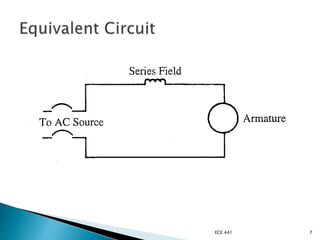
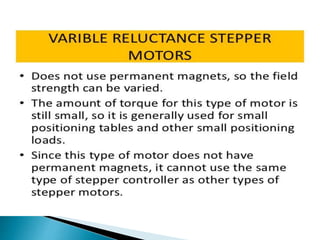
This document discusses several types of electric motors: AC series motors, universal motors, stepper motors, and shaded pole motors. It provides details on the construction and operation of universal motors and stepper motors. Universal motors can operate on either AC or DC power because the rotor and stator windings are connected in series. Stepper motors rotate in precise angular increments in response to applied digital pulses, making them well-suited for applications requiring precise positional control like printers and CNC machines. The document compares advantages and disadvantages of stepper motors.