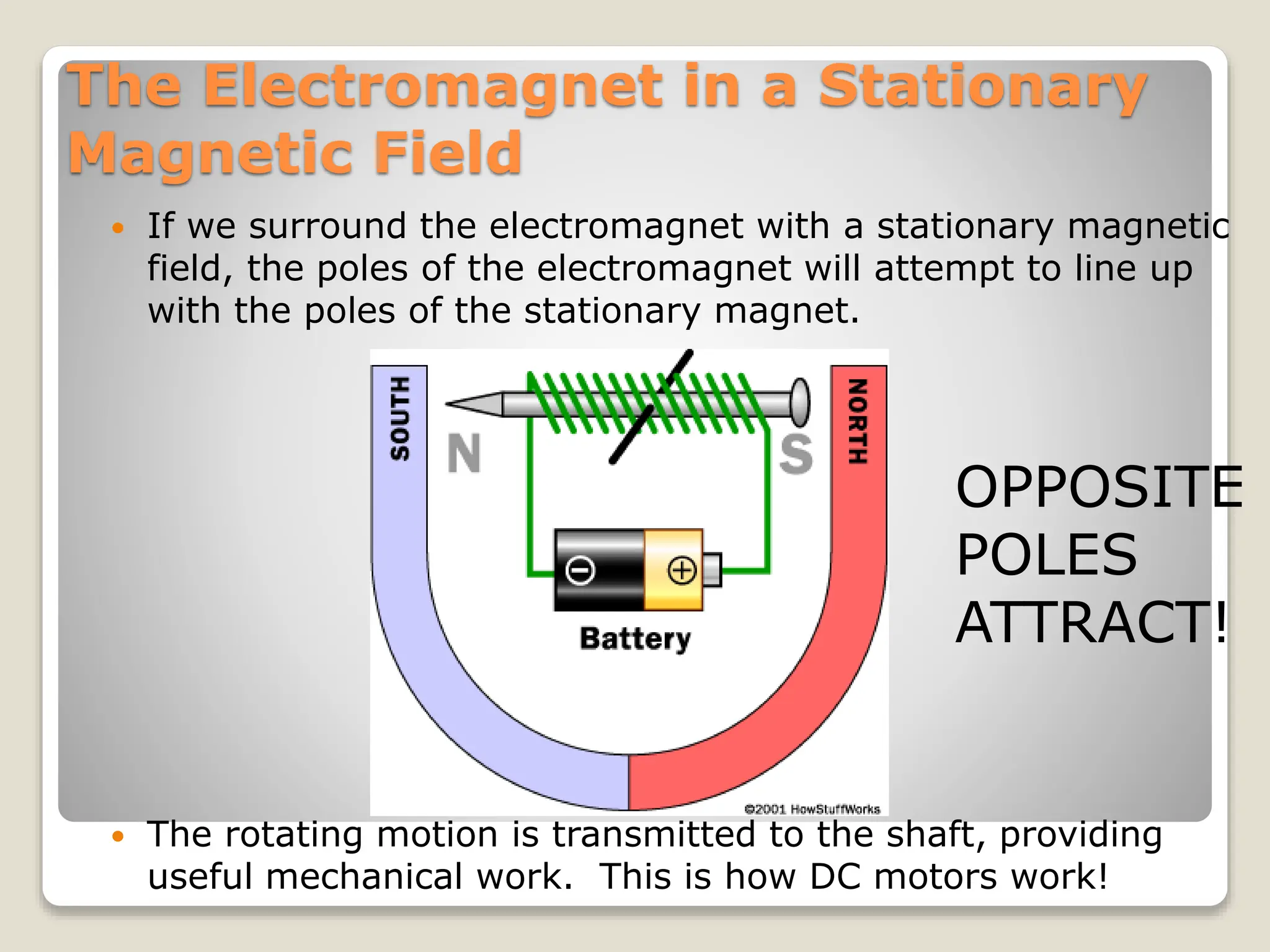
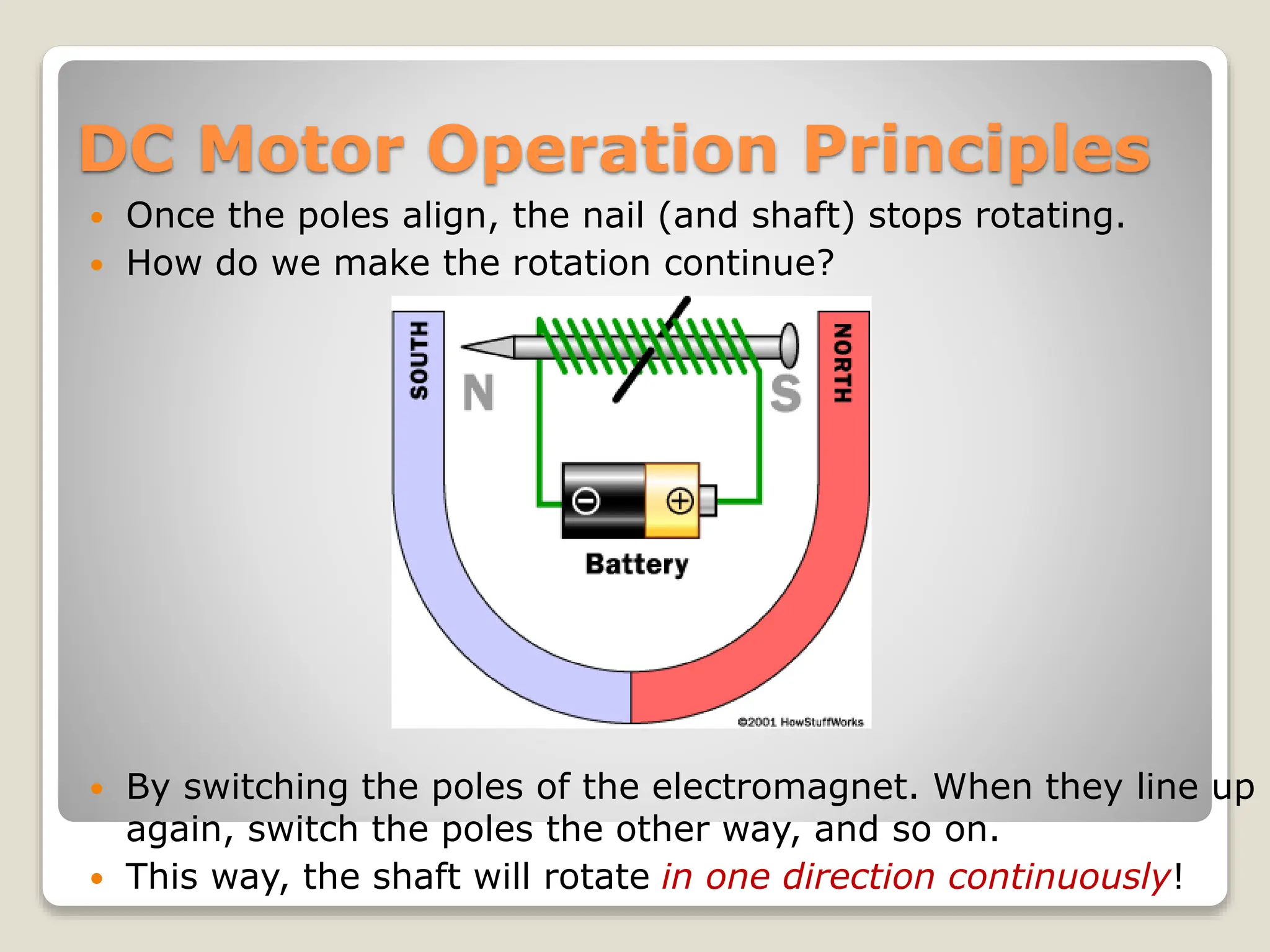
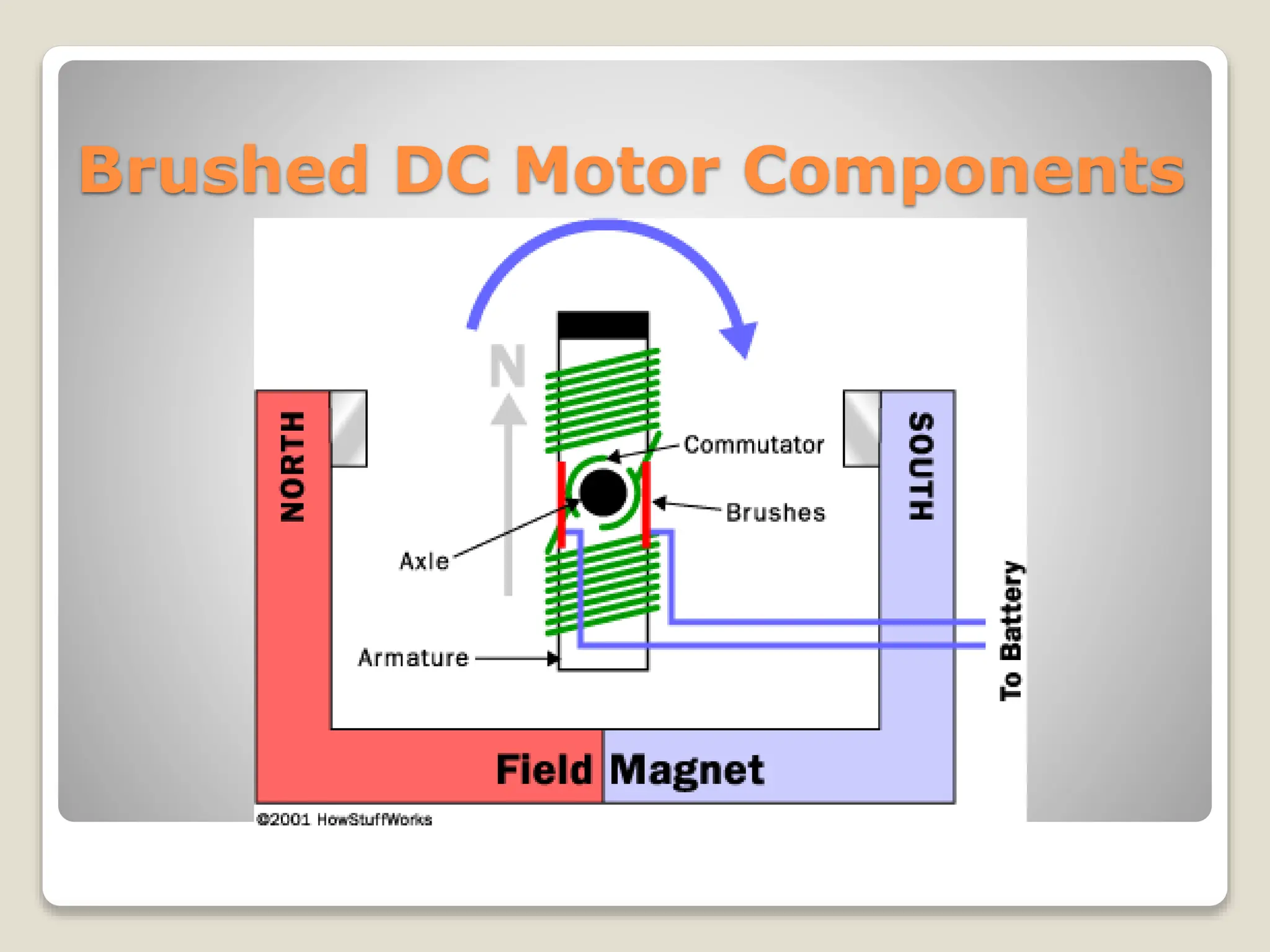
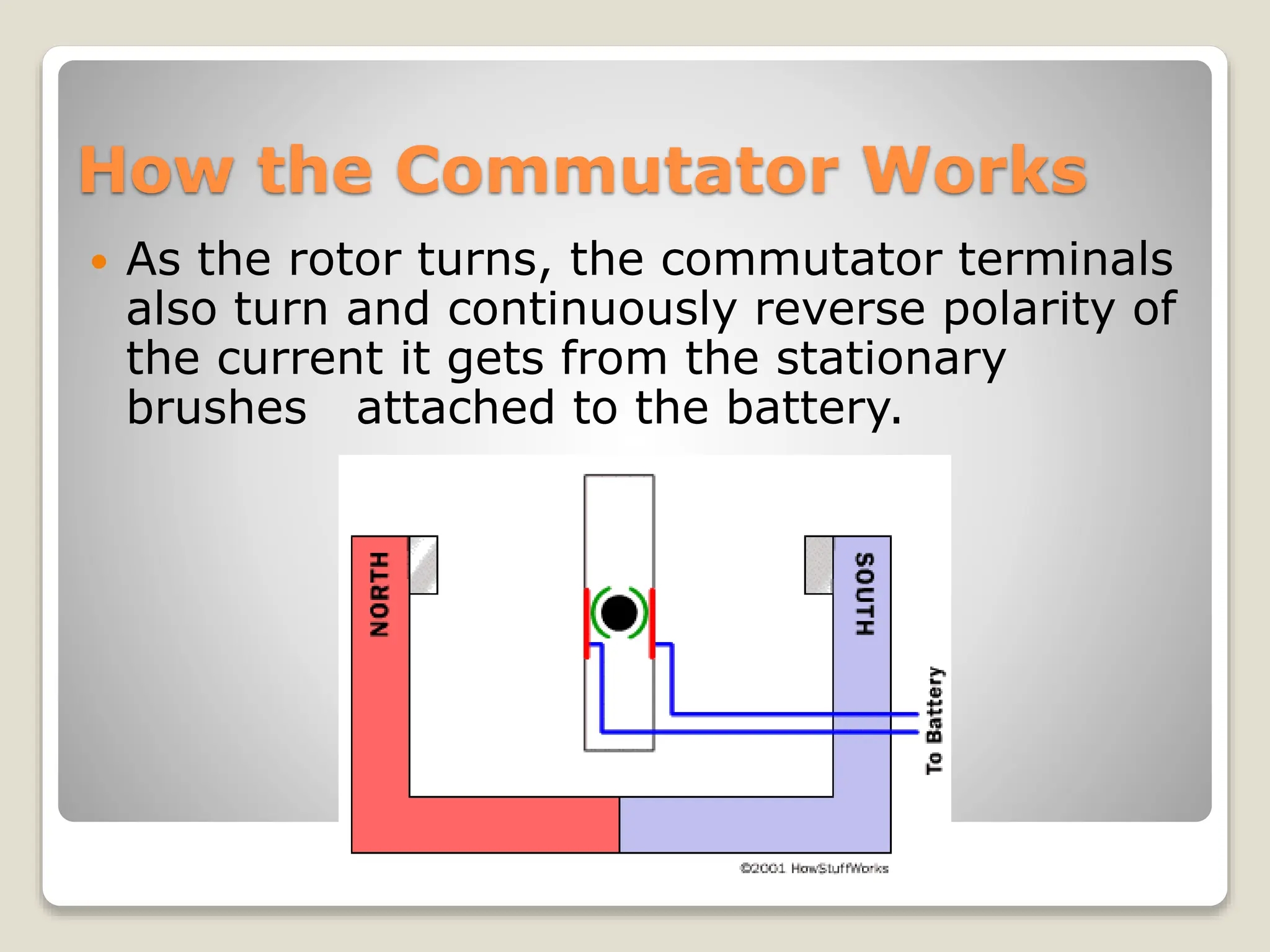
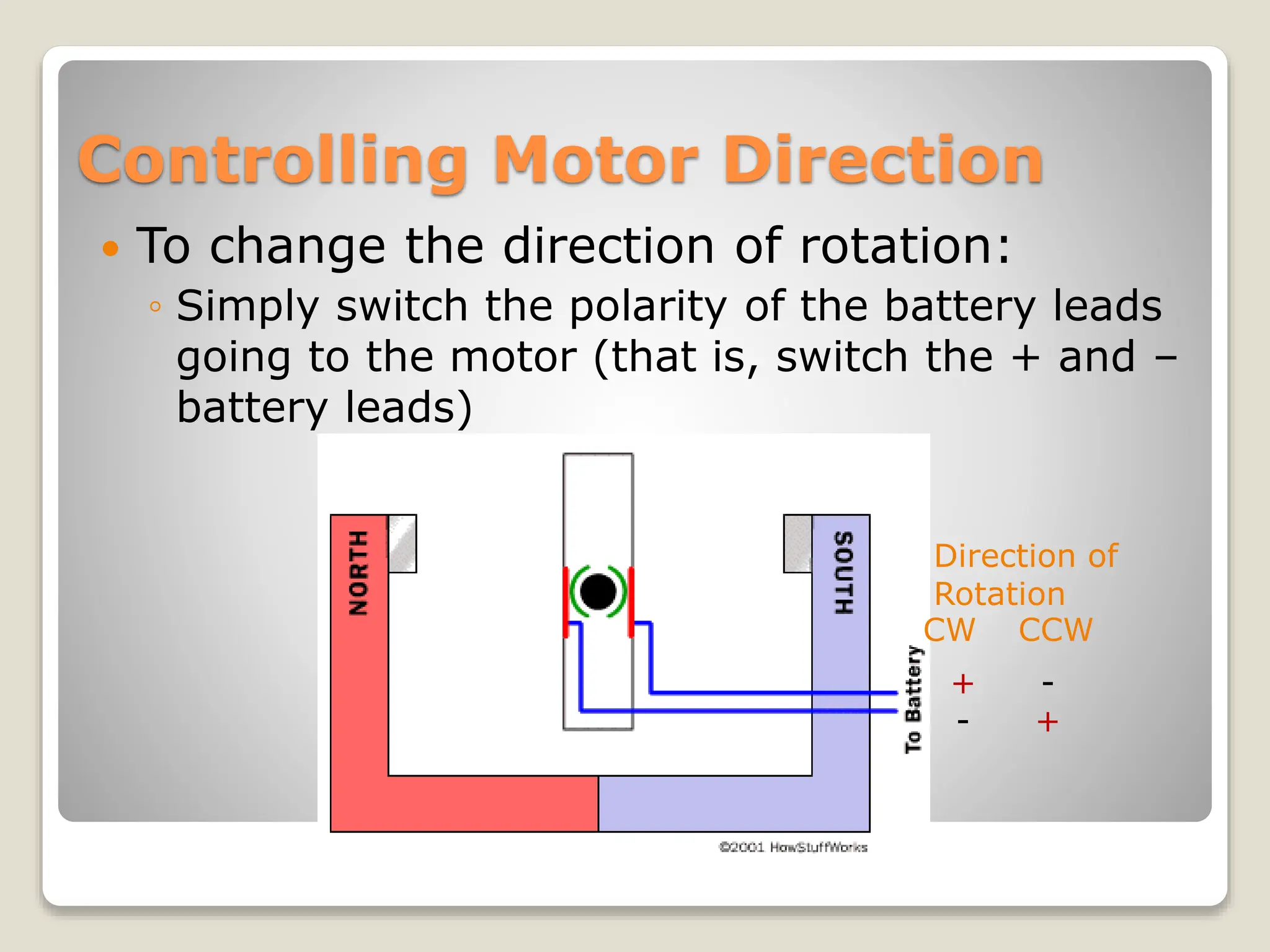
This document provides an overview of different types of motors used in robotics, including their characteristics and principles of operation. It discusses AC motors, DC motors, DC servo motors, and stepper motors. It specifically describes how the CEENBot uses stepper motors that provide accurate wheel positioning and speed control without position feedback. The stepper motors have a 1.8 degree resolution and precisely control wheel rotation through electromagnetic phases controlled by a microprocessor.