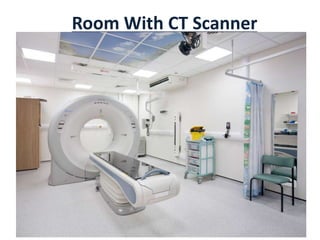
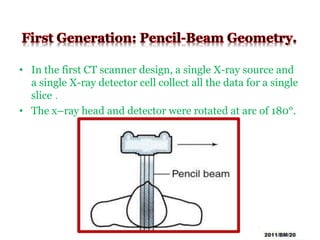
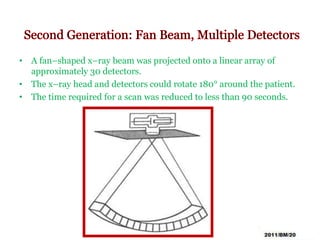
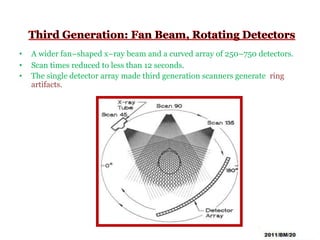
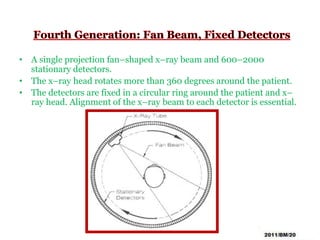
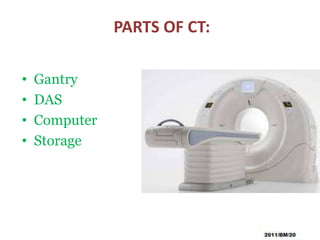
This document summarizes the history and technology of computed tomography (CT) scans. It discusses how CT scans were invented in the 1970s and have since advanced through 5 generations of technology. The key components of a modern CT scanner are described, including the gantry, data acquisition system, computer, and storage. CT scanning is highlighted as a valuable medical imaging tool that can create detailed cross-sectional images of multiple types of tissues simultaneously, aiding in disease diagnosis and treatment planning.