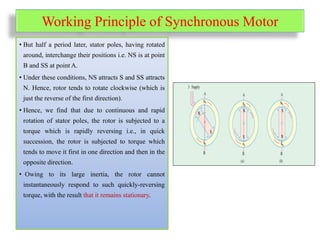
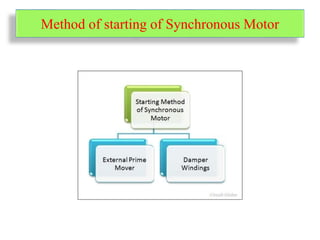
A synchronous motor operates at synchronous speed, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy, with the stator and rotor being the main components. Starting methods include using an external prime mover or damper windings, which help achieve synchronous speed before applying DC excitation to the rotor. The motor has various torque types, including starting torque, running torque, pull-in torque, and pull-out torque, each defining its performance under different operational conditions.