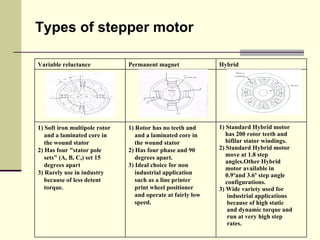
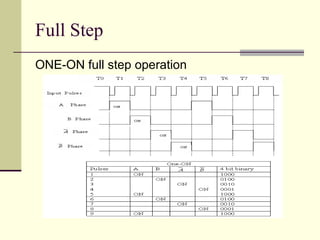
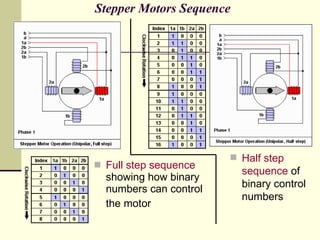
There are three main types of stepper motors: permanent magnet, variable reluctance, and hybrid. Hybrid stepper motors are most commonly used in industry applications due to their high static and dynamic torque. Stepper motors can operate in full step, half step, or microstep modes which determine the motor resolution in steps per revolution. Higher resolution modes like half stepping increase the number of steps per revolution.