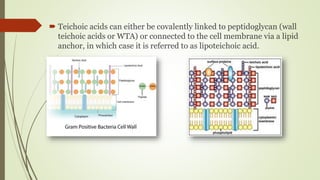
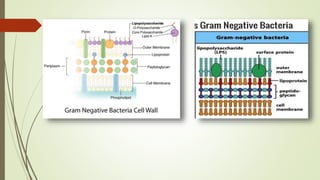
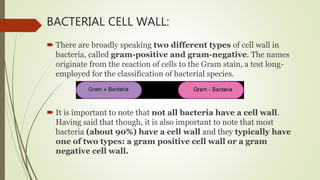
Bacteria typically have one of two types of cell walls: gram-positive or gram-negative. Gram-positive cell walls are thick and composed primarily of peptidoglycan and teichoic acid. Gram-negative cell walls are more complex, containing a thin peptidoglycan layer and an outer membrane with lipopolysaccharides. Both wall types contain the polysaccharide peptidoglycan, which provides structure and protection to the cell. The cell wall allows nutrient transport while protecting the cell from environmental threats.




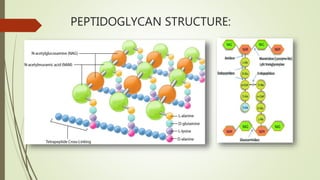
![ Typically only the L-isomeric form of amino acids are utilized by cells
but the use of the mirror image D-amino acids provides protection
from proteases that might compromise the integrity of the cell wall
by attacking the peptidoglycan.
The tetrapeptides can be directly cross-linked to one
another, with the D-alanine on one tetrapeptide binding to the L-
lysine/ DPA on another tetrapeptide.
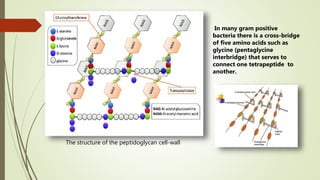
In many gram positive bacteria there is a cross-bridge of five amino
acids such as glycine (peptide interbridge) that serves to connect one
tetrapeptide to another.[slide number 10 figure]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cellwall-200822063058/85/Cell-wall-Bacteria-7-320.jpg)