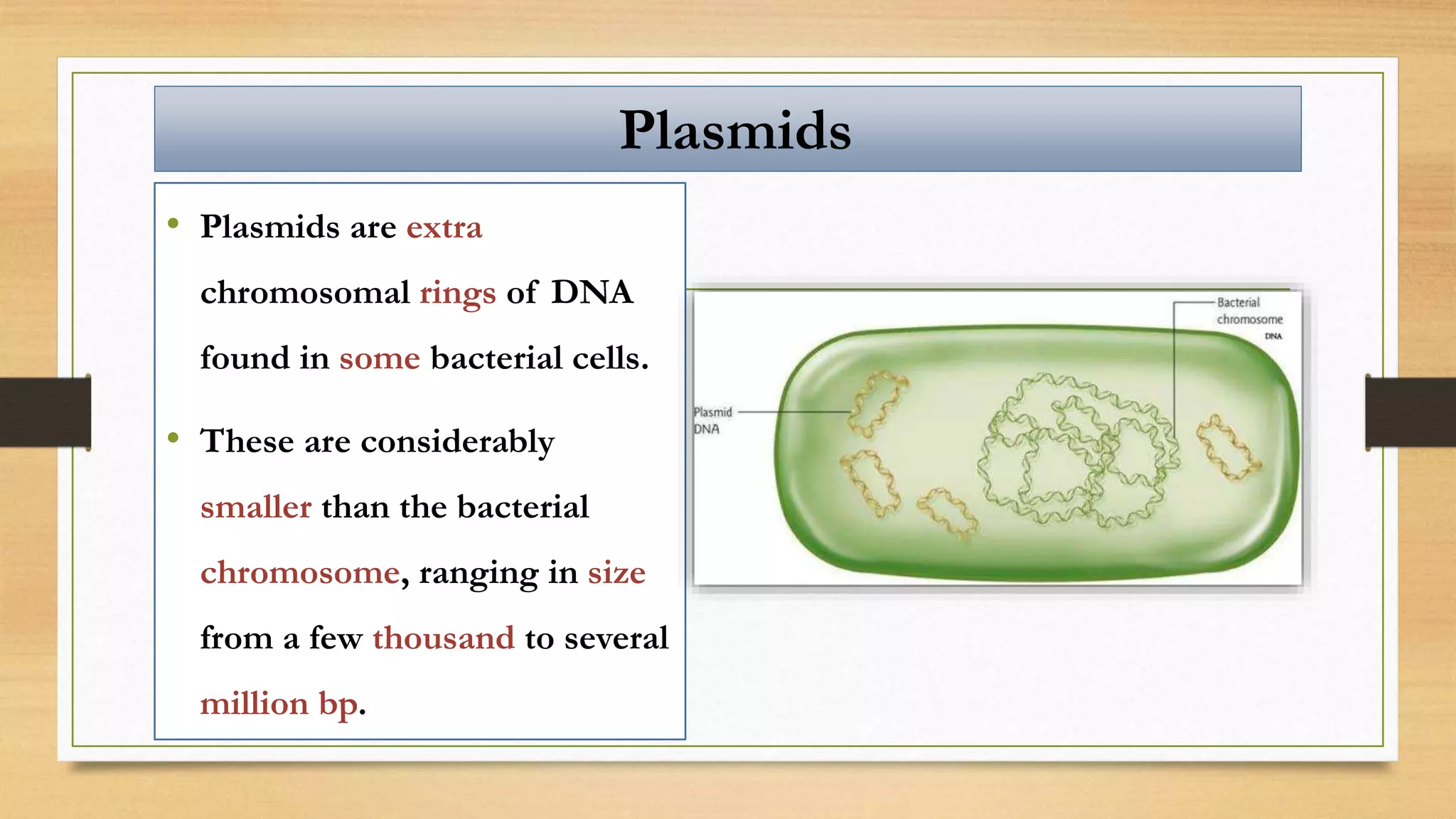
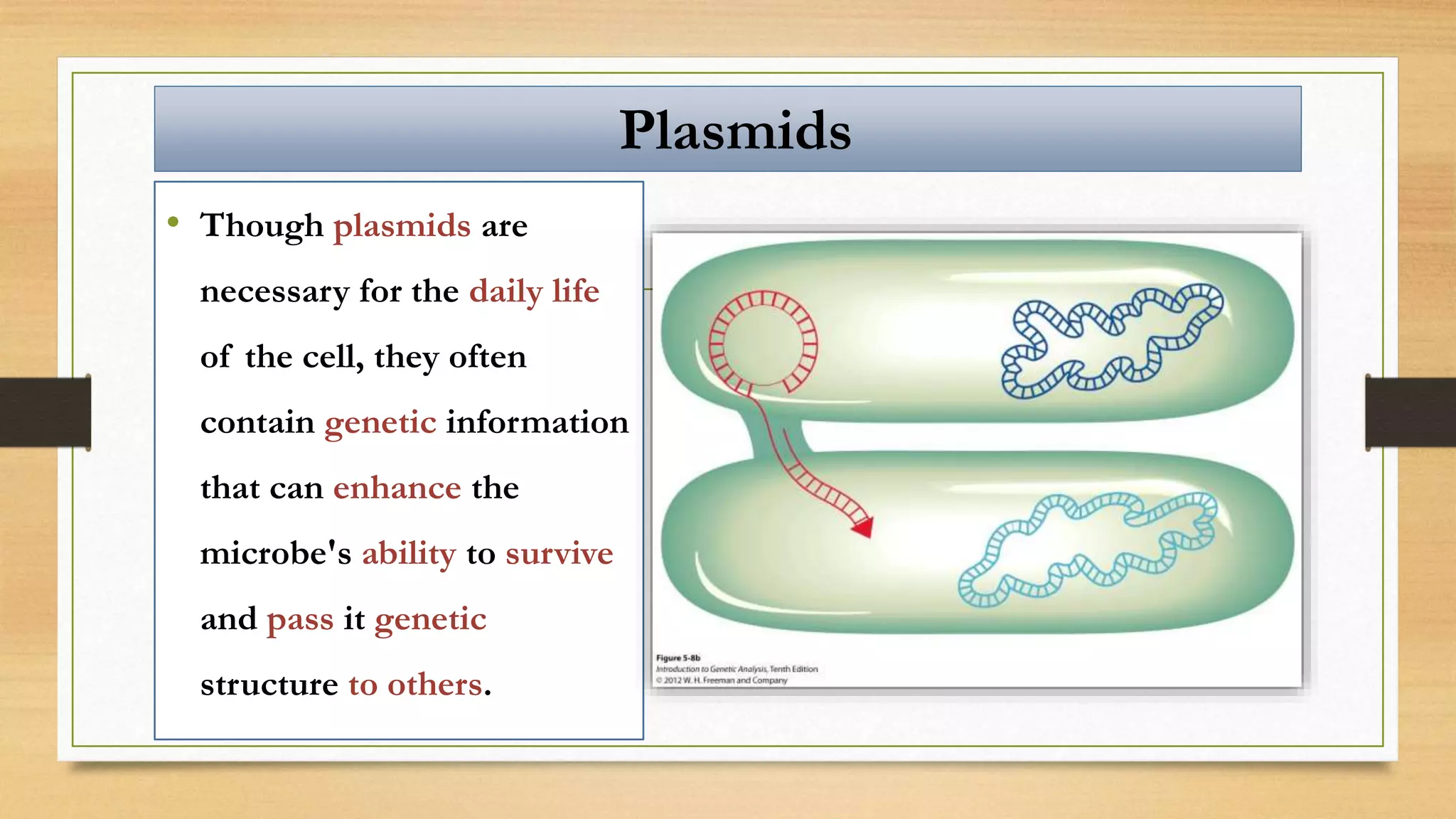
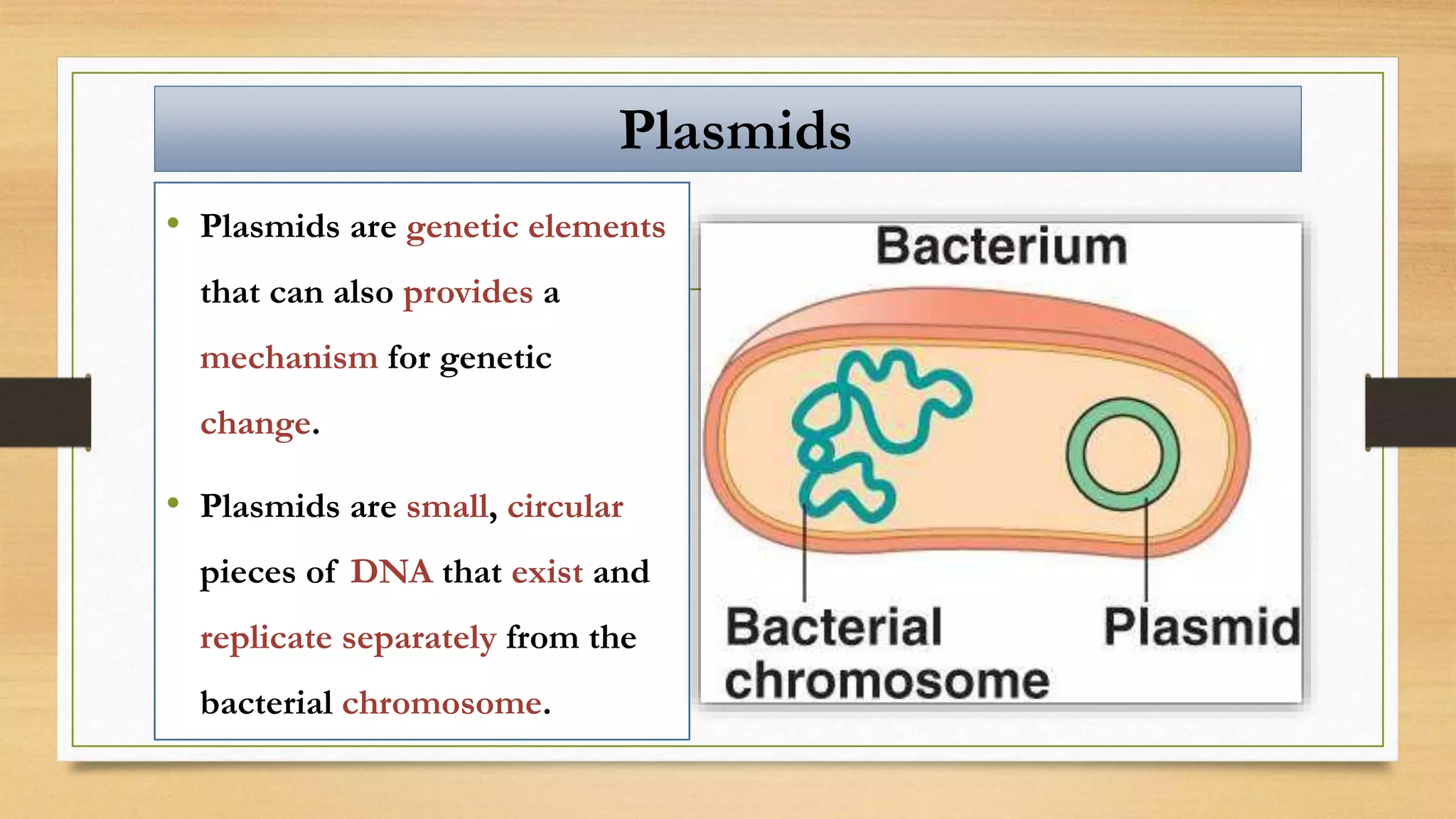
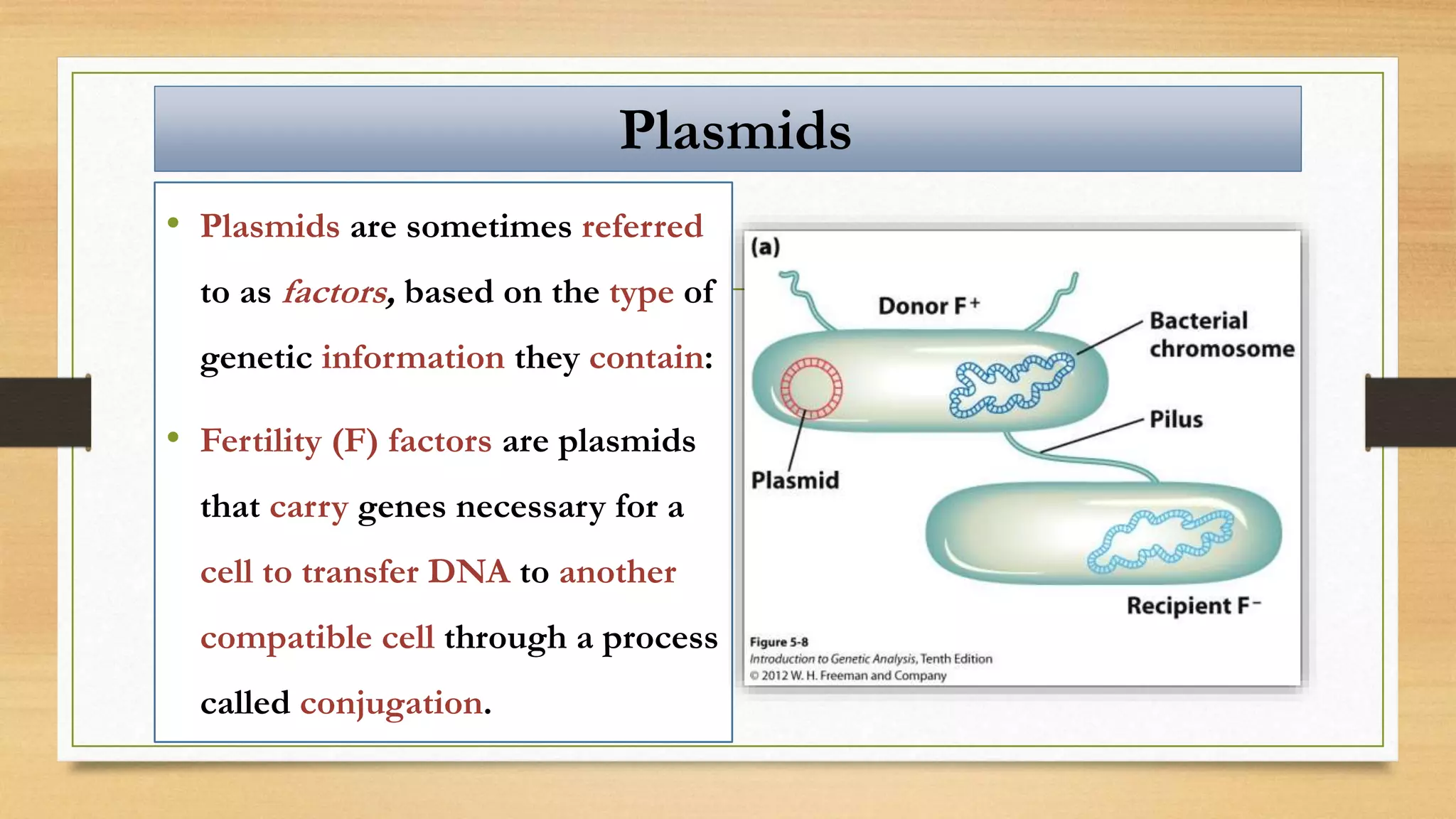
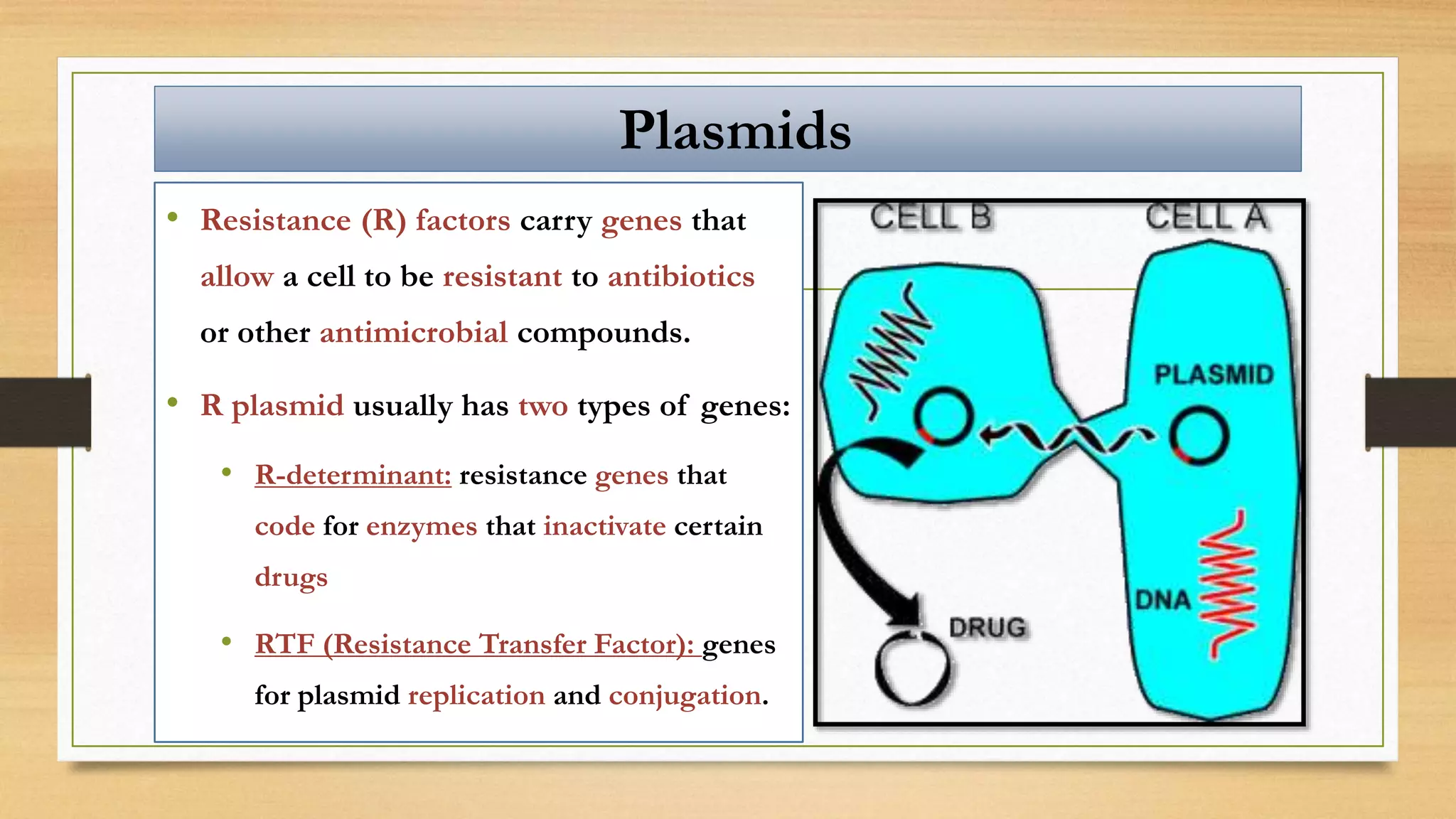
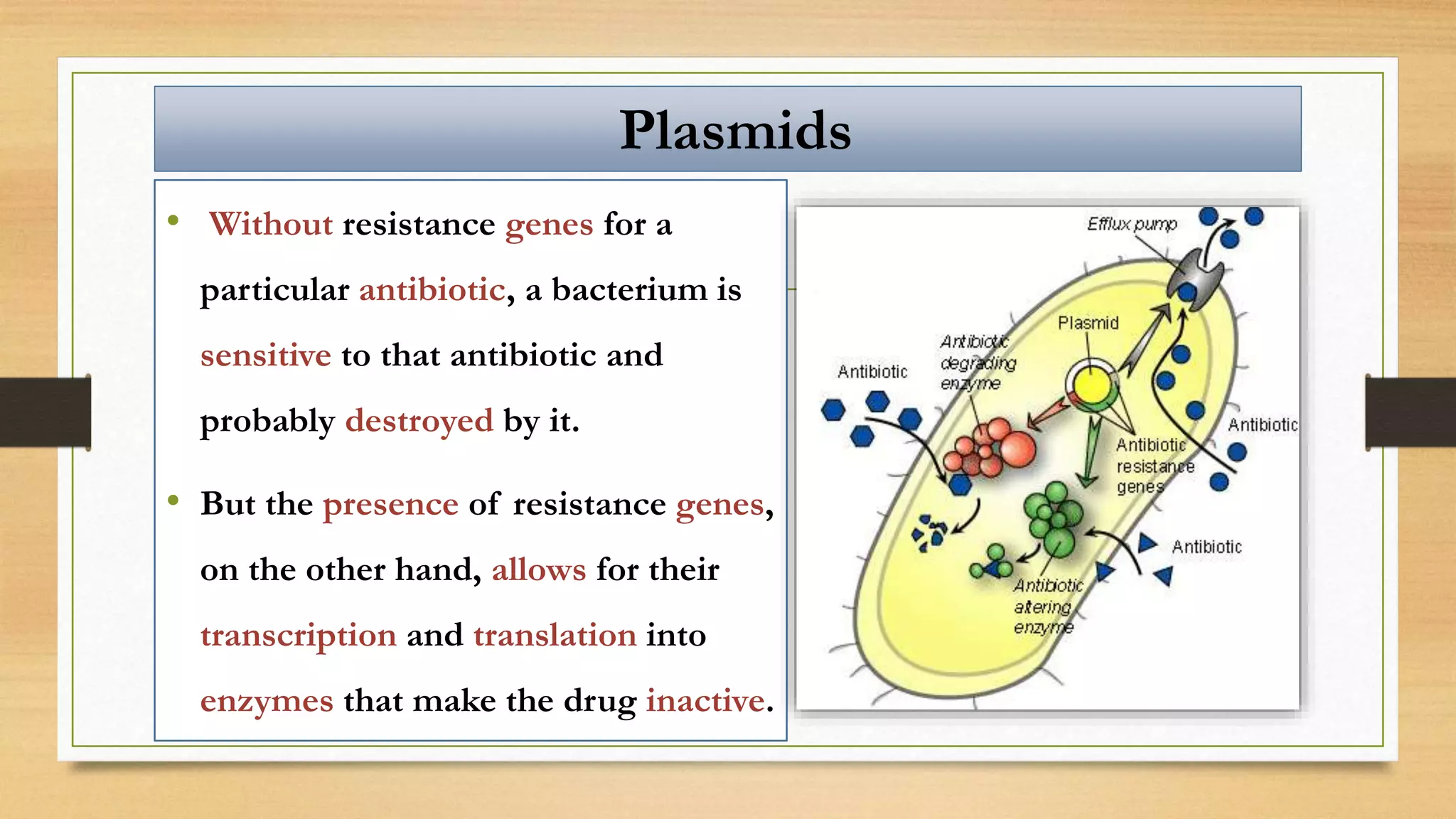
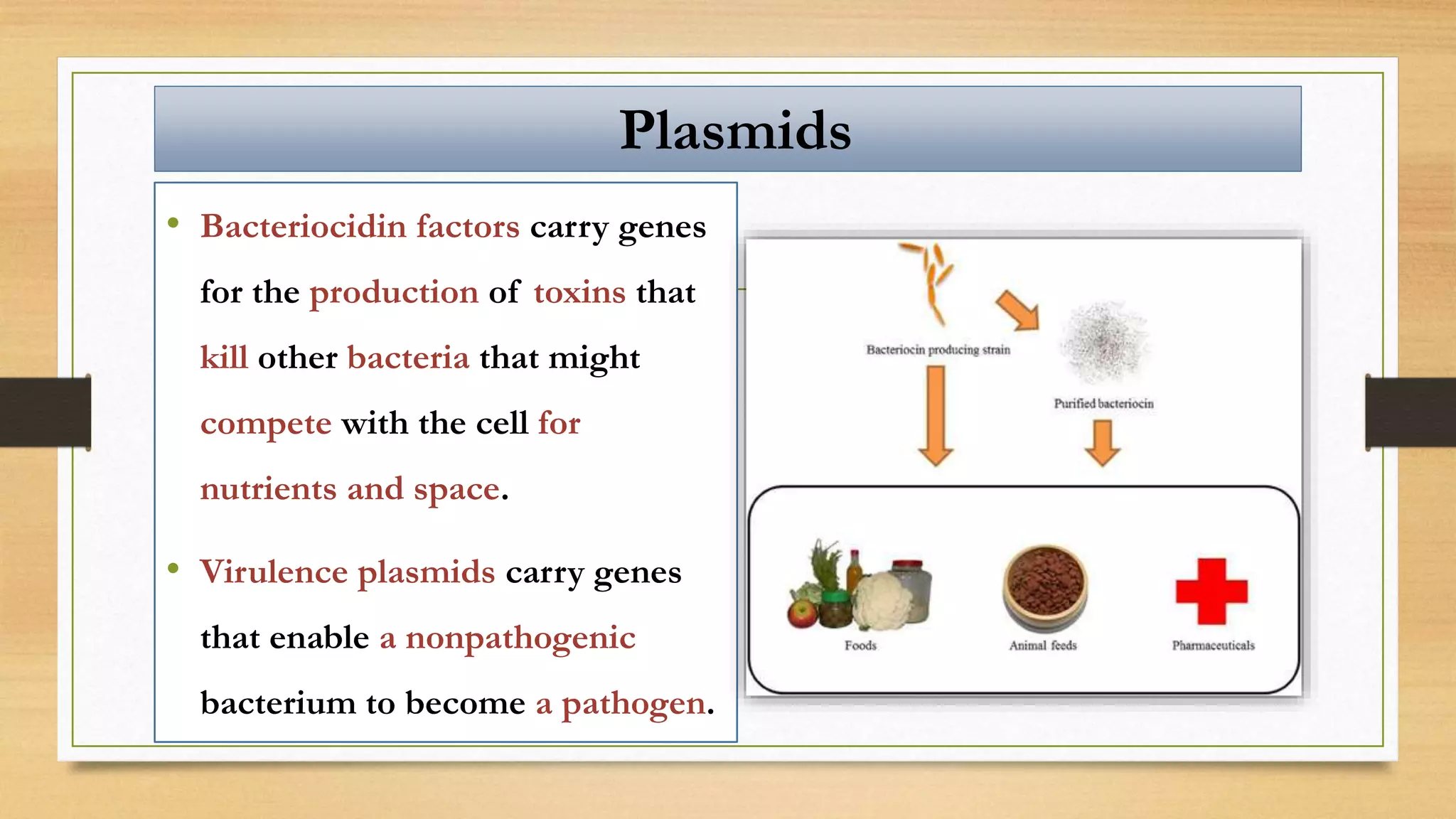
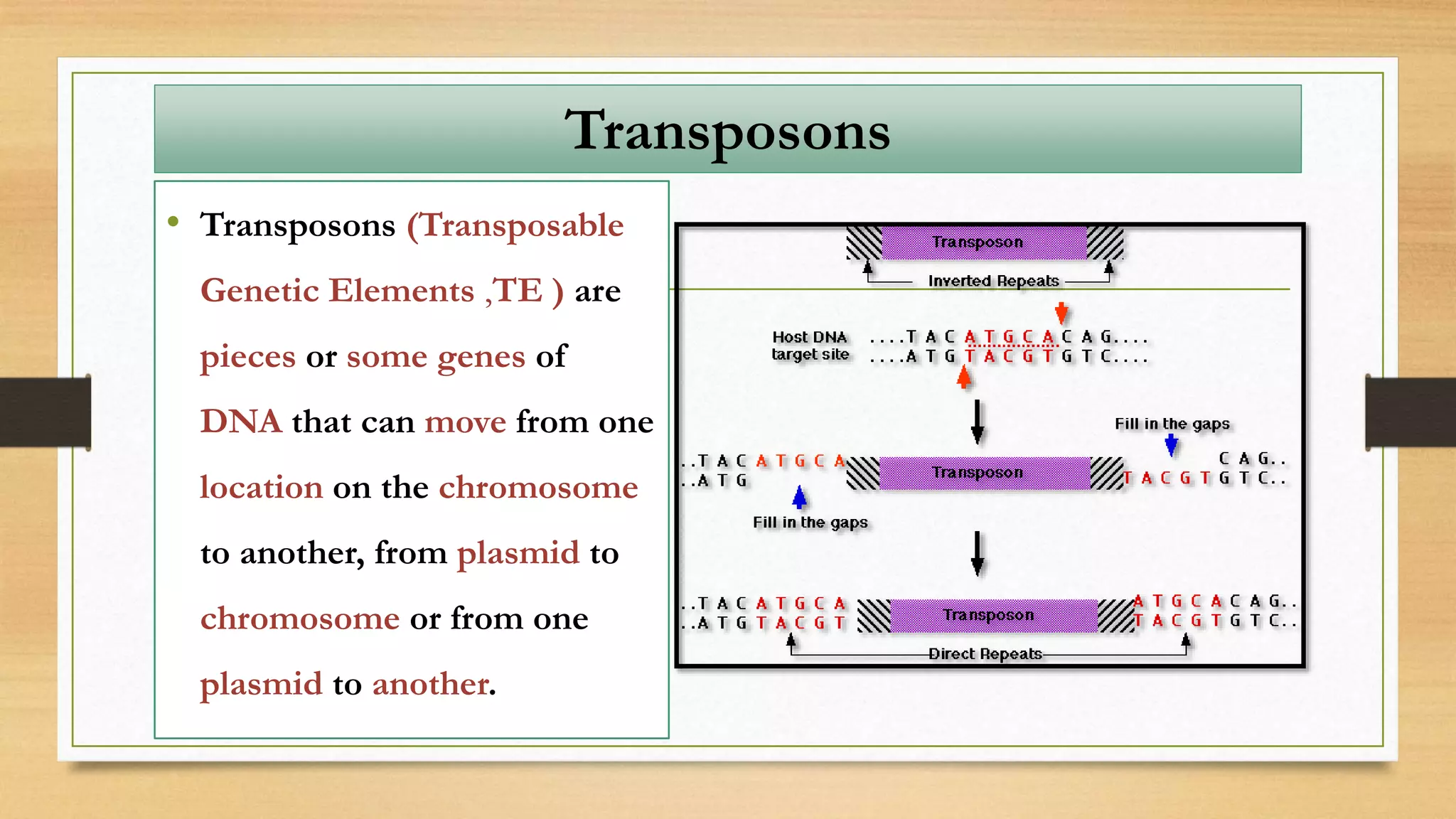
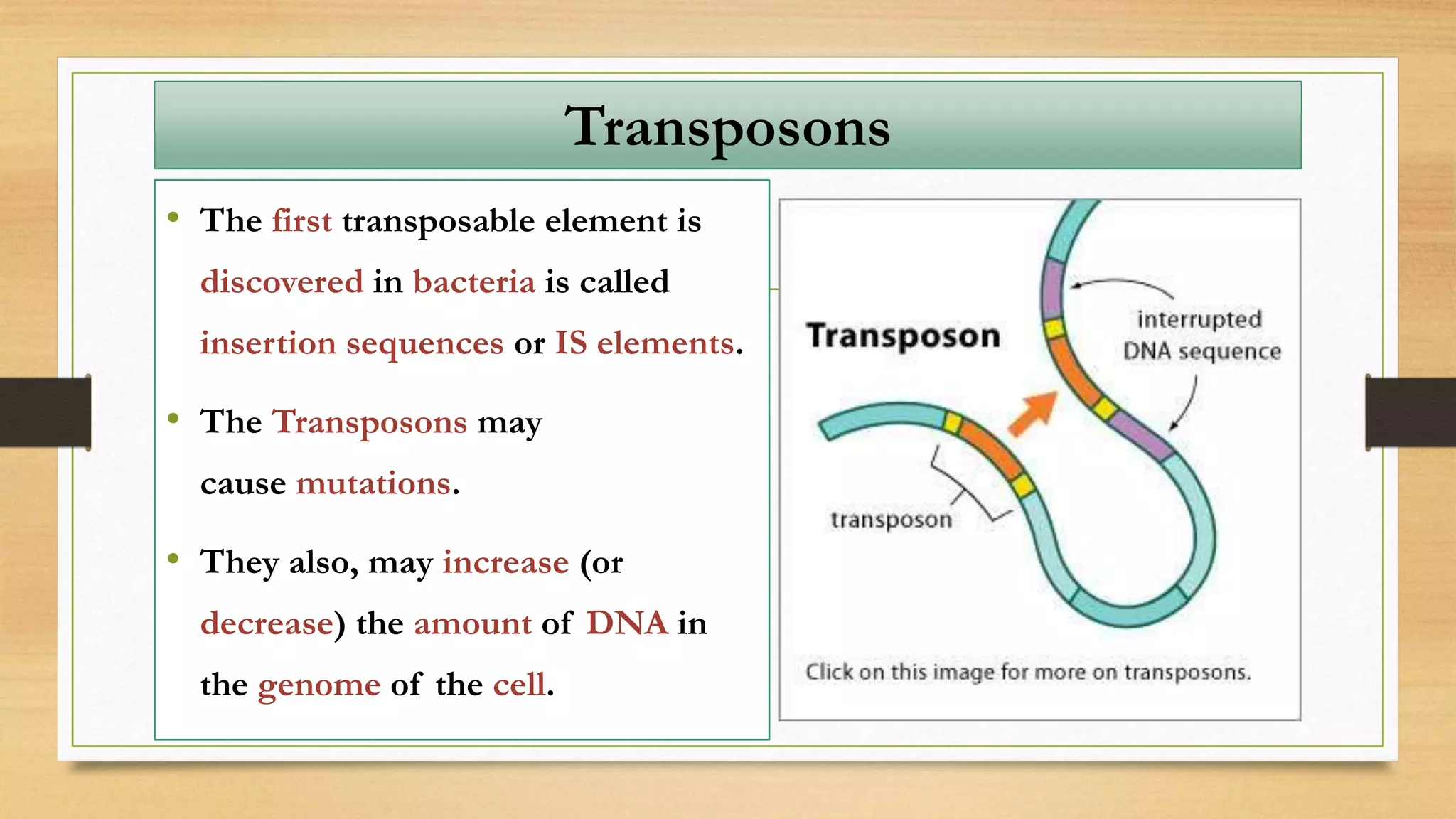
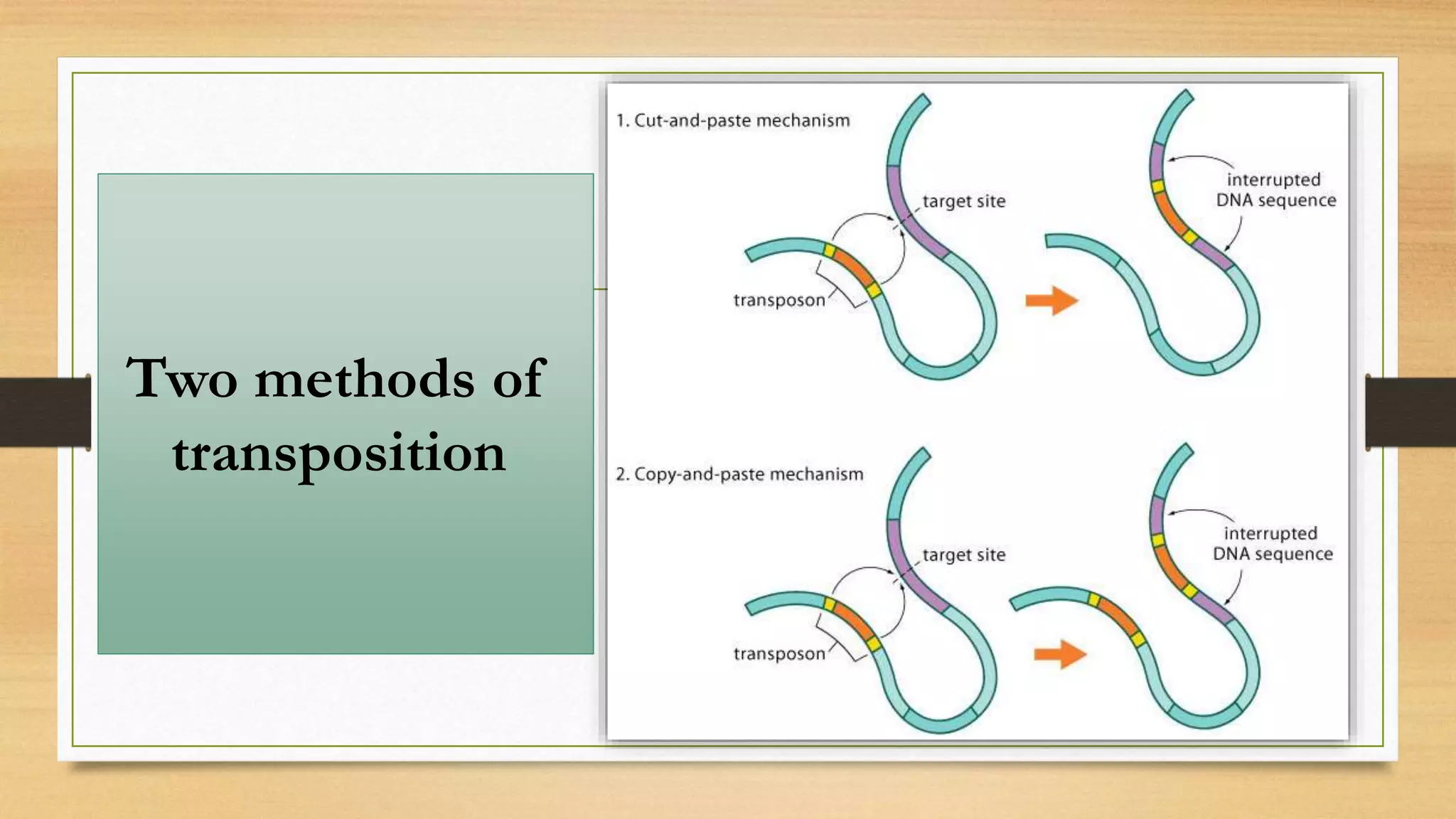
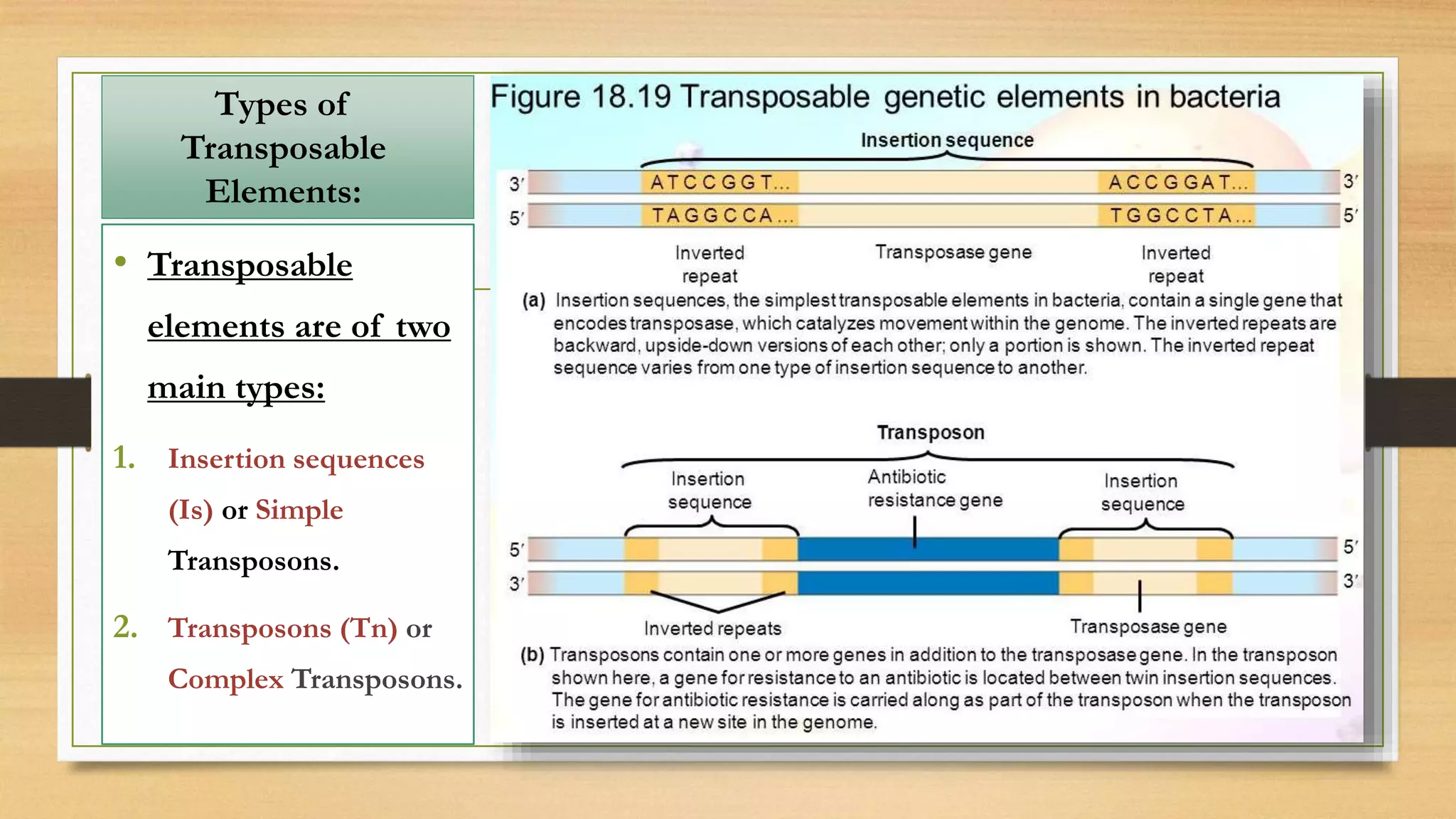
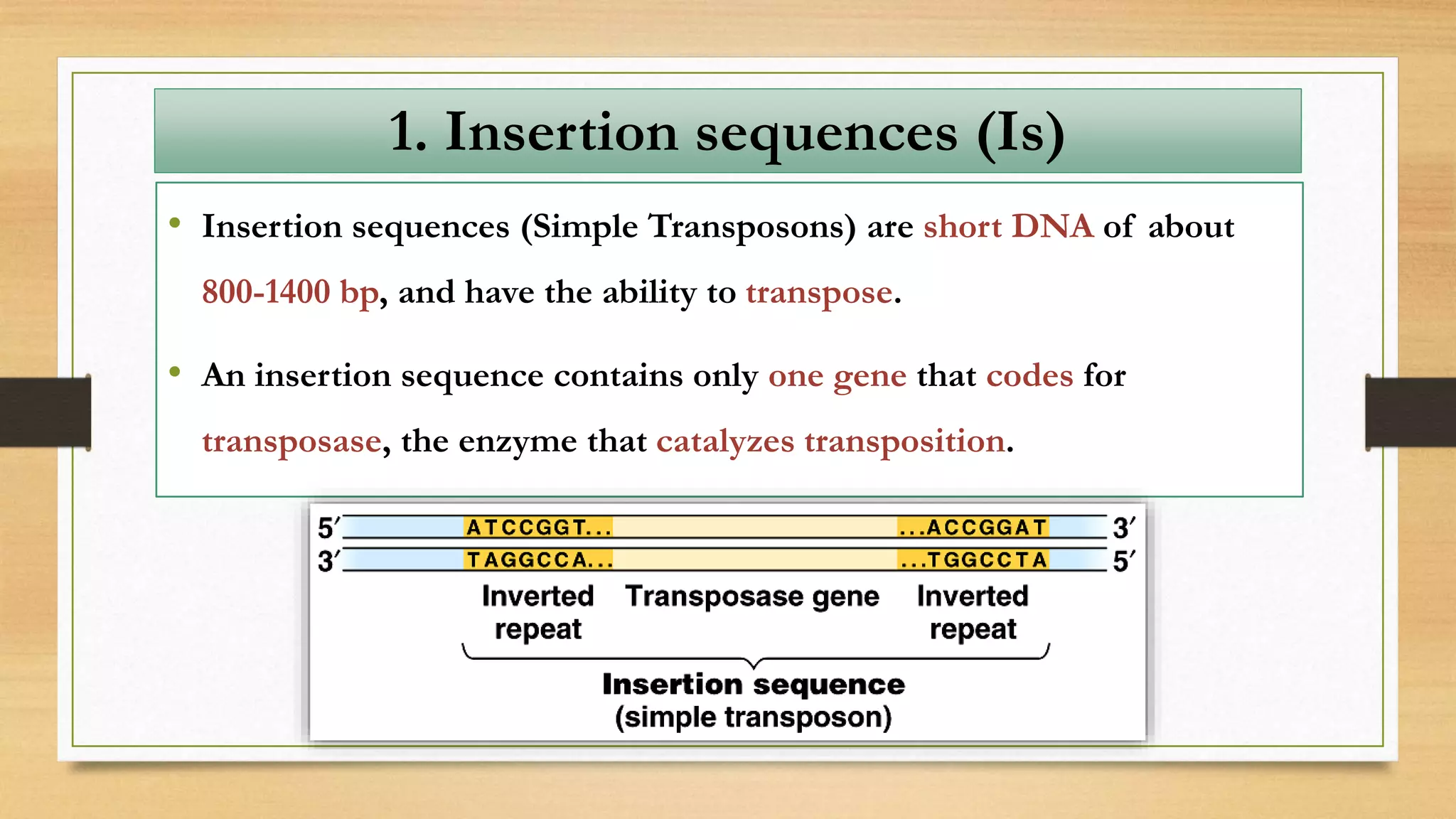
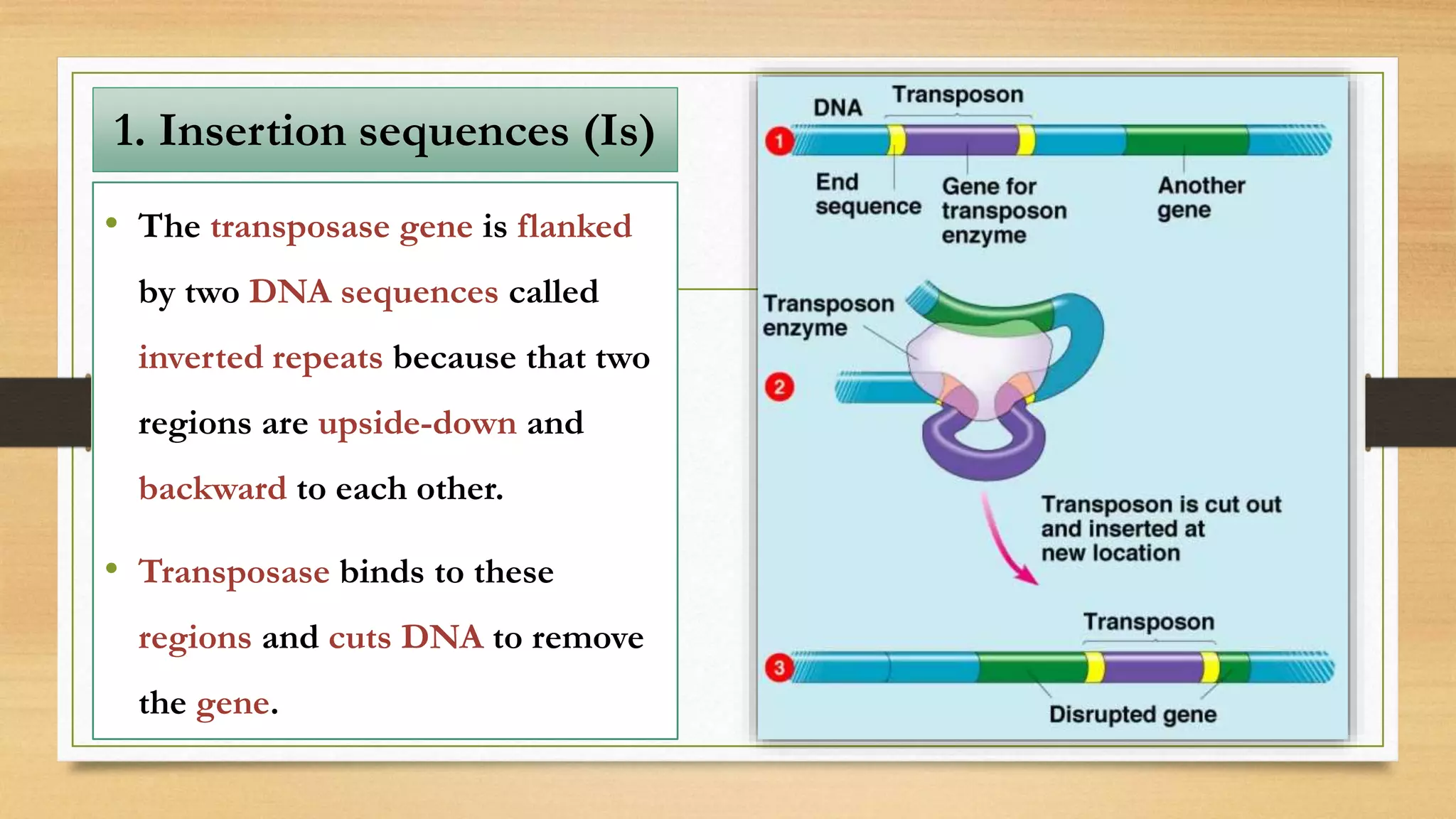
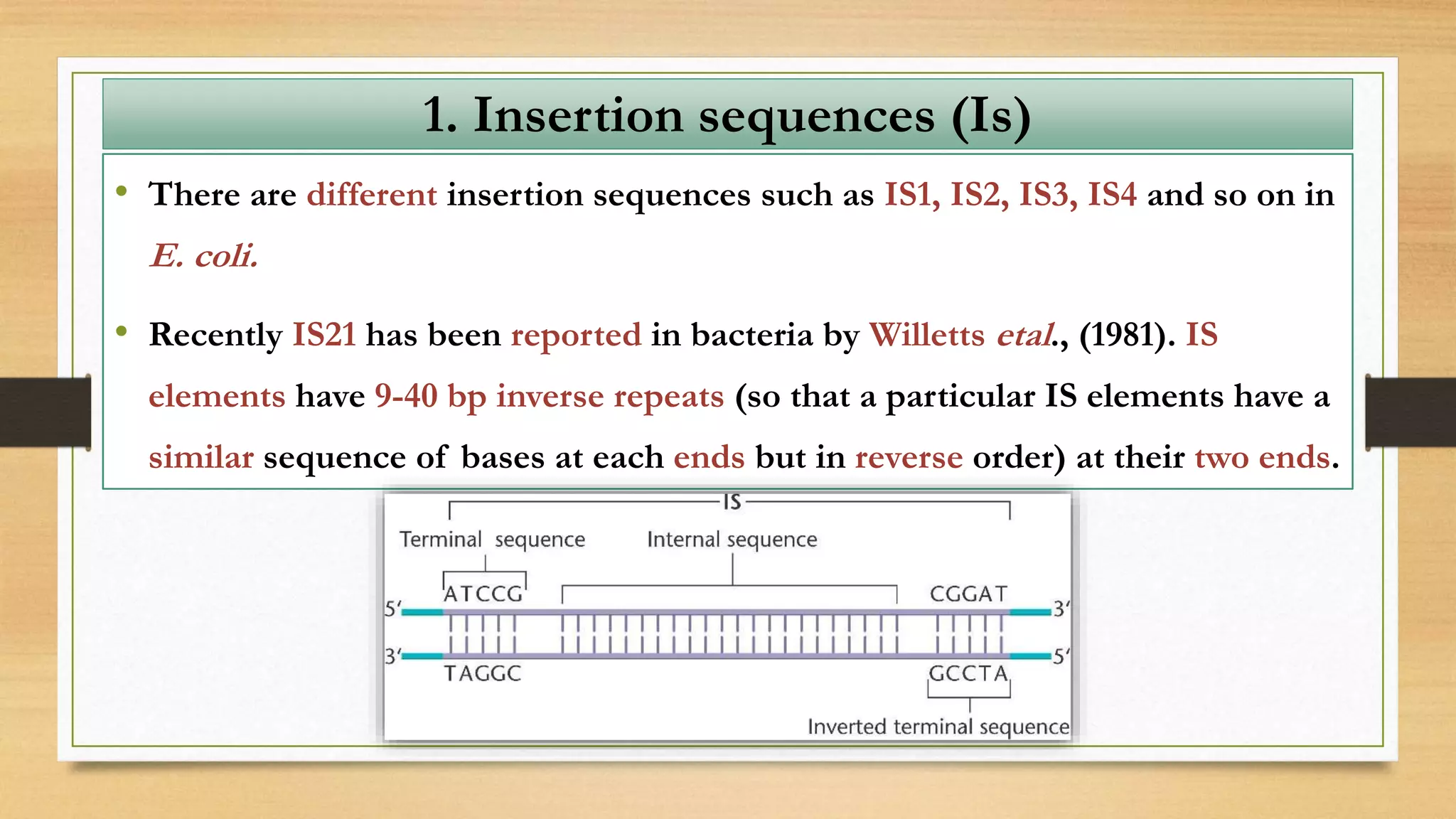
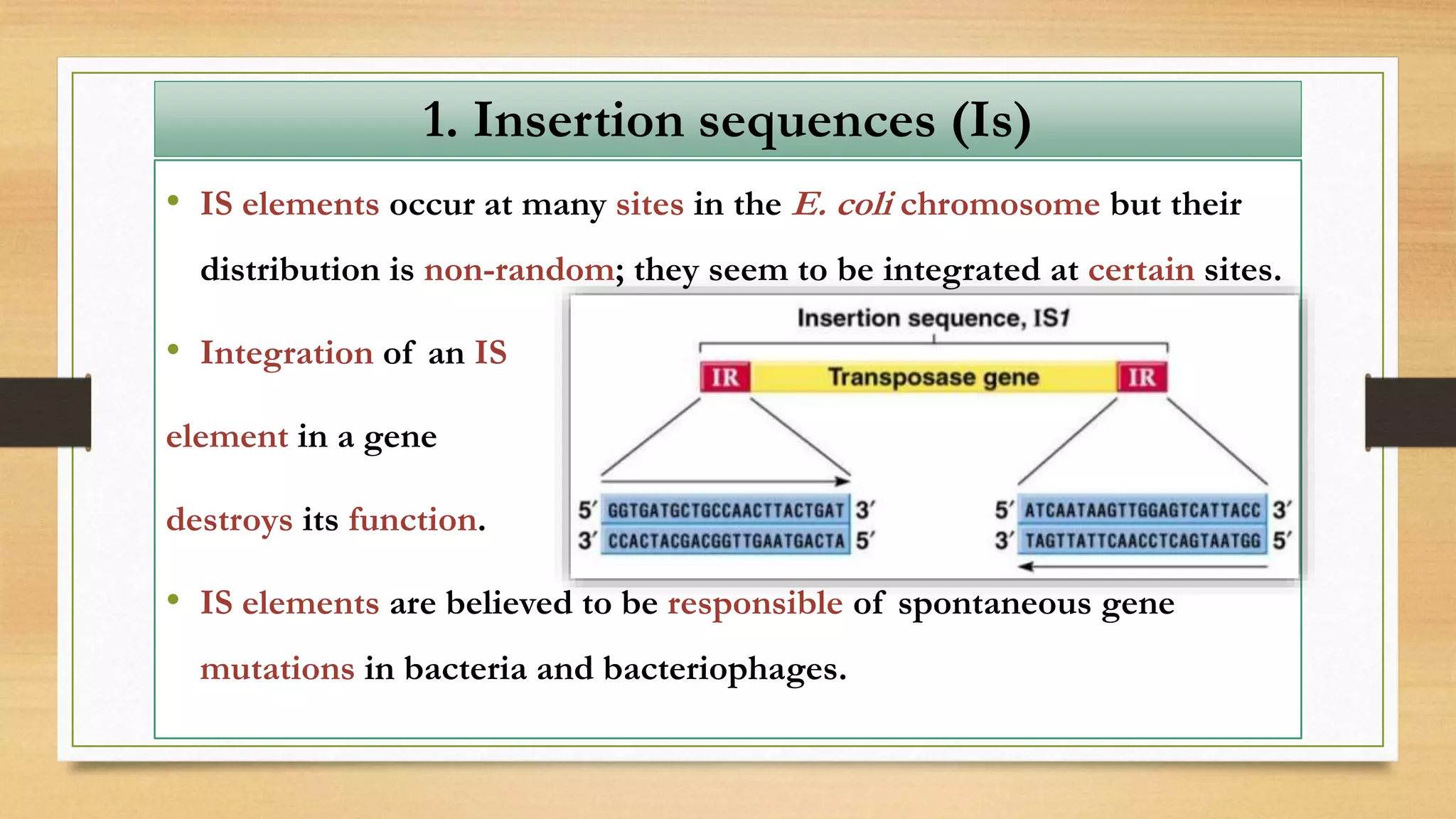
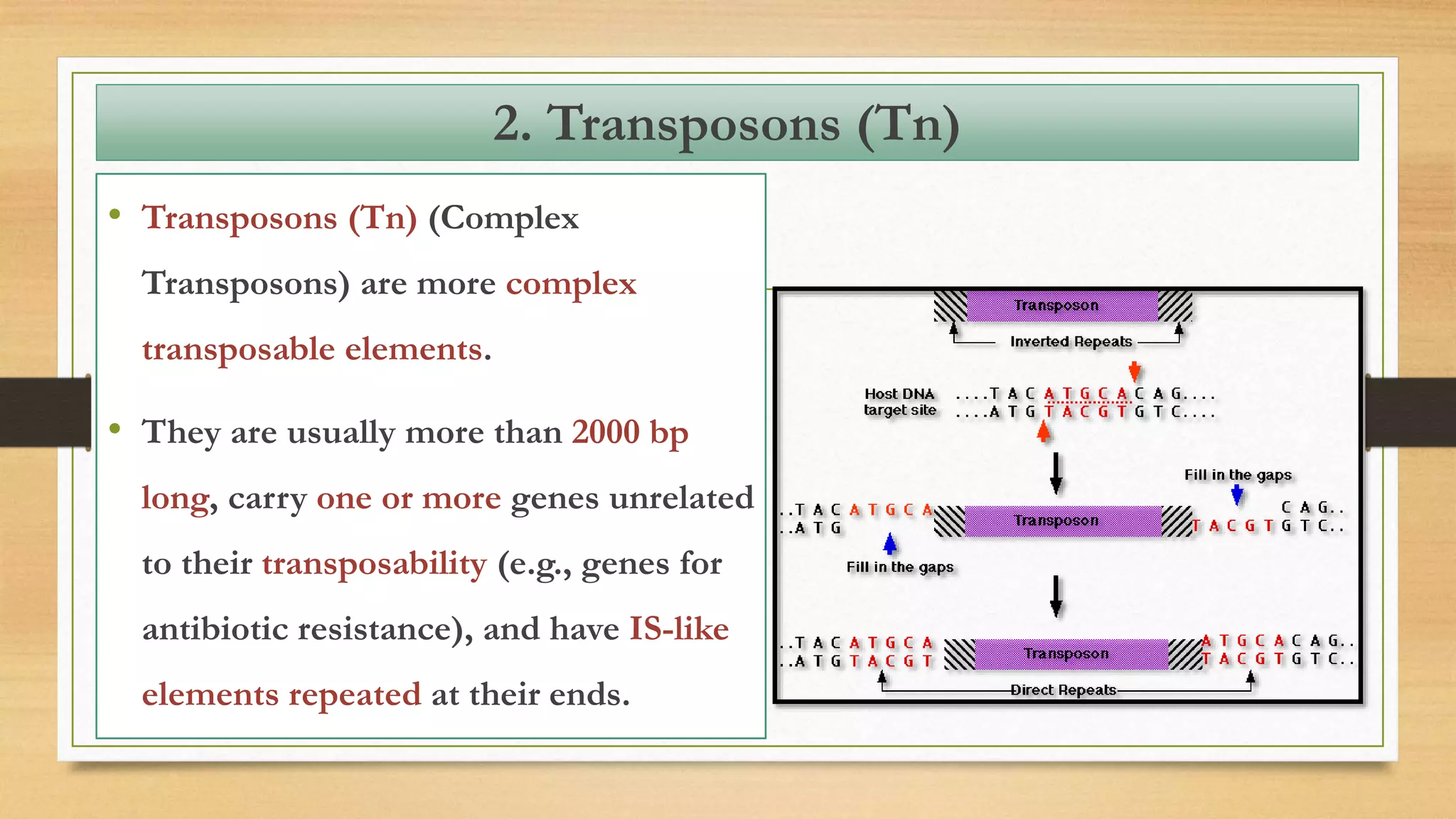
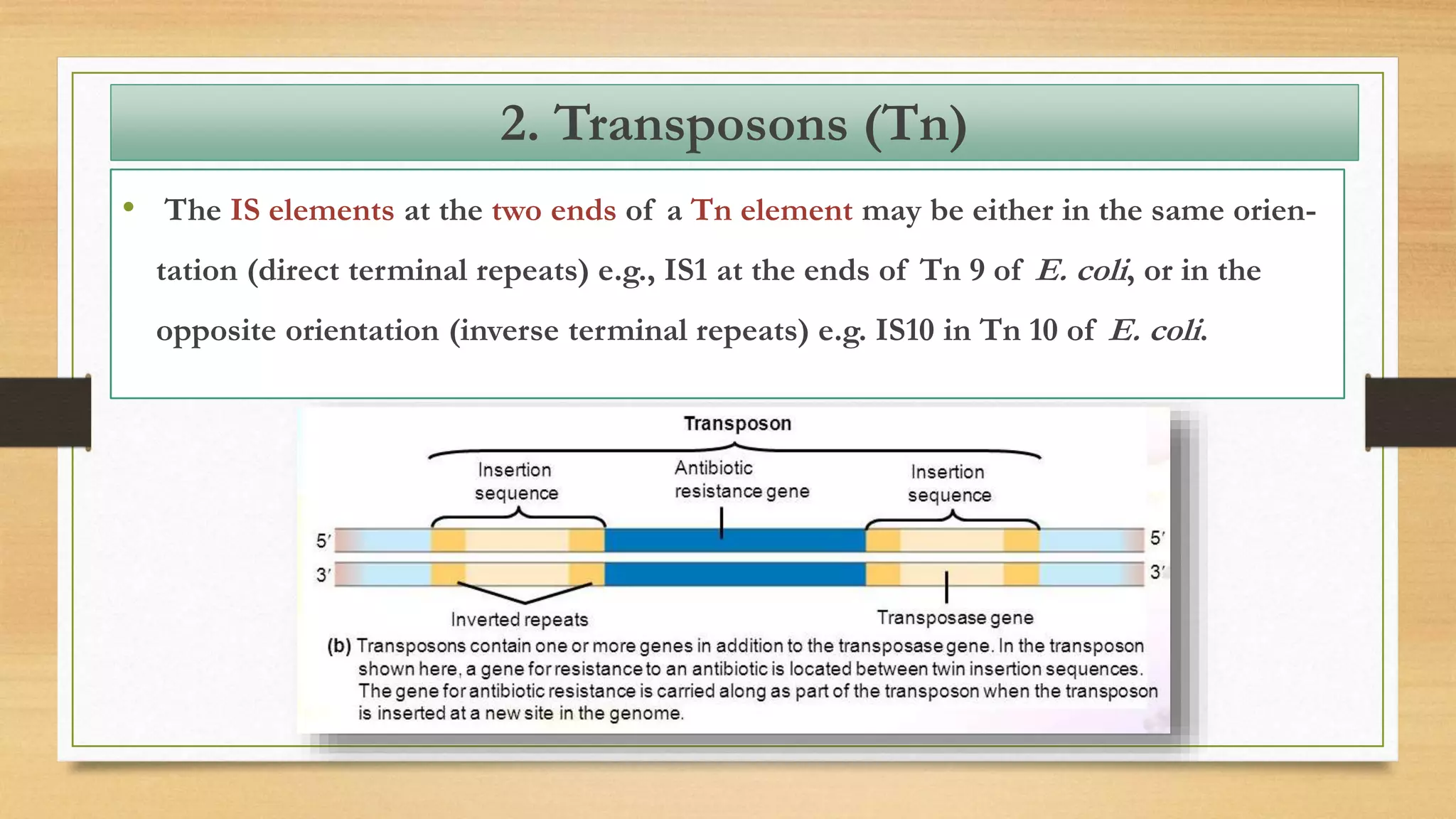
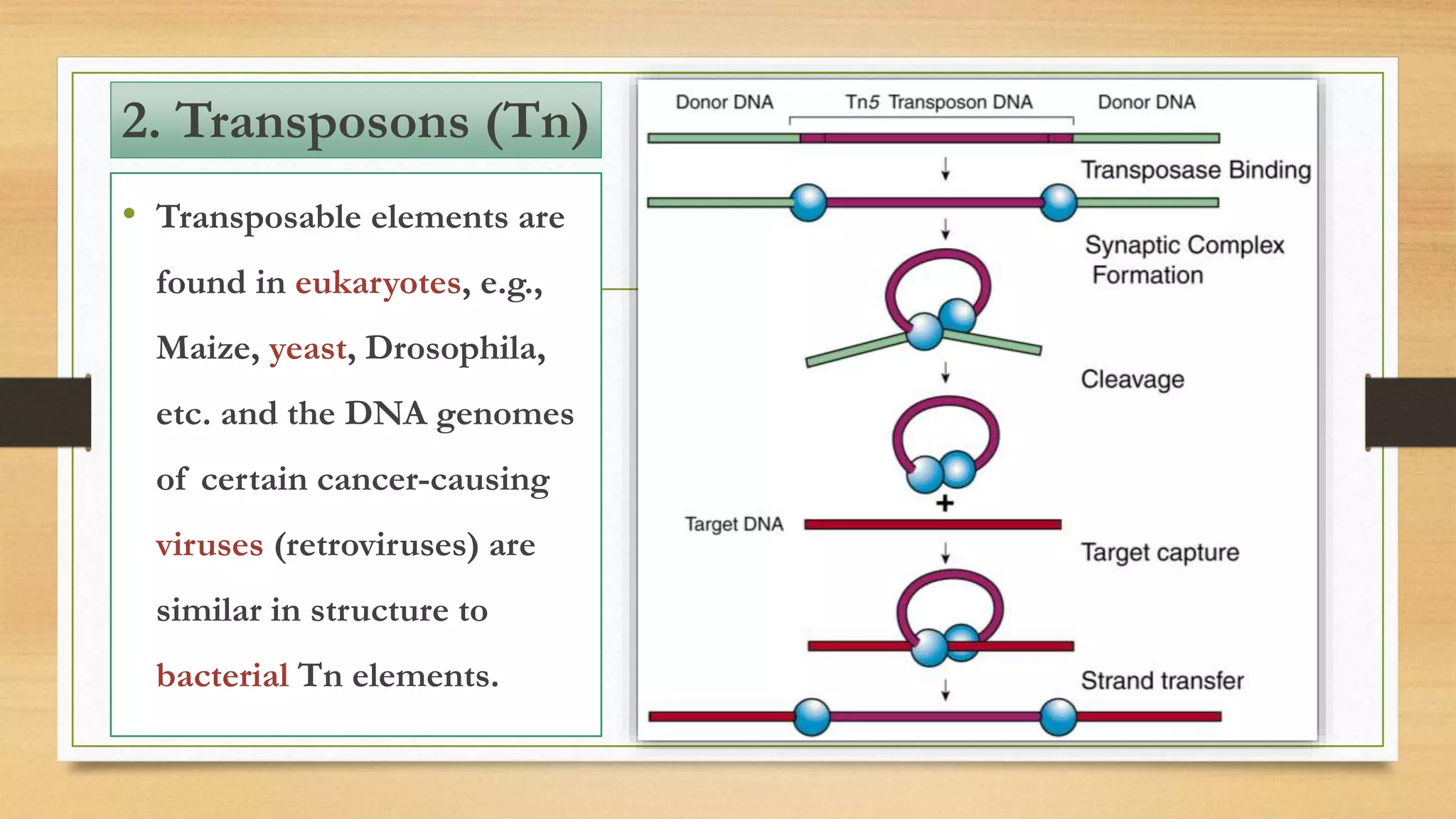
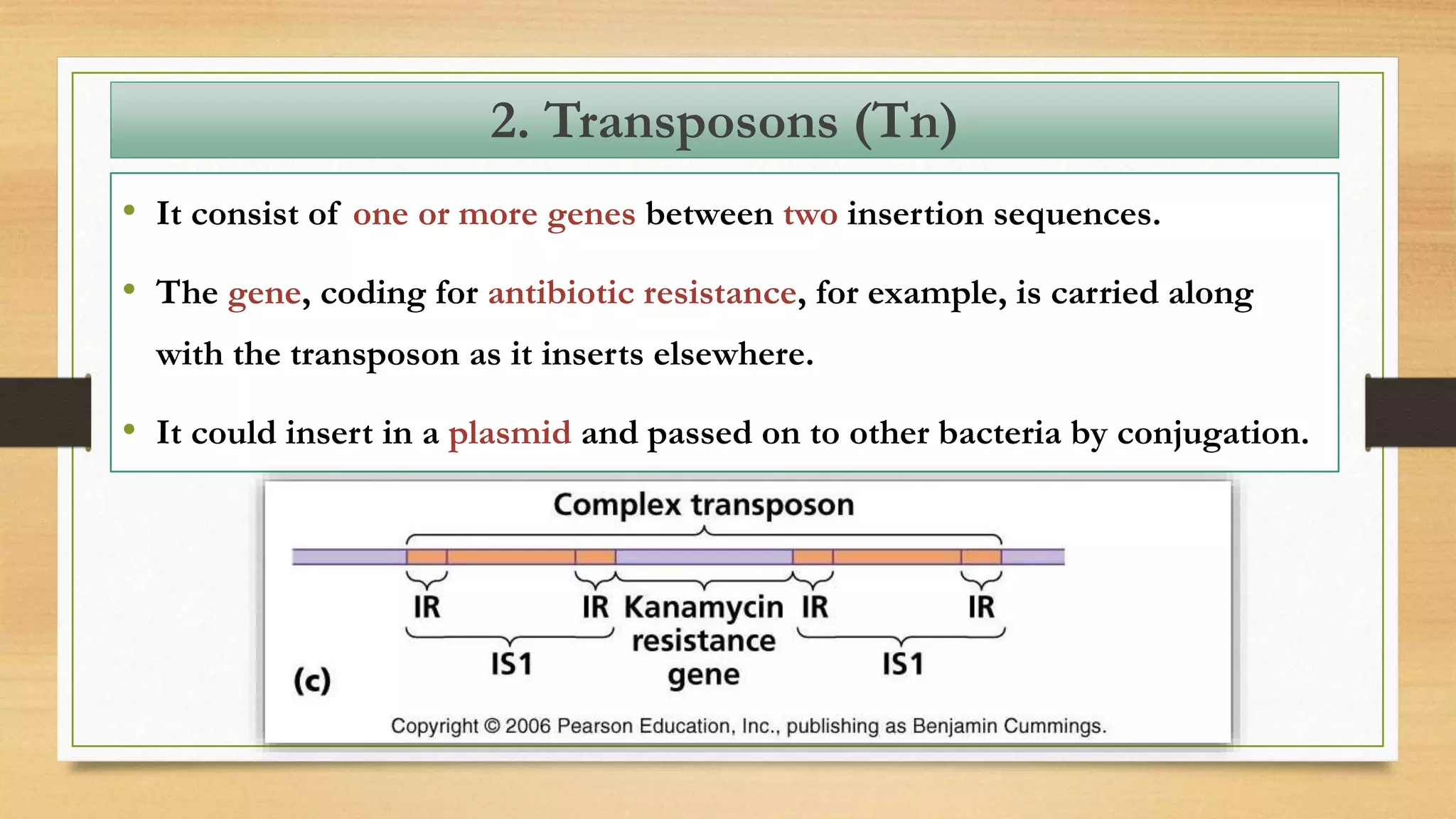
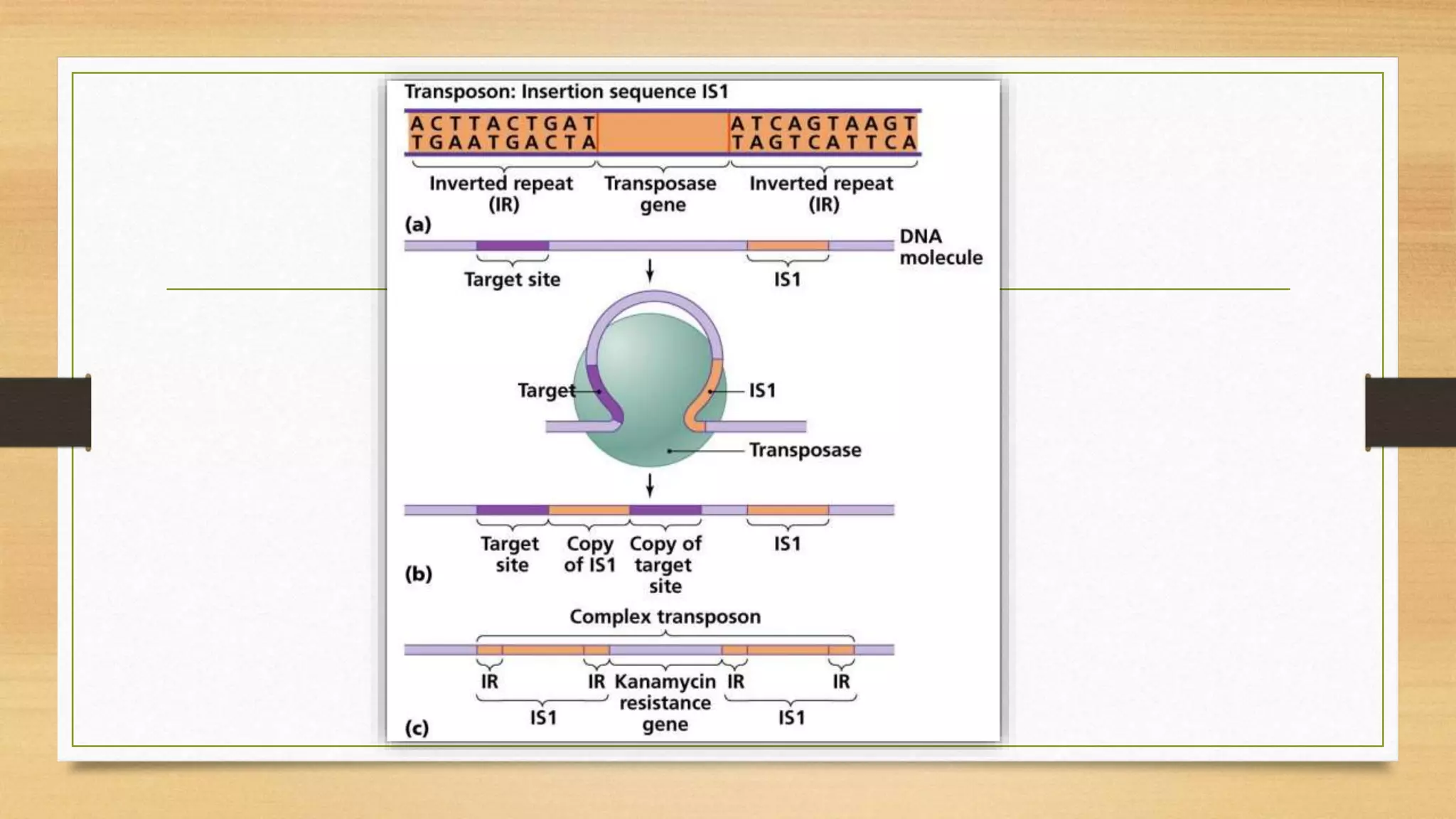
This document discusses plasmids and transposons in bacteria. It explains that plasmids are small, circular pieces of DNA separate from the bacterial chromosome that can contain genes enhancing survival. Plasmids can transfer genes horizontally through conjugation. Transposons are mobile DNA elements that can move locations within a genome, sometimes carrying antibiotic resistance genes. They include insertion sequences and larger transposons, which may contain resistance genes flanked by insertion sequences that allow for transposition. Together, plasmids and transposons facilitate horizontal gene transfer and generation of genetic diversity in bacteria.