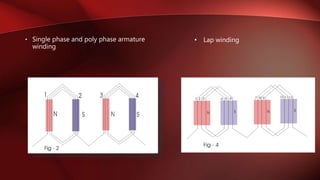
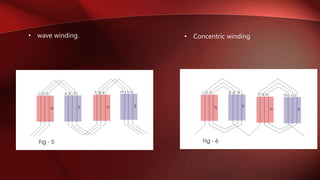
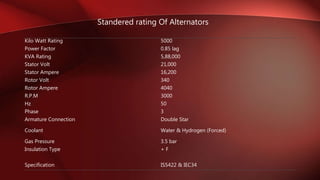
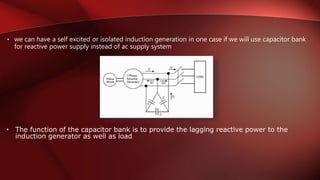
An alternator is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. It uses a rotating magnetic field with a stationary armature. The working principle relies on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. As the armature rotates within the magnetic field, an alternating current is produced. The main components are the stator with stationary armature windings and the rotor with a rotating magnetic field supplied by a DC current. Armature reaction causes the magnetic field to be distorted by the armature current. Alternators have various applications including in automobiles, power plants, and for providing regenerative braking in induction motors. Induction generators can also be used to convert the rotational energy of windmills into electrical energy.