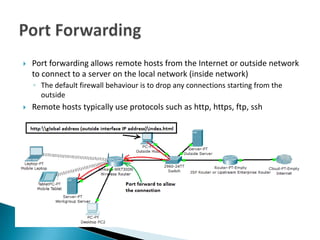
Port forward
- 1. Port forwarding allows remote hosts from the Internet or outside network to connect to a server on the local network (inside network) ◦ The default firewall behaviour is to drop any connections starting from the outside Remote hosts typically use protocols such as http, https, ftp, ssh
- 2. A remote host sends a request to the public global IP address of the inside server and the port number of the service required (usually the registered port no of the destination service e.g. port 80 for http) ◦ If the router is using PAT this is the outside interface address The wireless router uses PAT ◦ If the router is using static NAT this is mapped one-to-one address The request is routed to the outside interface of the router The router checks for a port forwarding rule that matches the protocol and the destination port of the request ◦ If a match to a rule exists the request is forwarded to the local IP address and the port number configured in the port forward rule Only one inside server can use the global IP/port number mapping E.g If there are 2 inside http servers one can use port 80 and one can use port 90 ◦ If a match to a rule does not exist the request is dropped
- 3. The remote host on the outside network must use the public global IP address to create the connection The port number used in the port forward rule is reserved for only 1 inside IP address ◦ A port number can’t be used to forward requests to a second server. To do this, select a different unused port no and create a second port forwarding rule Some applications; multimedia and torrents required several ports open for connections. ◦ Typically 1 or 2 ports are required for the control channels that setup and close the connection and monitor the connection. ◦ Extra ports may be required for the data stream, another for video, another for voice and another for chat ◦ Research the port nos required ◦ Use a port range in the forwarding rule
- 4. A port trigger is used to open a port temporarily for a particular inside host only ◦ The port trigger allows new connections from the outside network to an inside host that initiated the data flow ◦ E.g. Port 25 is defined as a trigger and 113 as the port ◦ A local host checks mail and triggers port 25. The port trigger allows a back connection on port 113 (Identity information for mail) to the originating host ◦ The trigger times out and new connections to 113 are dropped The wireless router monitors outgoing traffic for the port numbers specified in the trigger ◦ When a match is made the IP address of the sending host (local address) is saved. ◦ When the return traffic arrives back at the router it is forwarded to the original sending host. Port triggers might be used in online gaming