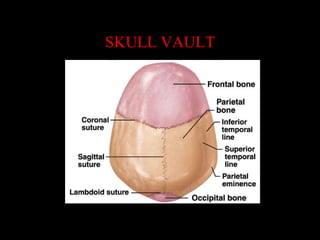
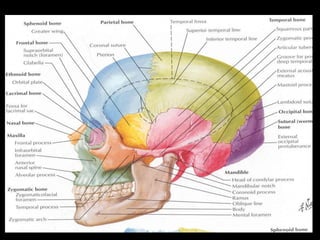
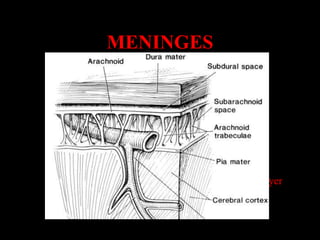
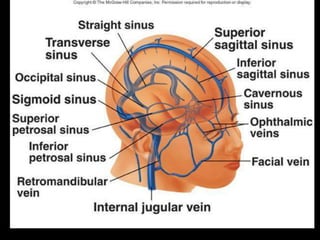
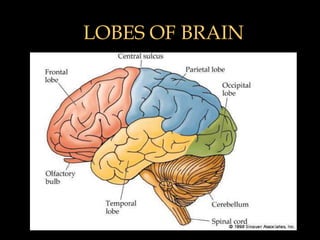
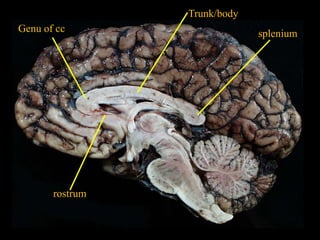
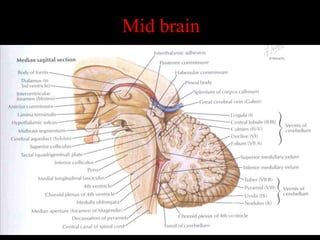
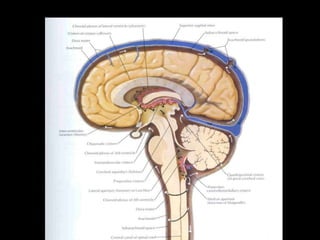
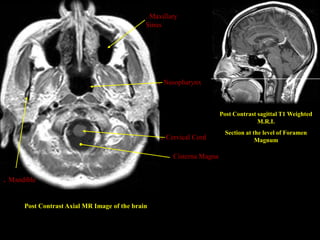
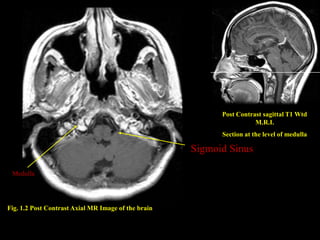
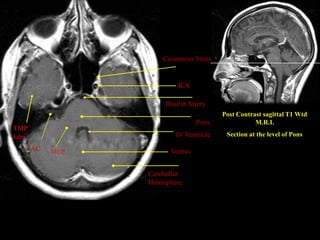
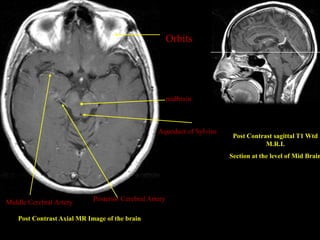
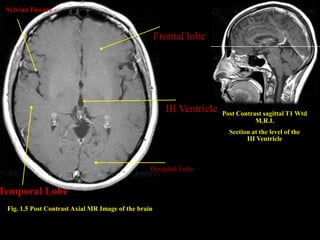
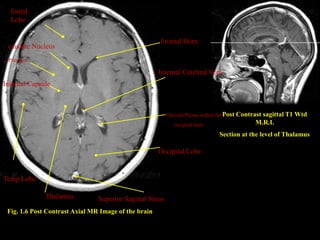
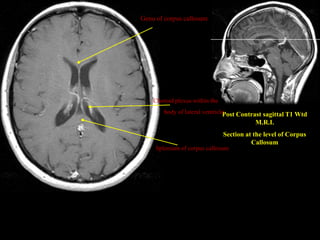
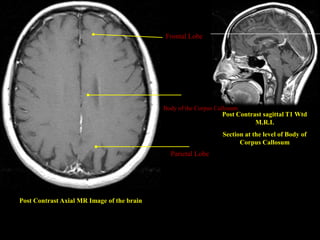
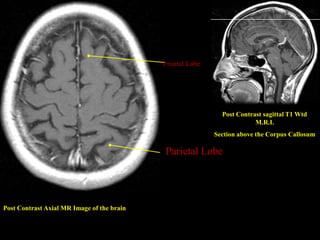
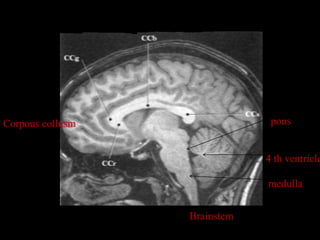
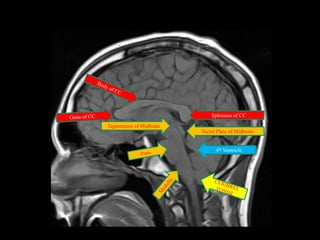
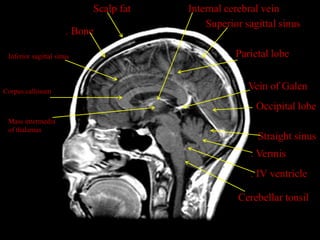
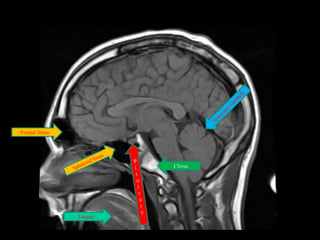
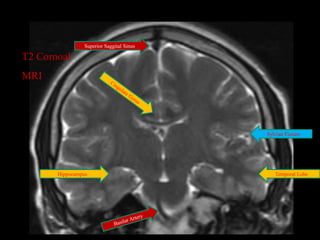
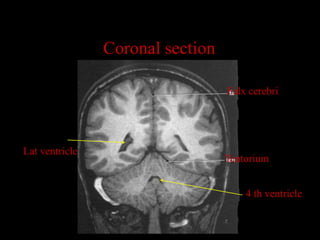
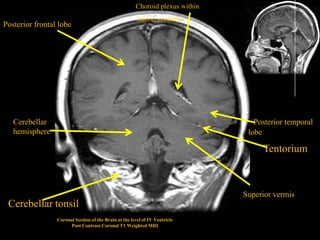
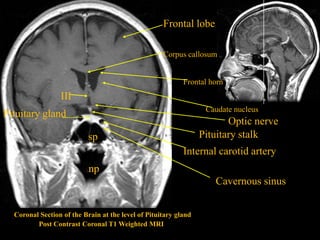
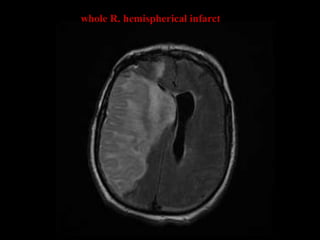
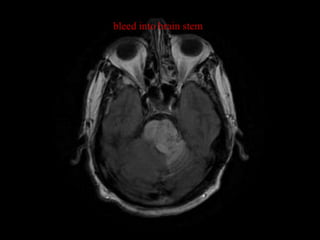
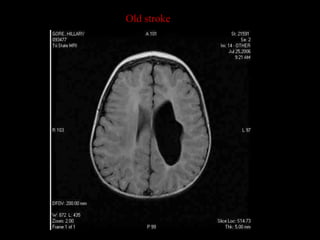
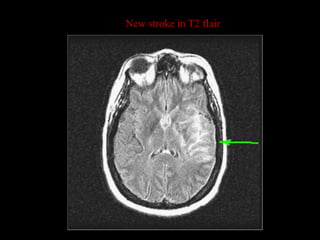
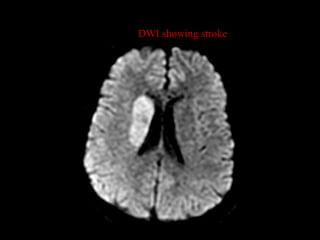
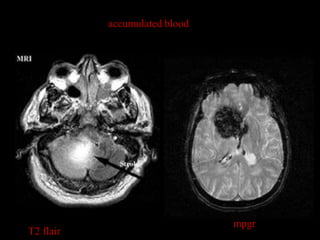
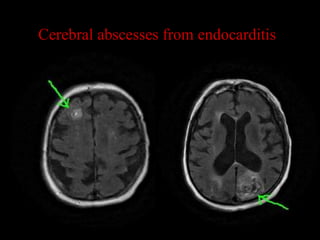
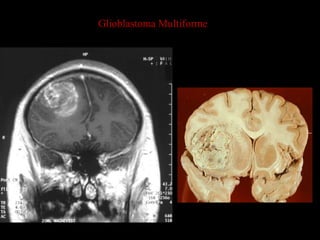
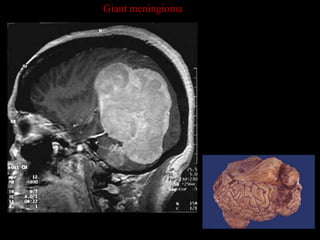
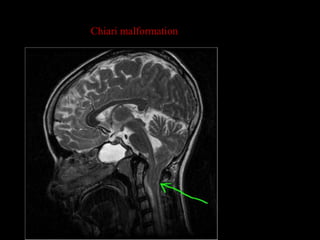
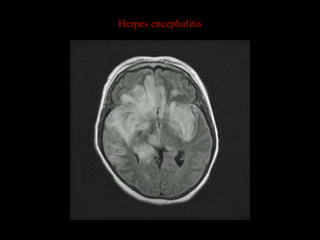
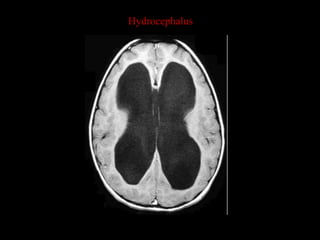
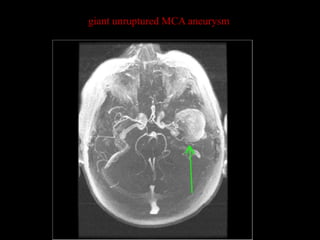
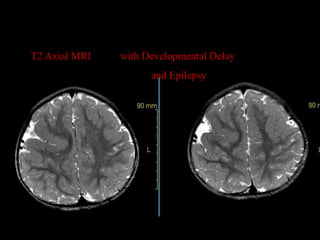
This document provides an overview of brain anatomy, beginning with the structures of the skull and meninges. It describes the major divisions of the brain including the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. It outlines the lobes of the cerebral hemispheres and internal structures such as the basal ganglia and corpus callosum. Key structures such as the ventricles and cisterns are identified. The rest of the document illustrates various sections of the brain with labeled diagrams and MRI images.