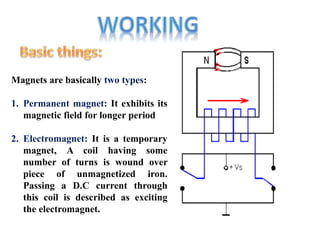
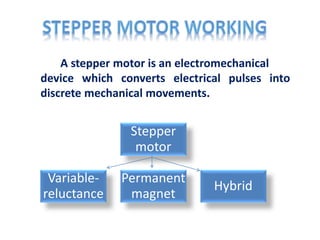
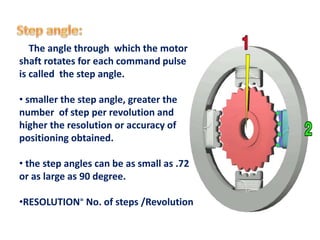
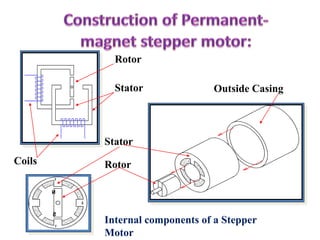
This document provides an overview of different types of motors including stepper motors, servo motors, DC motors, and AC motors. It discusses the basic components and operating principles of stepper motors and servo motors. Some key points covered include:
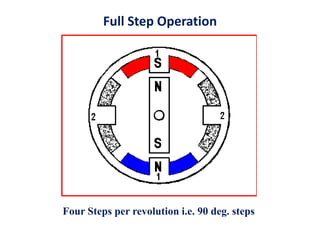
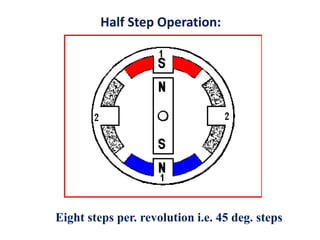
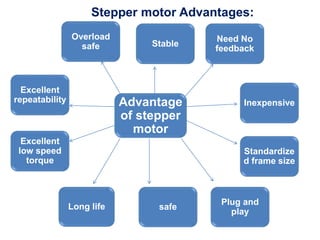
- Stepper motors can be precisely controlled by computer and are well-suited for applications requiring precise positioning or speed control.
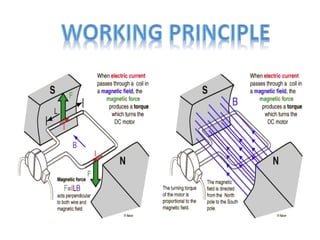
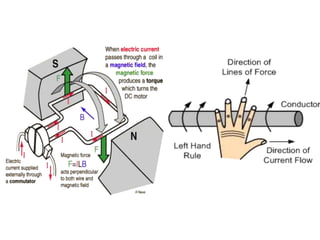
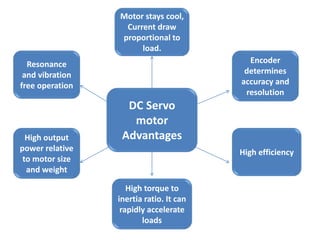
- Servo motors produce high torque at all speeds including zero speed and can hold a static position precisely.
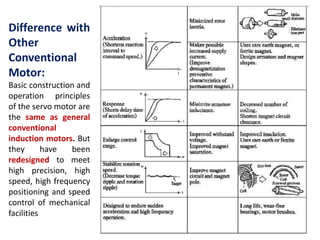
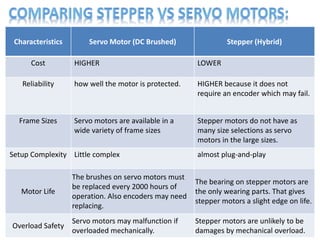
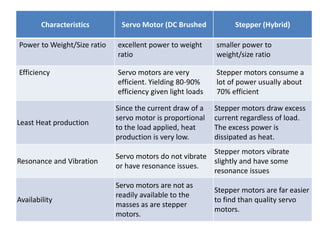
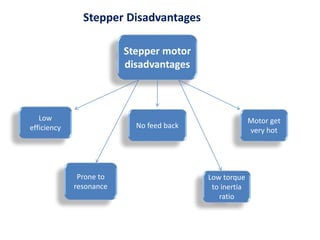
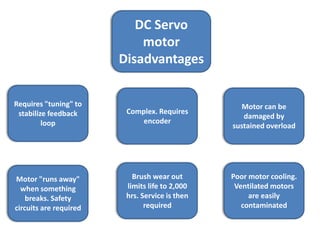
- The document compares characteristics of DC servo motors and hybrid stepper motors such as cost, reliability, setup complexity, efficiency, and vibration.
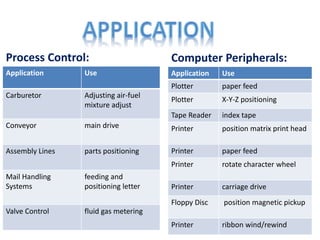
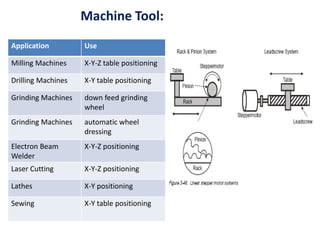
- Finally, examples of applications for stepper motors and servo motors in industrial machinery, computer peripherals