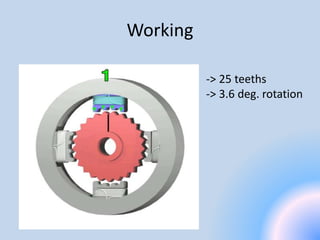
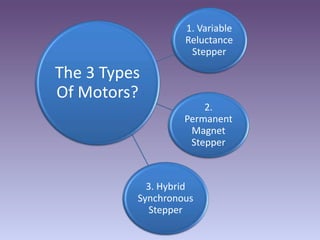
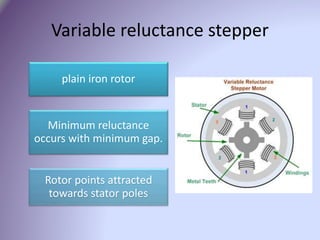
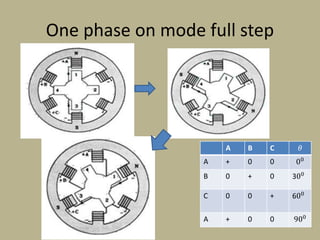
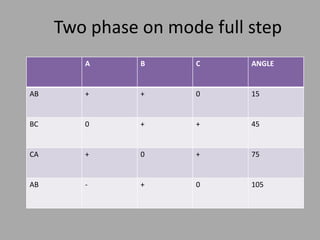
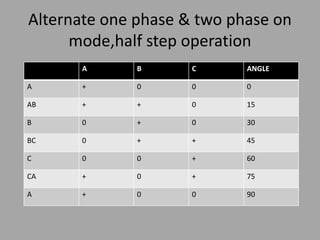
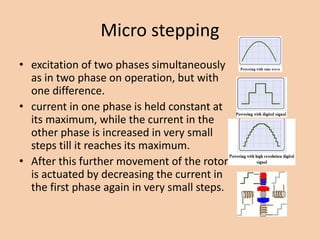
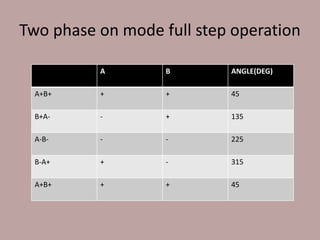
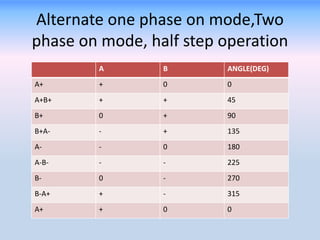
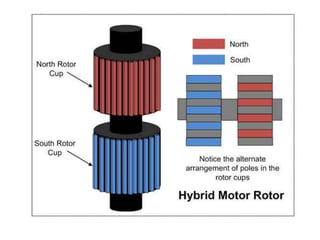
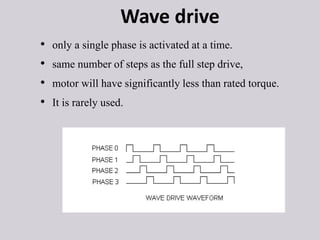
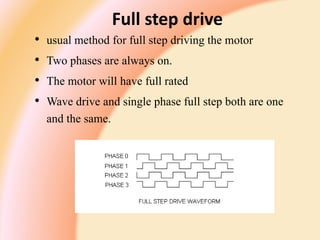
A stepper motor is an electric motor that rotates in discrete steps. It uses electromagnetic coils to move a rotor in synchronized steps. There are three main types of stepper motors: variable reluctance, permanent magnet, and hybrid synchronous. Stepper motors are commonly used in industrial applications like printers, robotics, and CNC machines due to their precise positioning ability without the need for feedback sensors.