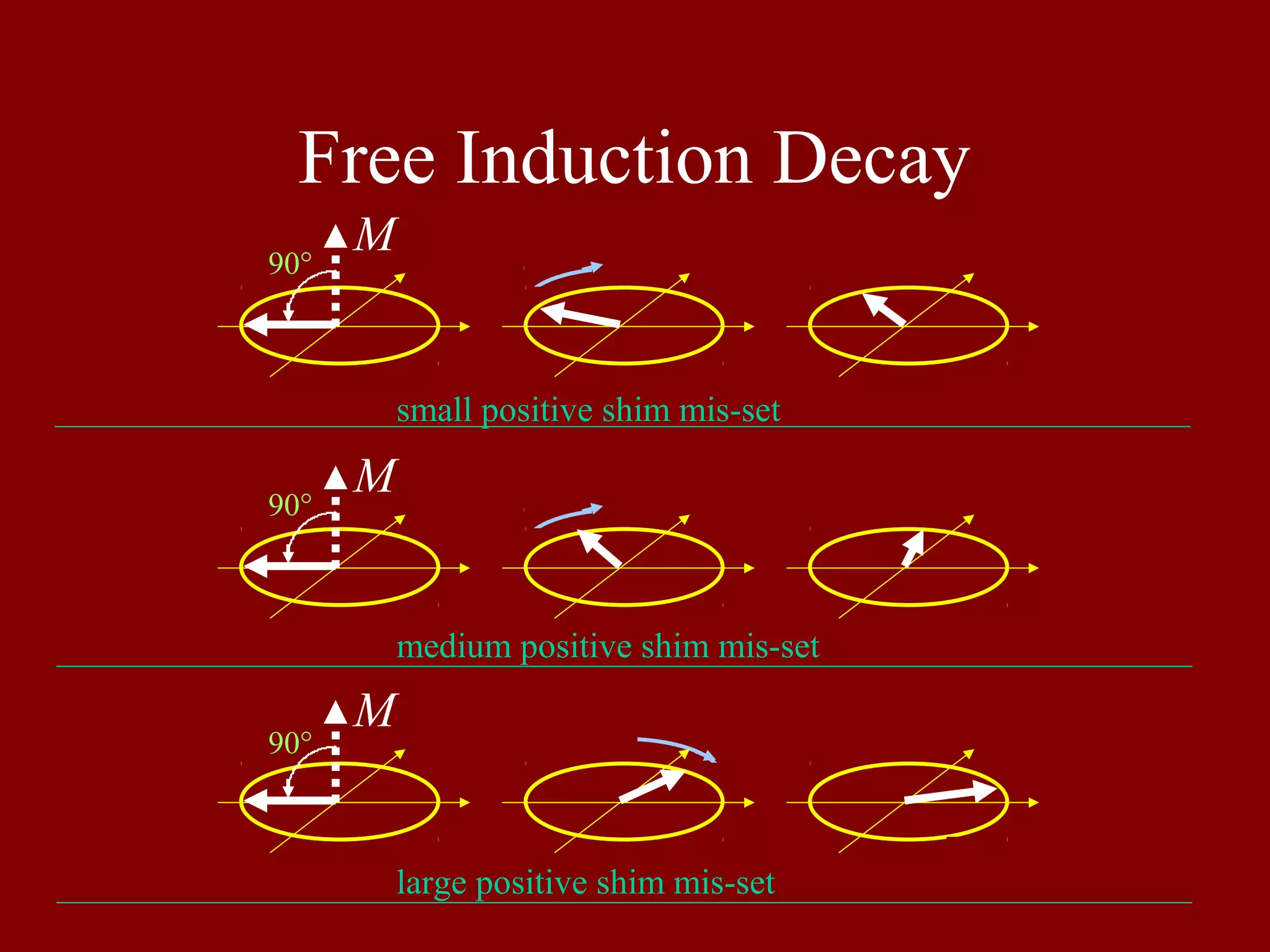
Illustrates Free Induction Decay with varying positive shim mis-settings across multiple scans.
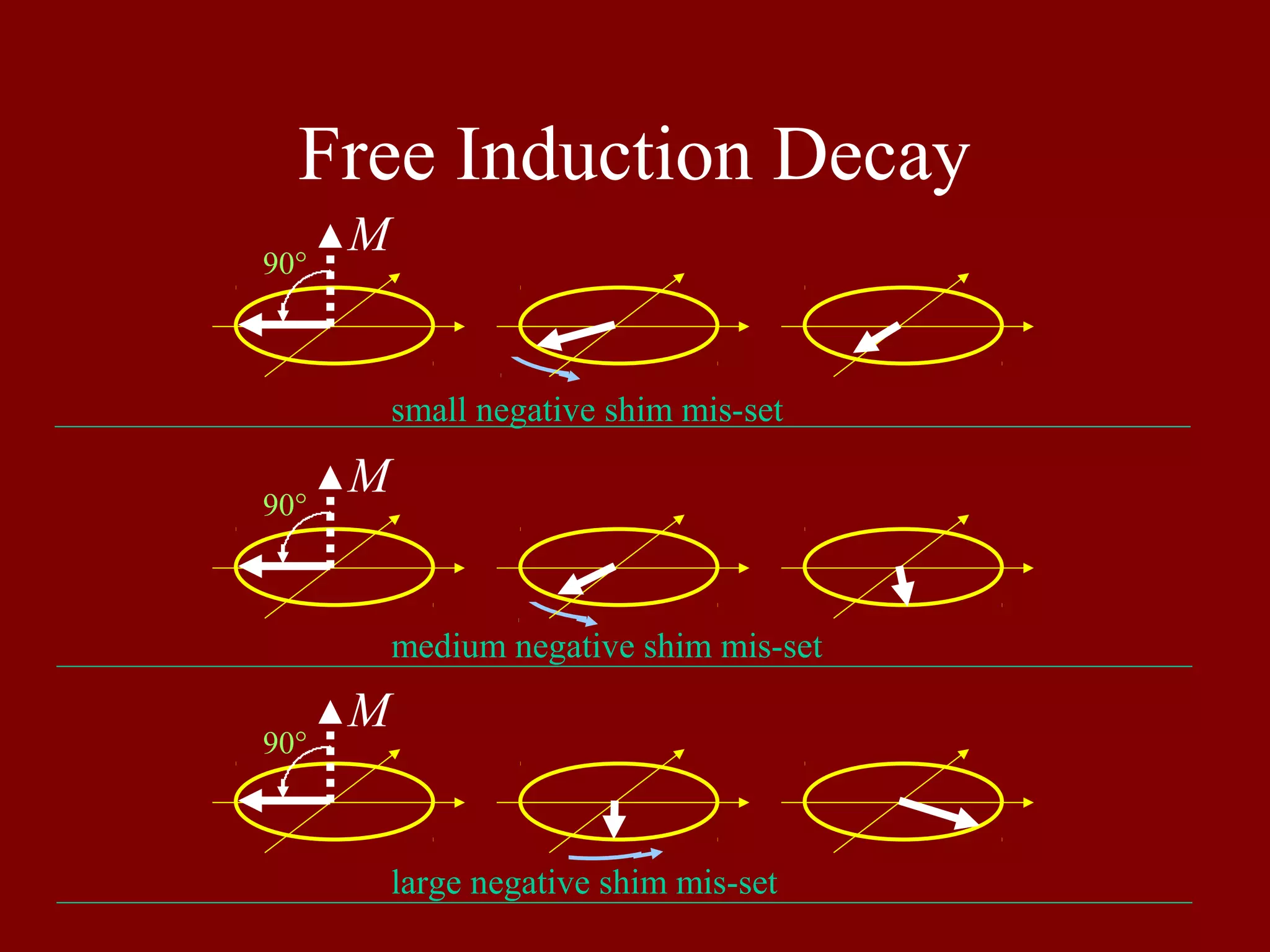
Shows the effect of negative shim mis-settings on Free Induction Decay in different scenarios.
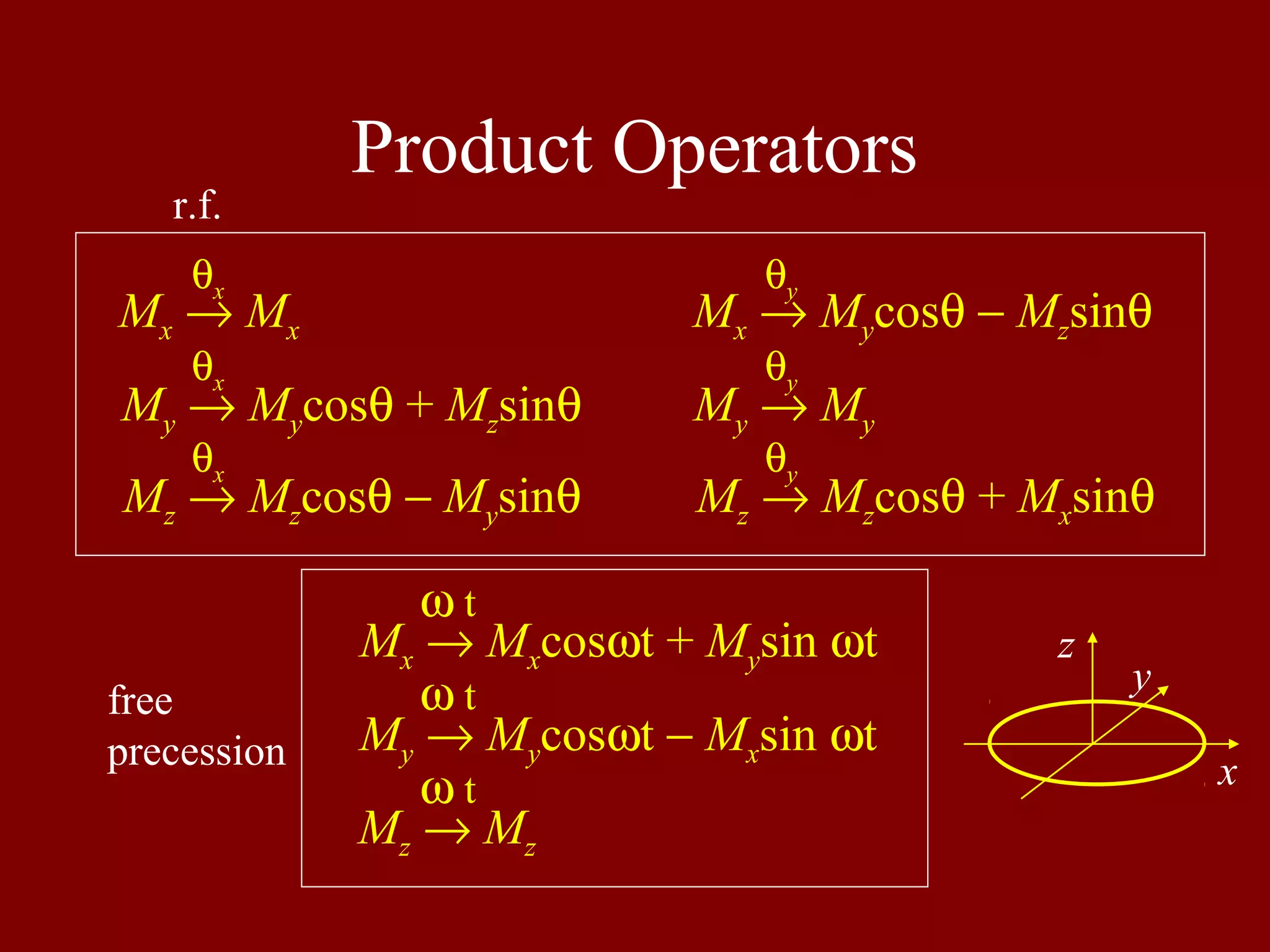
Discusses product operators in MRI, detailing transformations of magnetic moments under rotation.
Presents the Bloch equations governing the dynamics of spin magnetization in MRI.
Describes T1 relaxation processes in MRI, illustrating saturation and recovery mechanisms.
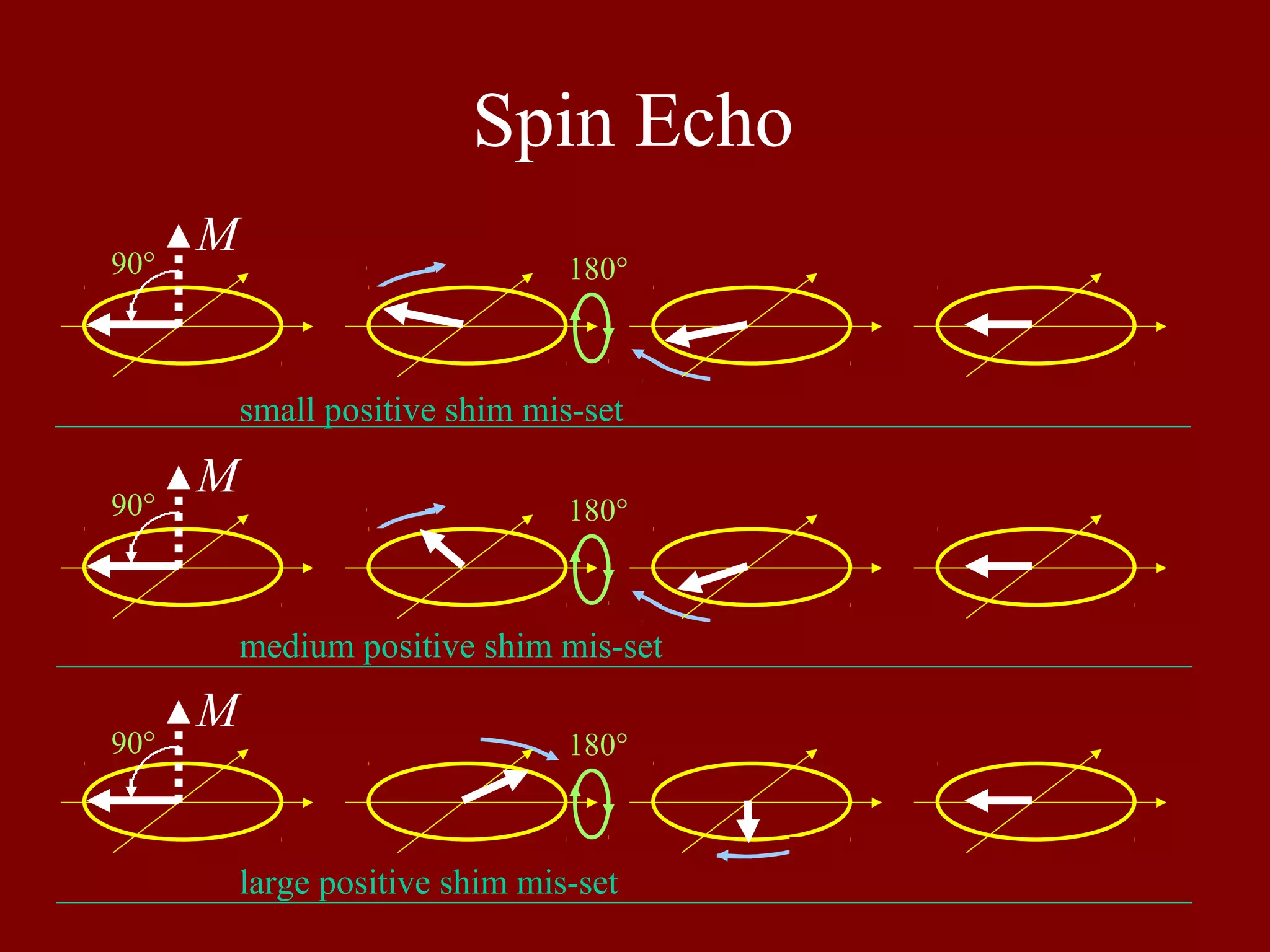
Explains the spin echo sequence in MRI, addressing the impact of positive shim mis-settings.
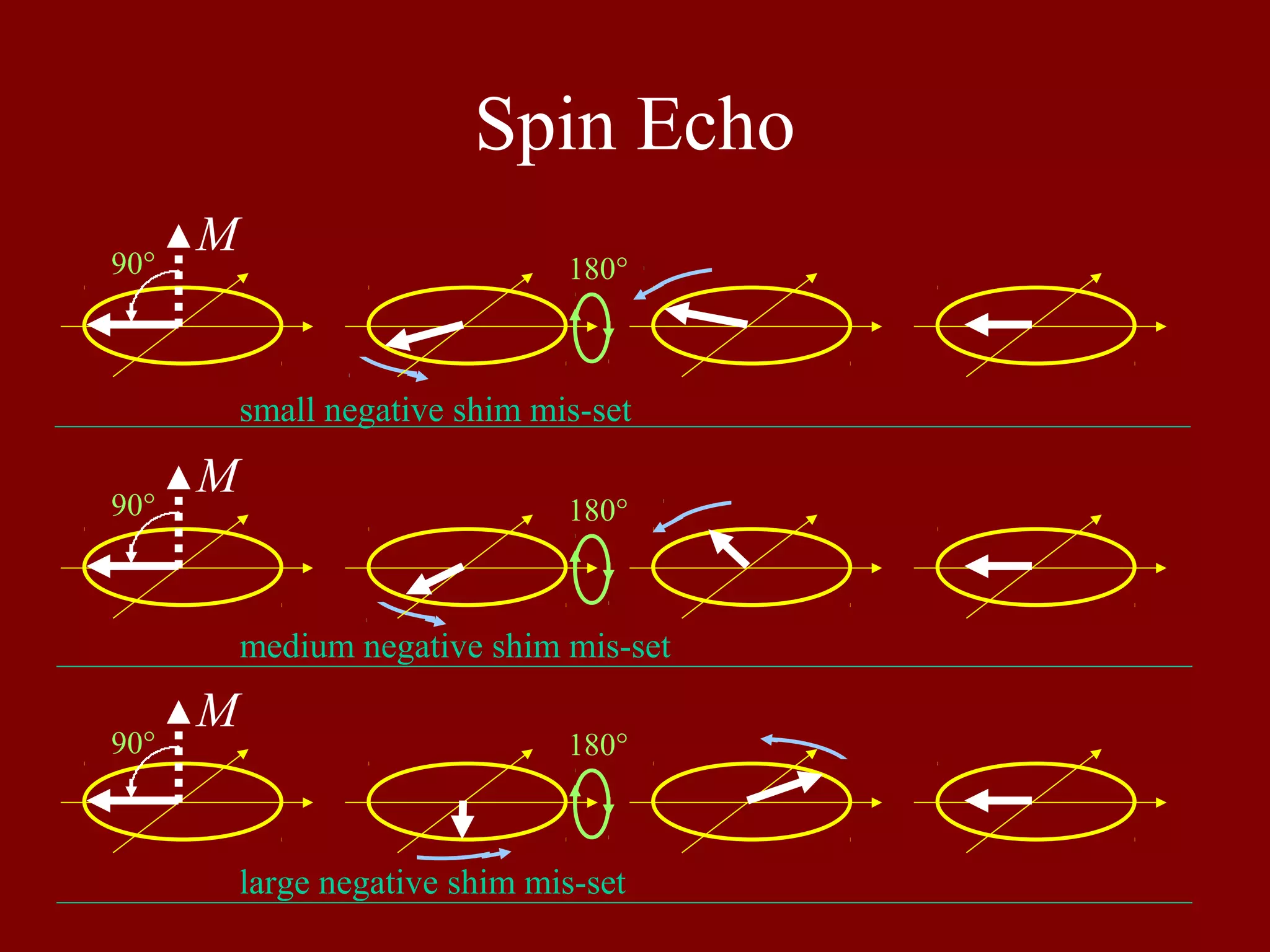
Demonstrates the spin echo sequence effects with negative shim mis-settings during the MRI process.
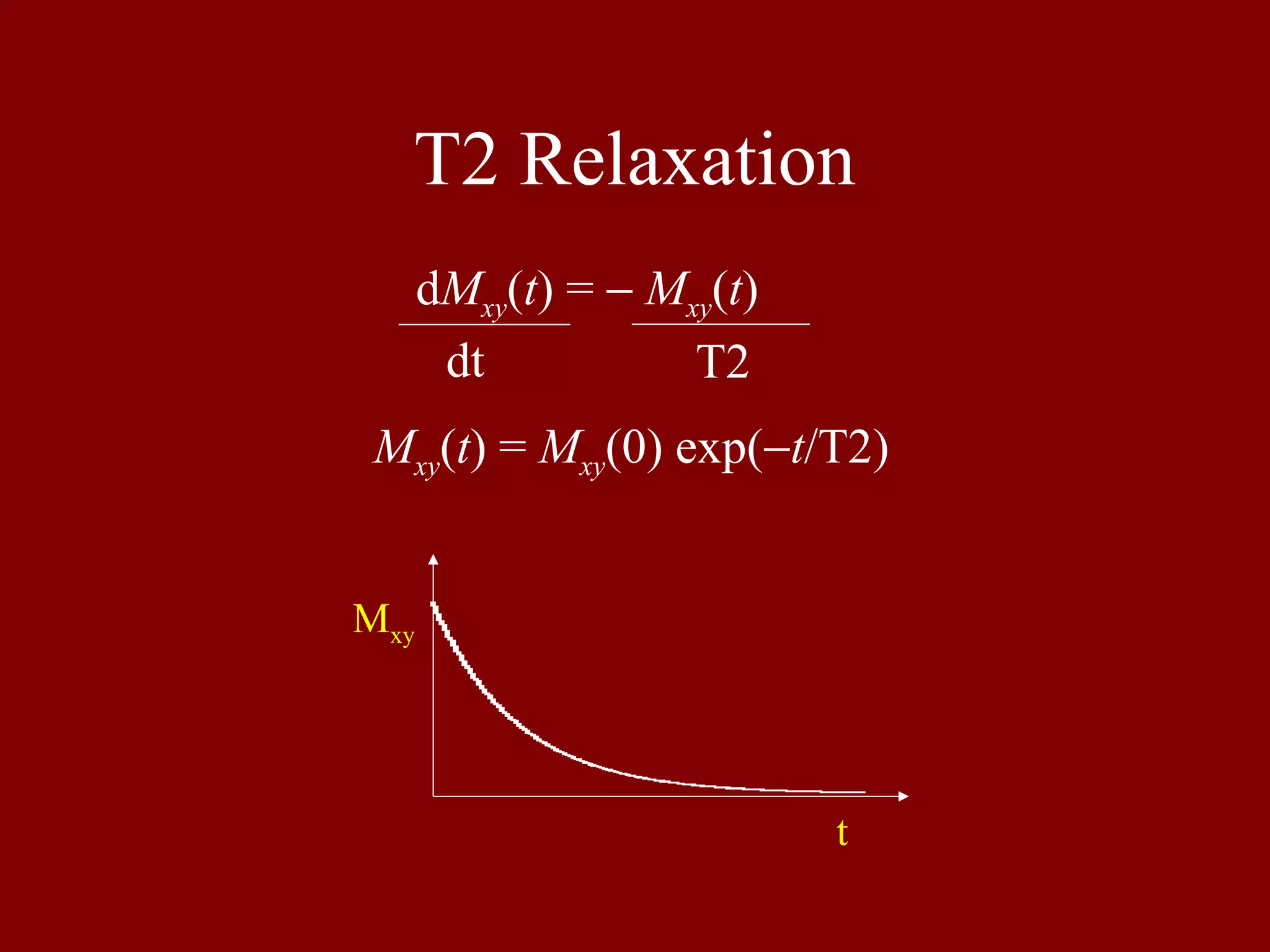
Details T2 relaxation characteristics, showing how transverse magnetization evolves over time.
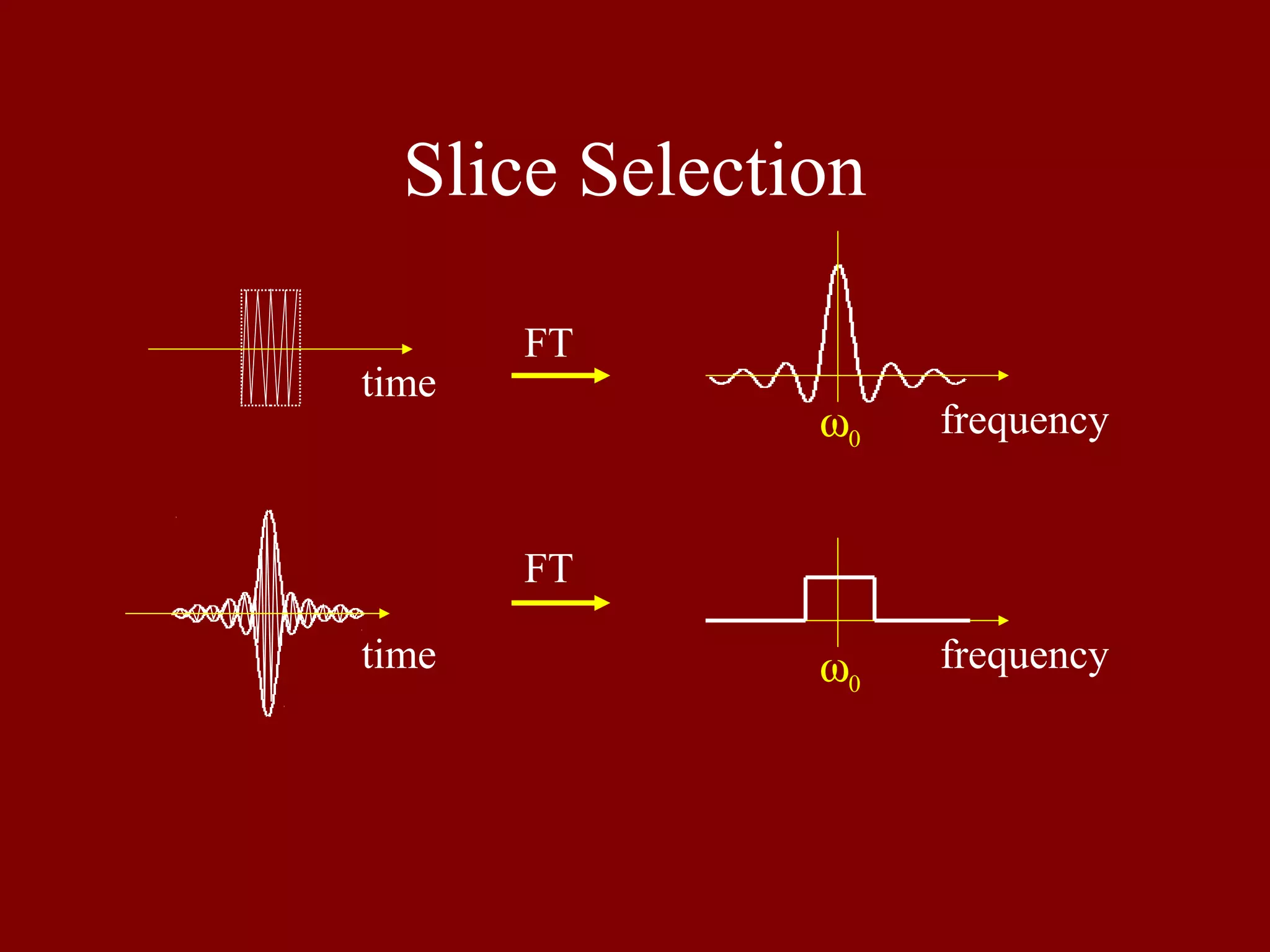
Introduces slice selection in MRI, linking frequency-selective excitation with spatial localization.
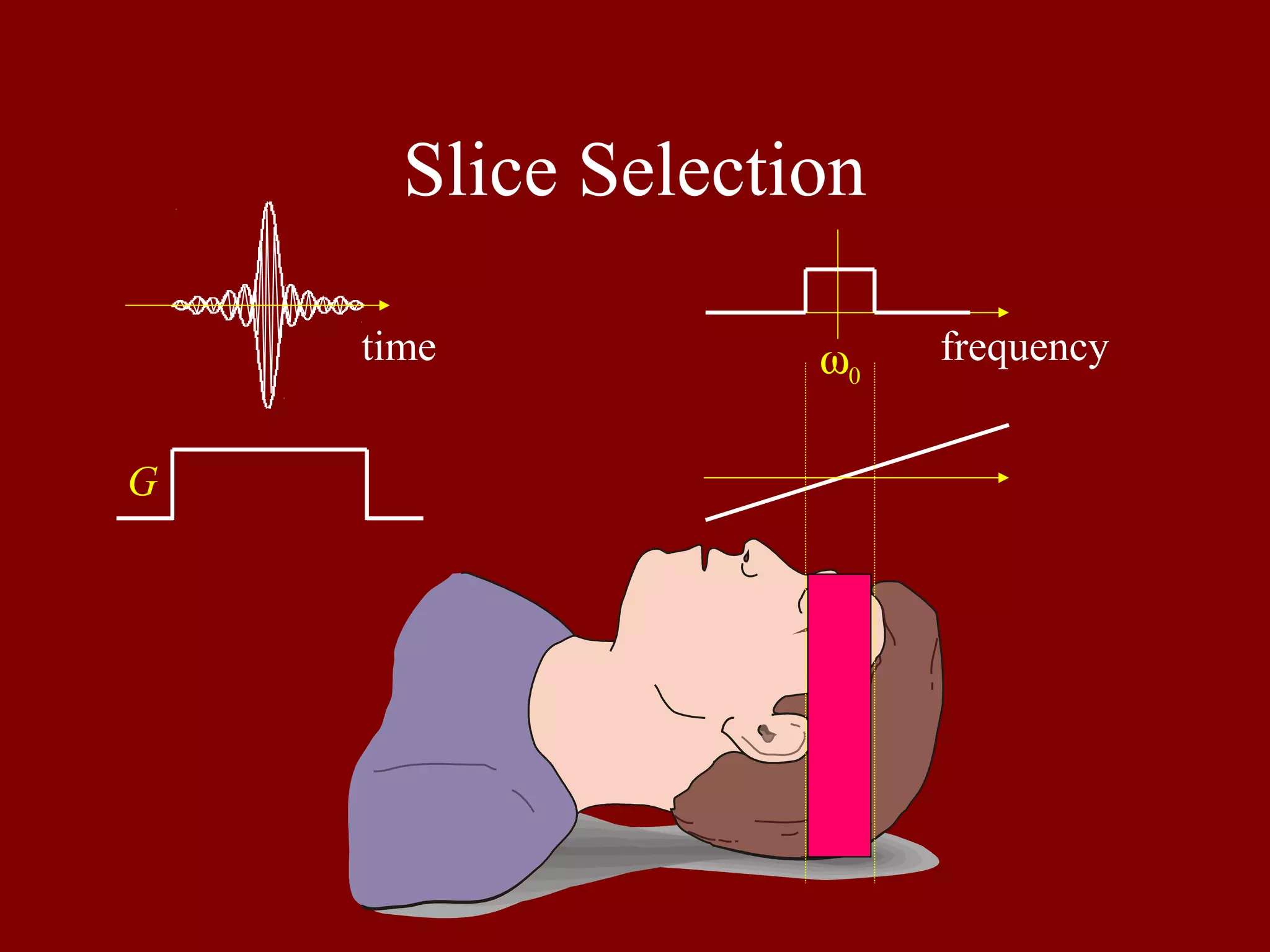
Expands on slice selection methods using gradient fields and frequency manipulations in MRI.