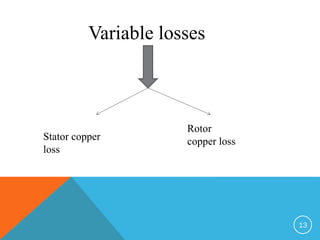
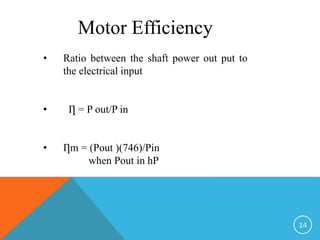
This document discusses electric motors and provides information on various types of electric motors including AC and DC motors. It describes how electric motors work by converting electric energy to mechanical energy using magnetic fields and winding currents. It also discusses the different losses that occur in induction motors including electrical losses from heat in the stator and rotor windings, magnetic losses in the iron, and mechanical losses from friction. The document notes that efficient motors can achieve the same output while consuming less power through improvements like more copper in the windings, reduced fan loss, higher quality steel, and an optimal air gap.