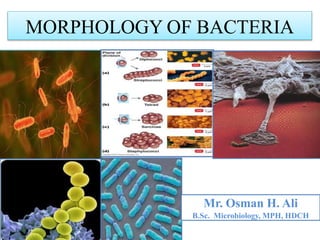
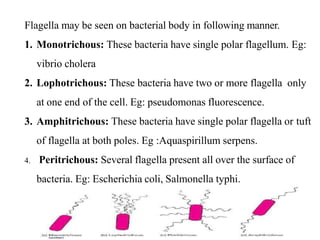
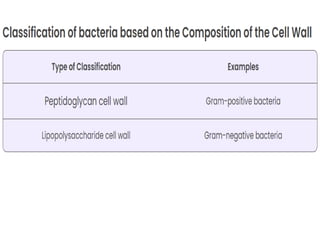
Bacteria come in a variety of shapes and sizes. They can be spherical (cocci), rod-shaped (bacilli), spiral (spirilla), or slender and flexible (spirochetes). Some bacteria arrange in pairs (diplococci), chains (streptococci), or clusters (staphylococci). Bacterial cells have a cell wall, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and often flagella, pili, or a capsule. The cell wall provides shape and some protection, while the plasma membrane controls what enters and exits the cell. Bacteria can form tough endospores to survive unfavorable conditions. Understanding bacterial morphology is important for classification and identification.