Embed presentation
Downloaded 15 times
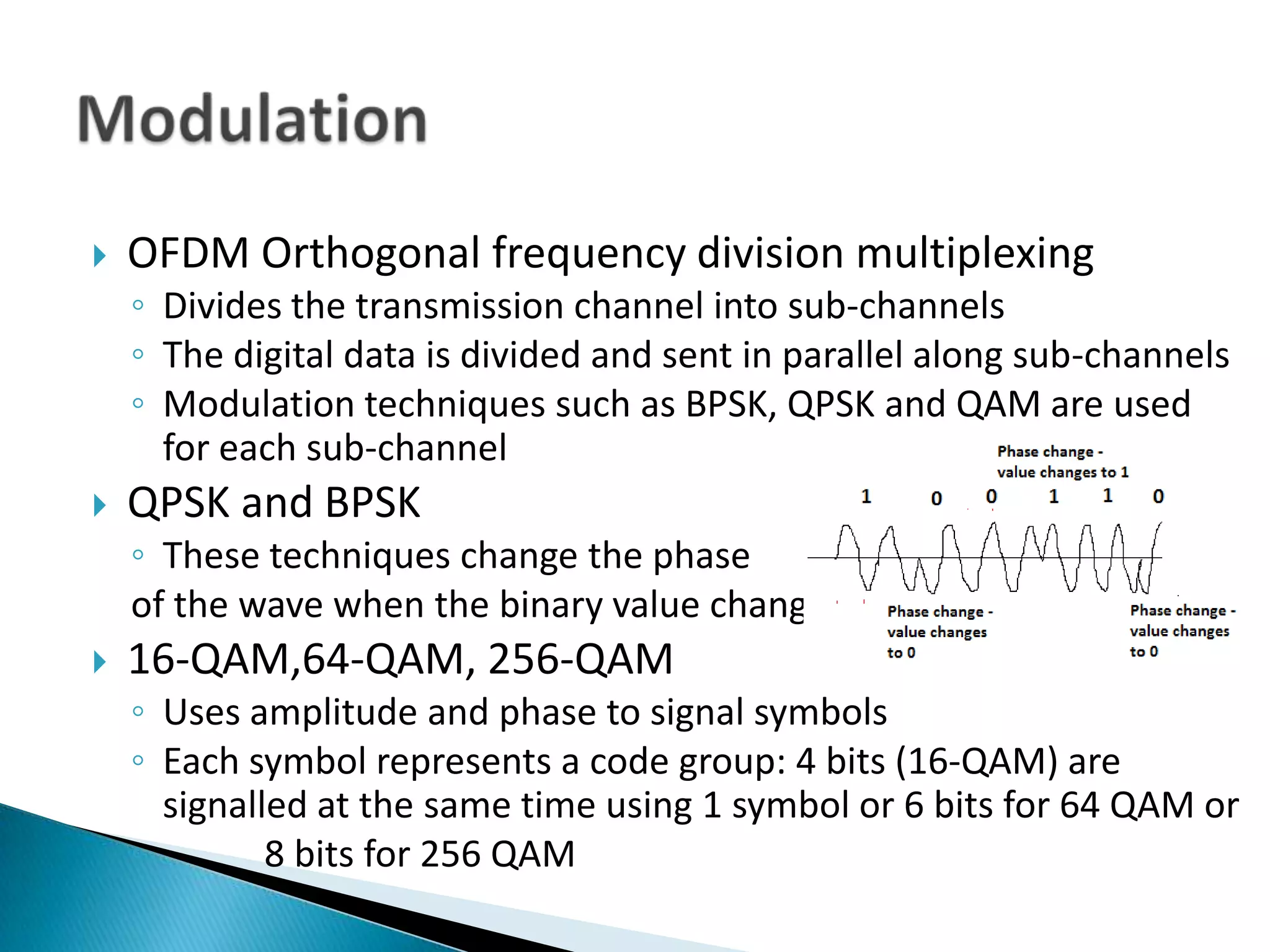
Modulation involves encoding binary data onto a sine wave by changing the wave's amplitude, frequency, or phase. Common modulation techniques include amplitude shift keying, frequency shift keying, and phase shift keying. More advanced techniques like orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing divide the channel into sub-channels and use modulation such as BPSK, QPSK, and QAM to send data in parallel across sub-channels. Higher order QAM encodings use amplitude and phase to represent more bits per symbol.

