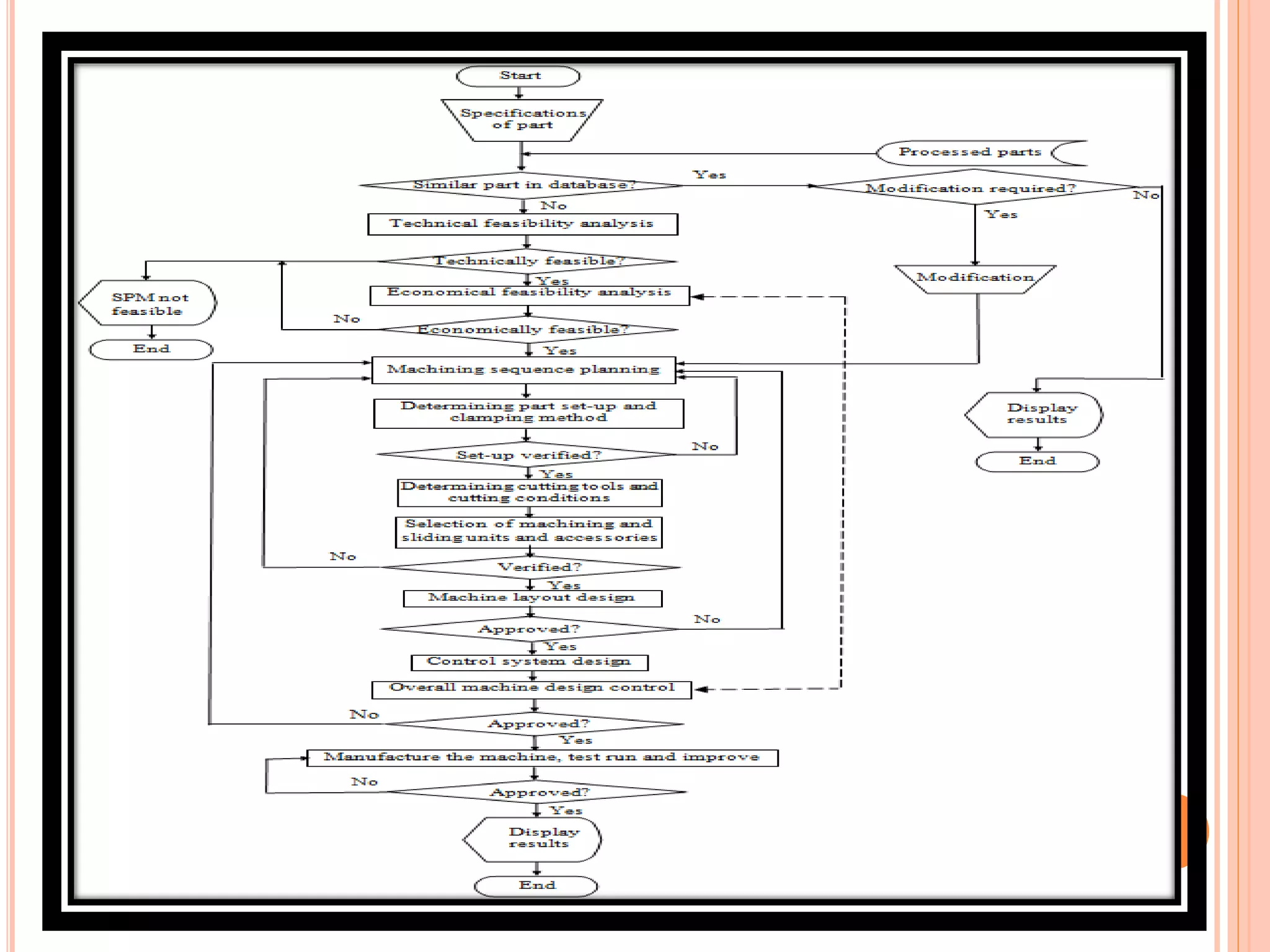
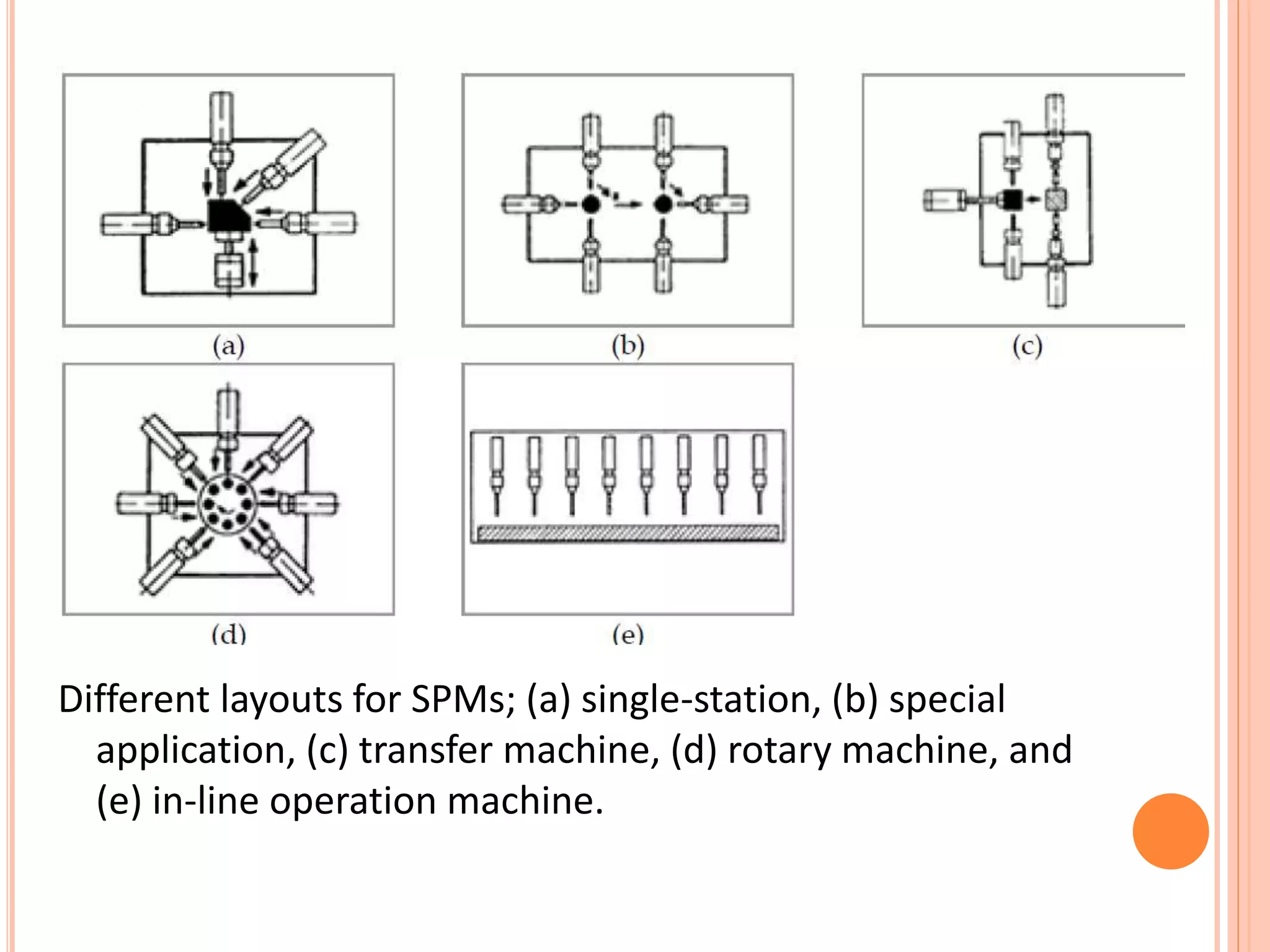
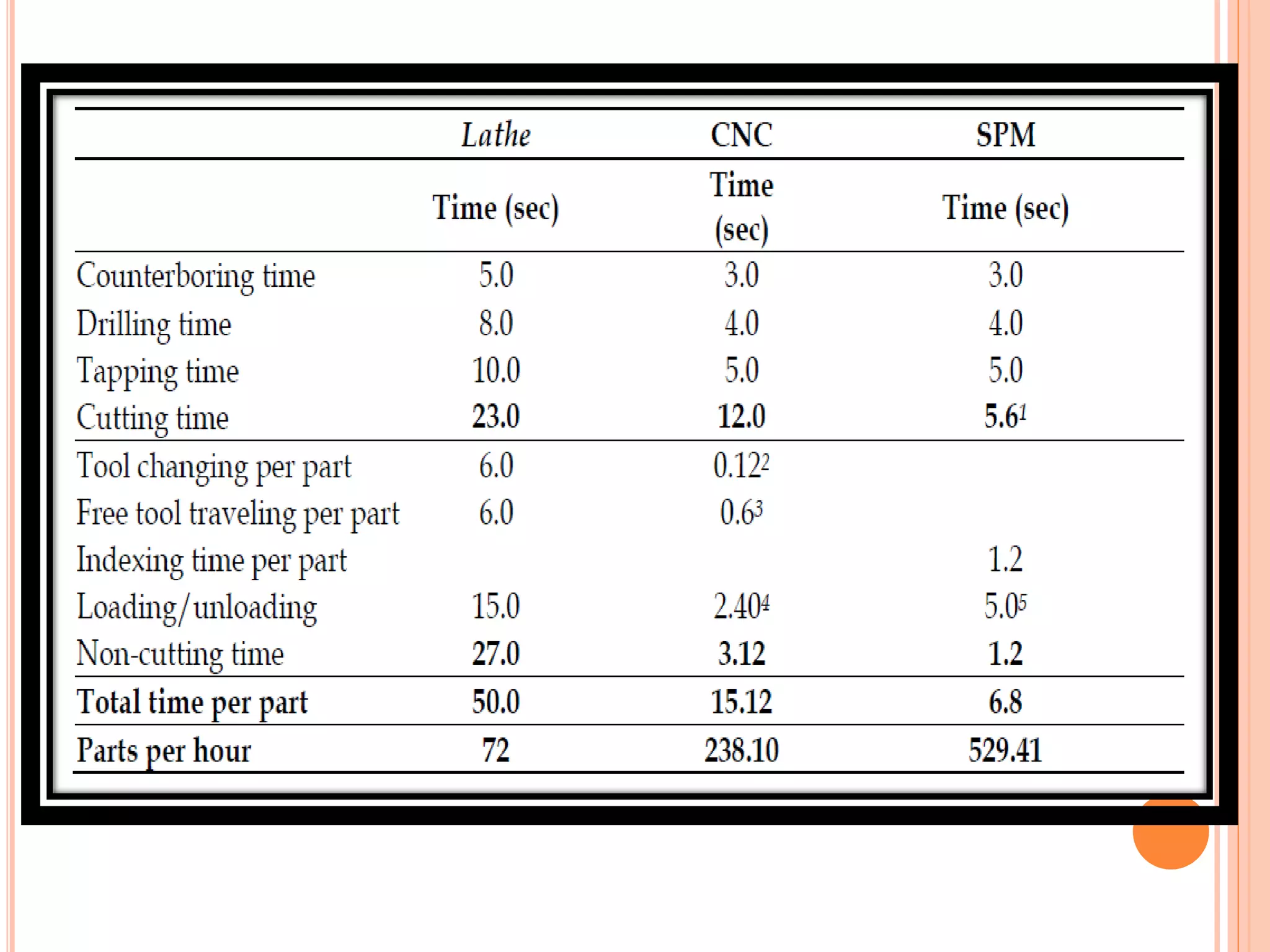
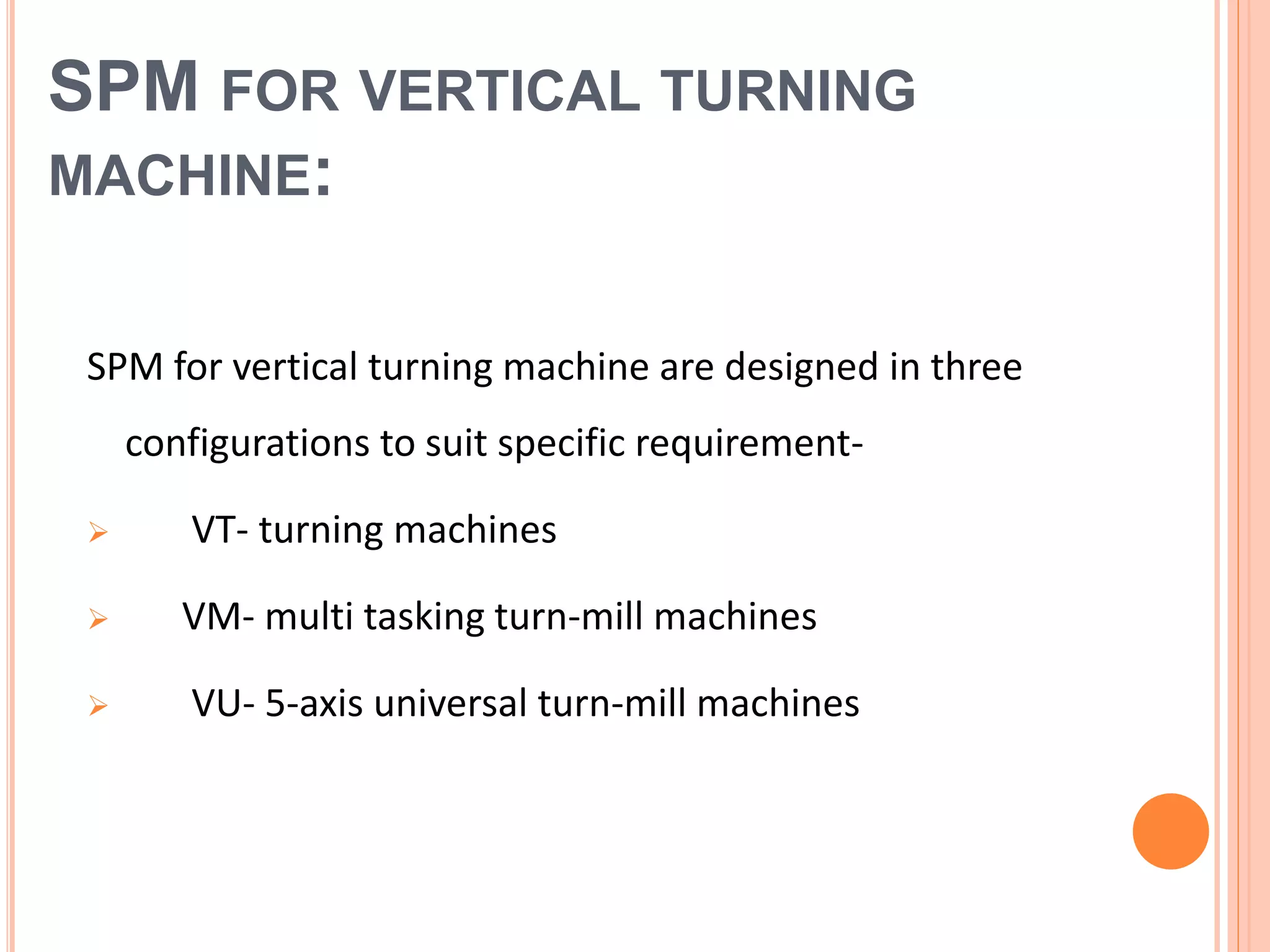
This document discusses special purpose machines (SPMs), which are custom-made machines designed for specific manufacturing processes. SPMs are used for mass production and can perform specialized operations like gear cutting. They are more efficient than general purpose machines due to lower costs, power usage, waste, and time spent on processes. SPMs require consideration of their unique purpose and design. They are typically single-station or multi-station and have advantages like increased productivity but limitations like high initial investment and less flexibility compared to general purpose machines.