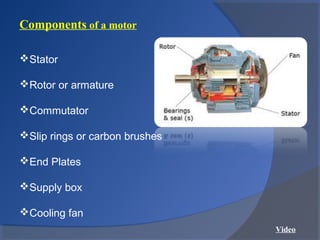
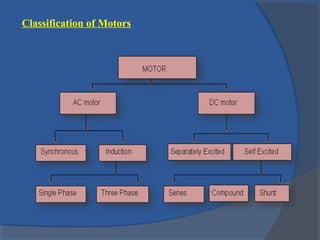
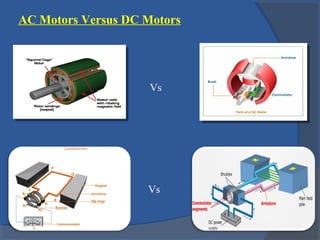
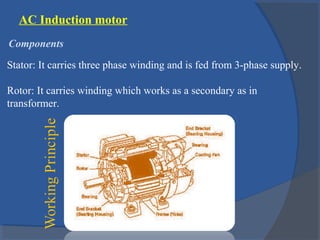
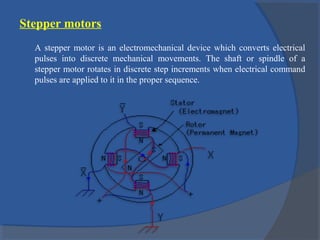
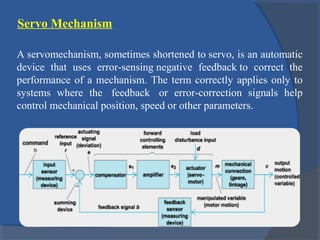
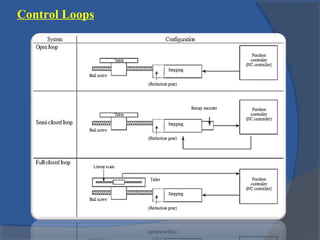
This document provides an overview of different types of motors used in computer numerical control (CNC) machines. It describes the basic components and working principles of motors. It then compares alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) motors, discussing stepper motors, servo mechanisms, and the motors typically used in CNC machines including spindle motors and linear motors. Key selection criteria for motors in CNC applications include revolutions per minute, torque, standards compliance, power requirements, and motor load.