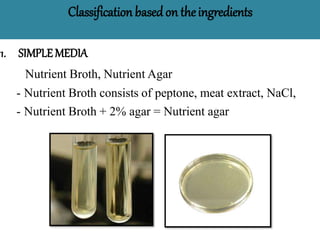
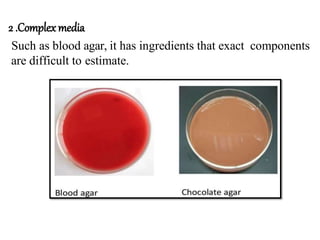
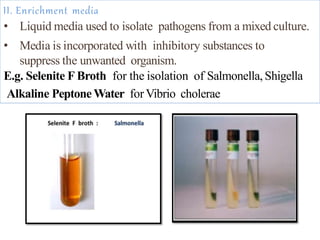
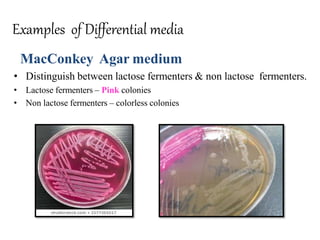
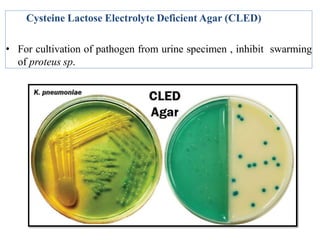
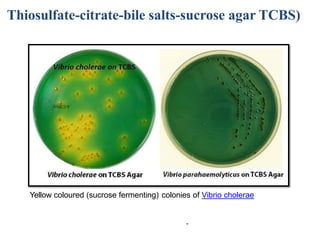
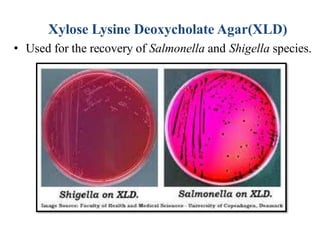
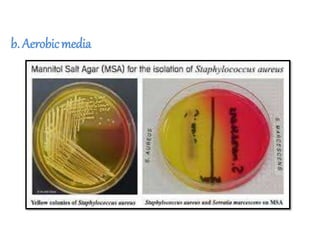
The document discusses culture media, which are substances required for growing microorganisms outside the body, with applications for identifying infections, studying microorganisms, and preparing biological products. It categorizes culture media based on physical state (solid, liquid, semi-solid), ingredients (simple, complex, synthetic), and special purposes (enriched, selective, differential, transport). It also emphasizes the importance of proper preparation and sterilization of media for successful microbial growth.