Embed presentation


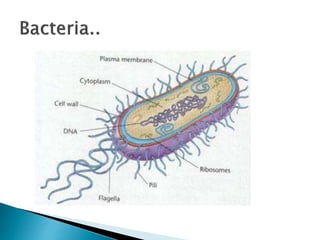



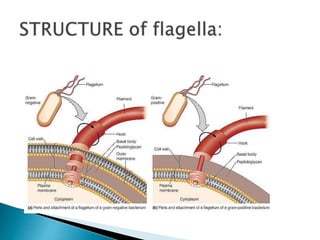



Flagella are whip-like structures that allow cells to move. They are found in bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. While all three types are used for locomotion, their structures differ. Flagella consist of three main parts - the filament, hook, and basal body. The filament forms the outer region and is composed of flagellin proteins arranged in helical chains. The filament attaches to the hook, while the basal body anchors the flagellum and consists of rings and rods that insert into the cell. Bacteria can have flagella in different arrangements including single, tufts, both ends, or all over the cell surface.











