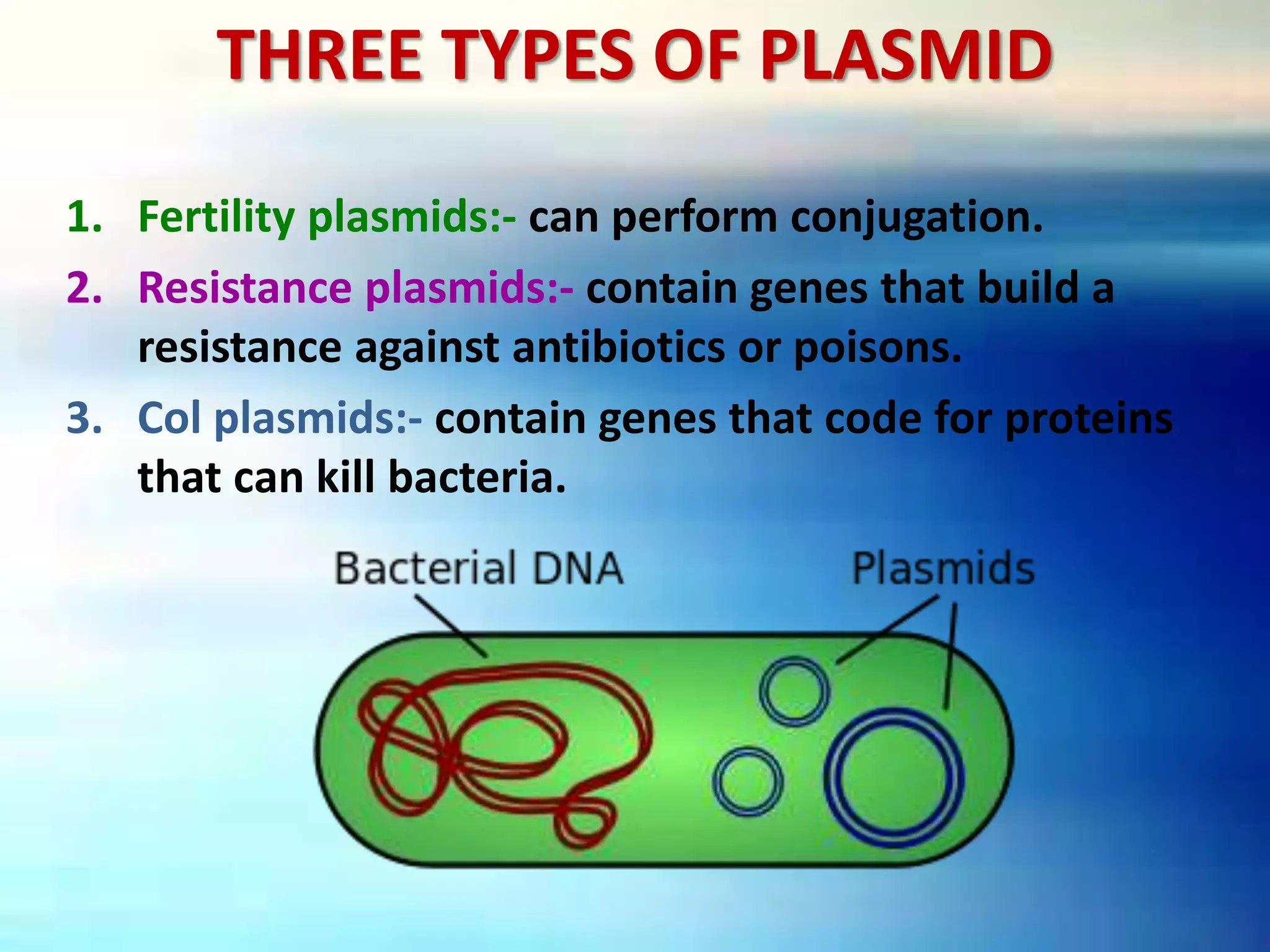
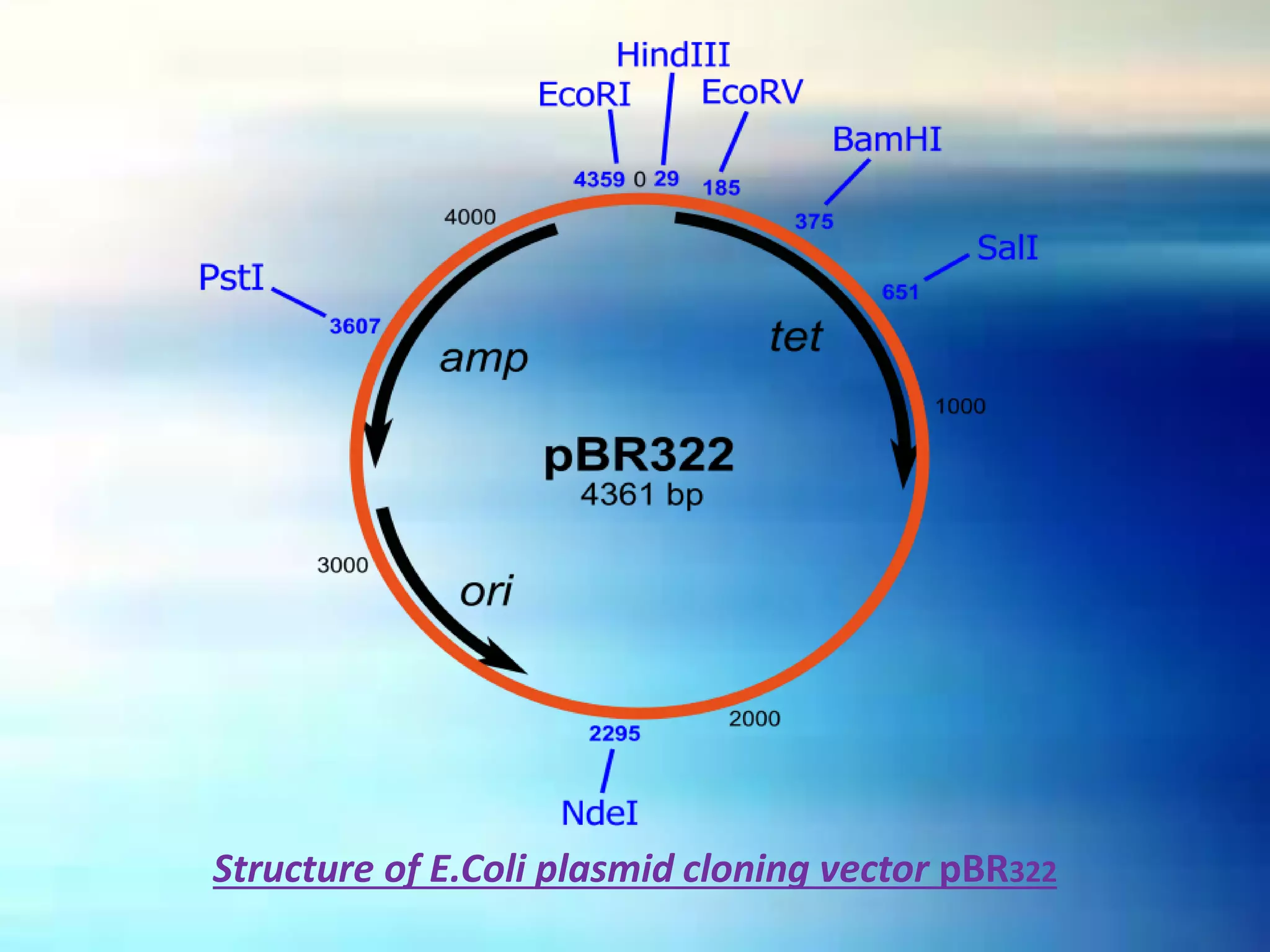
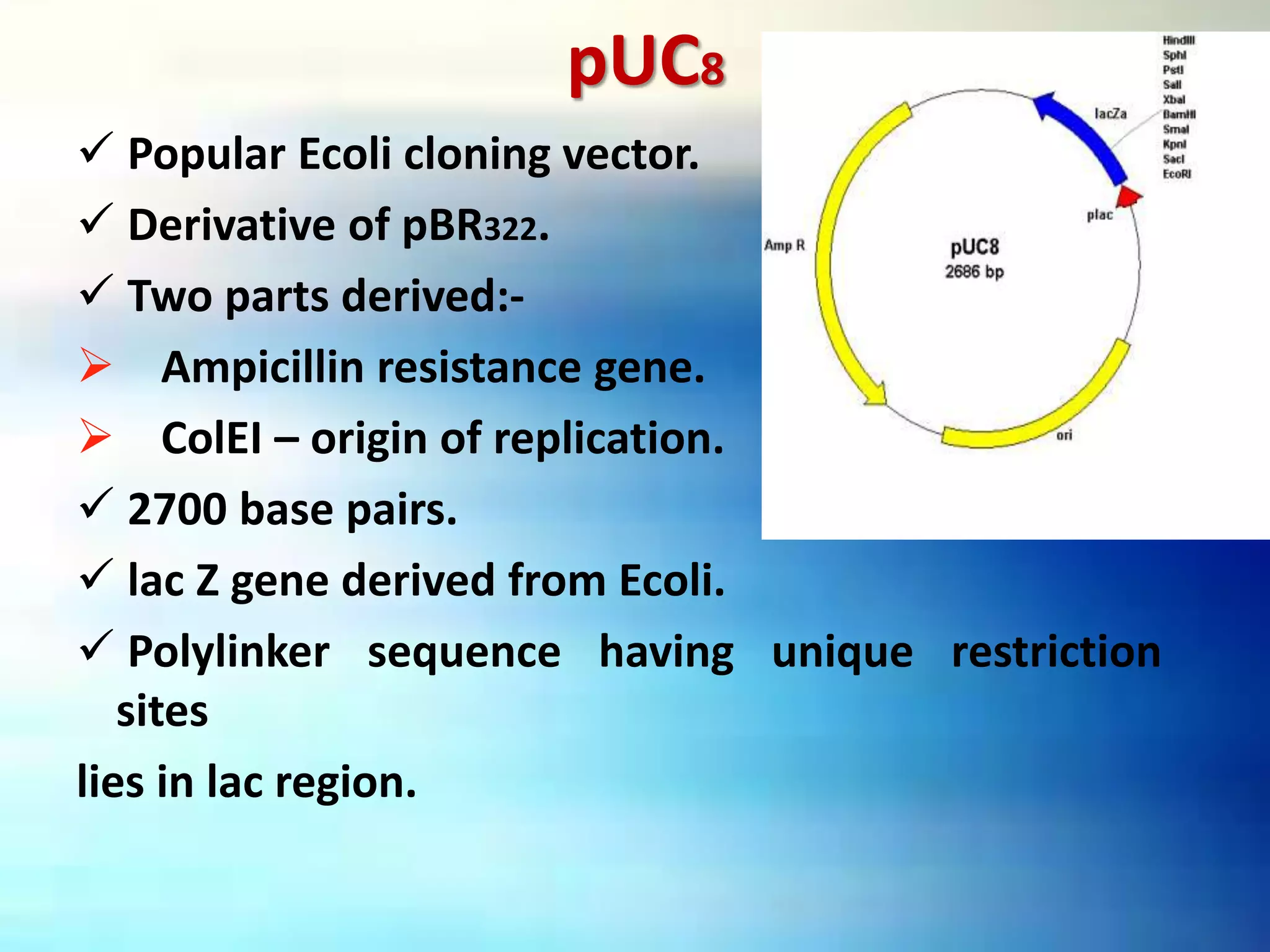
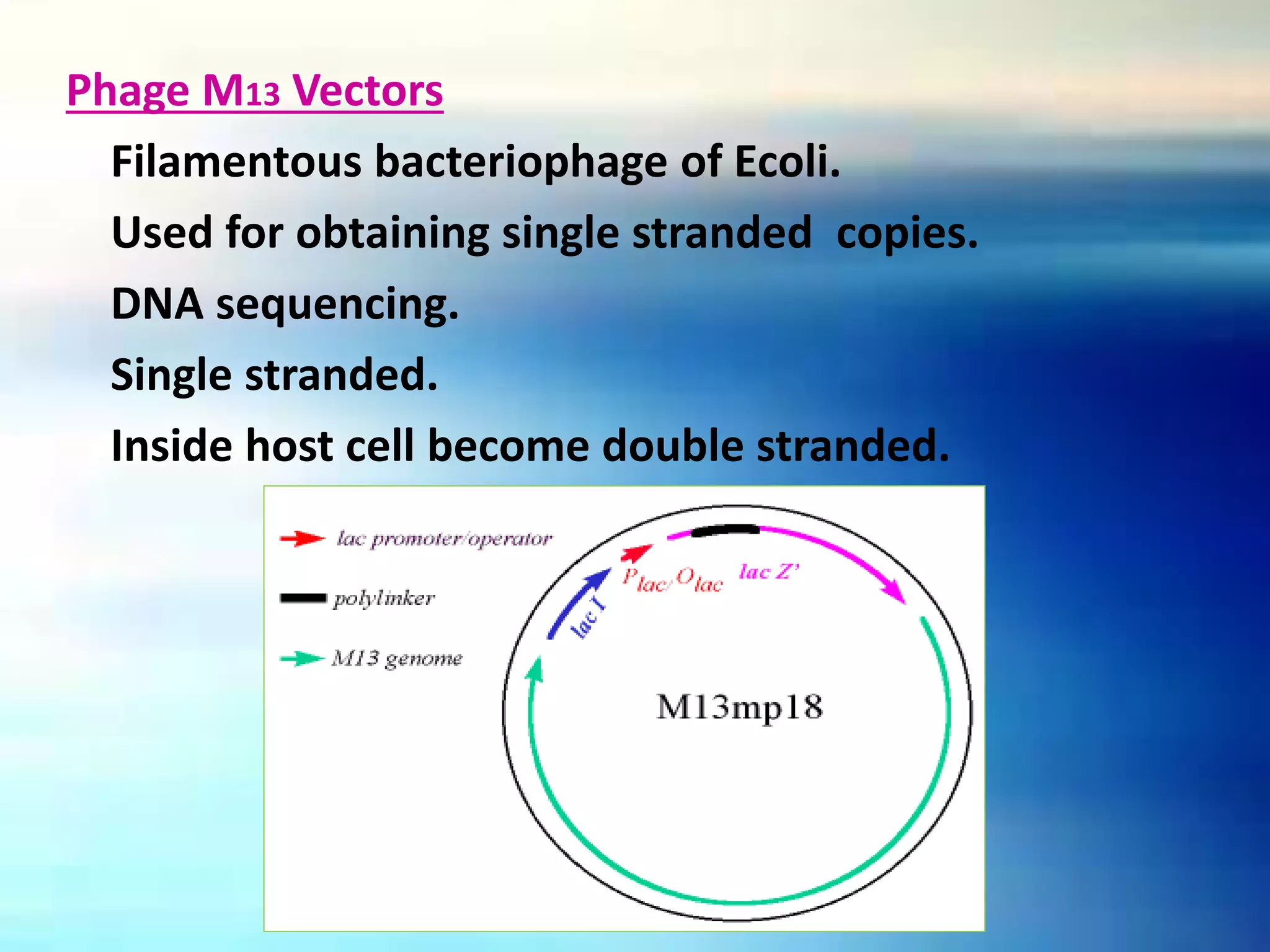
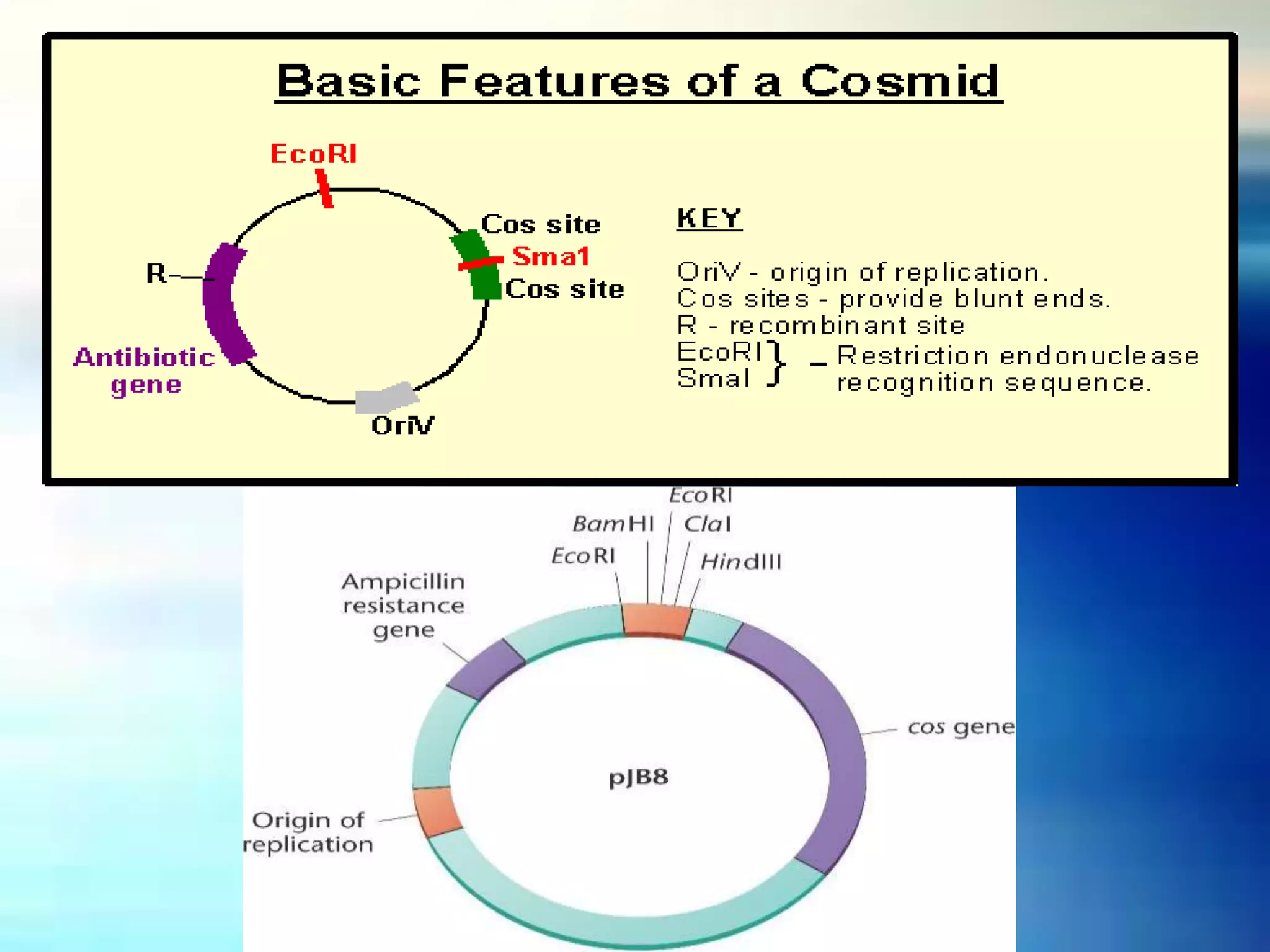
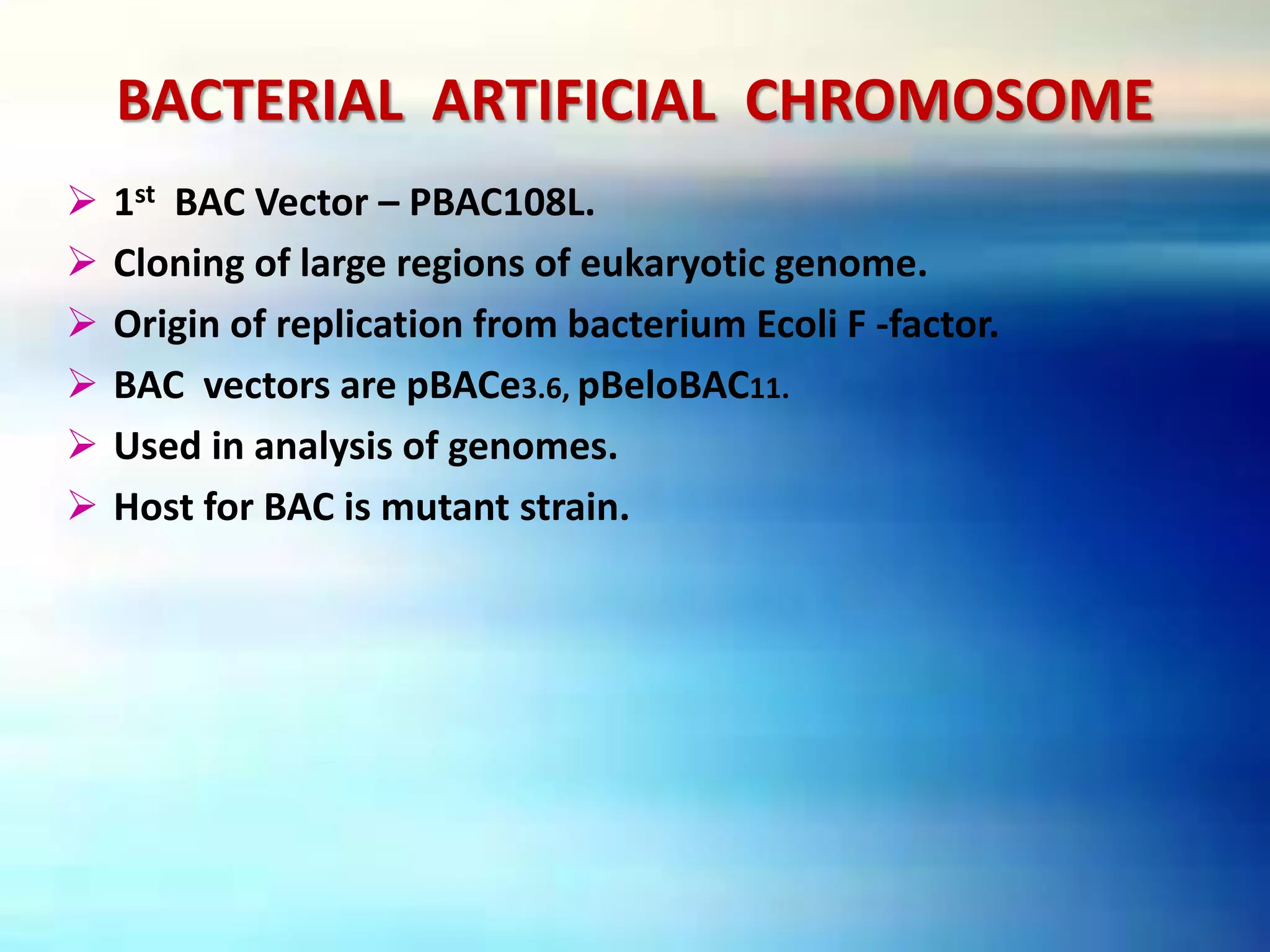
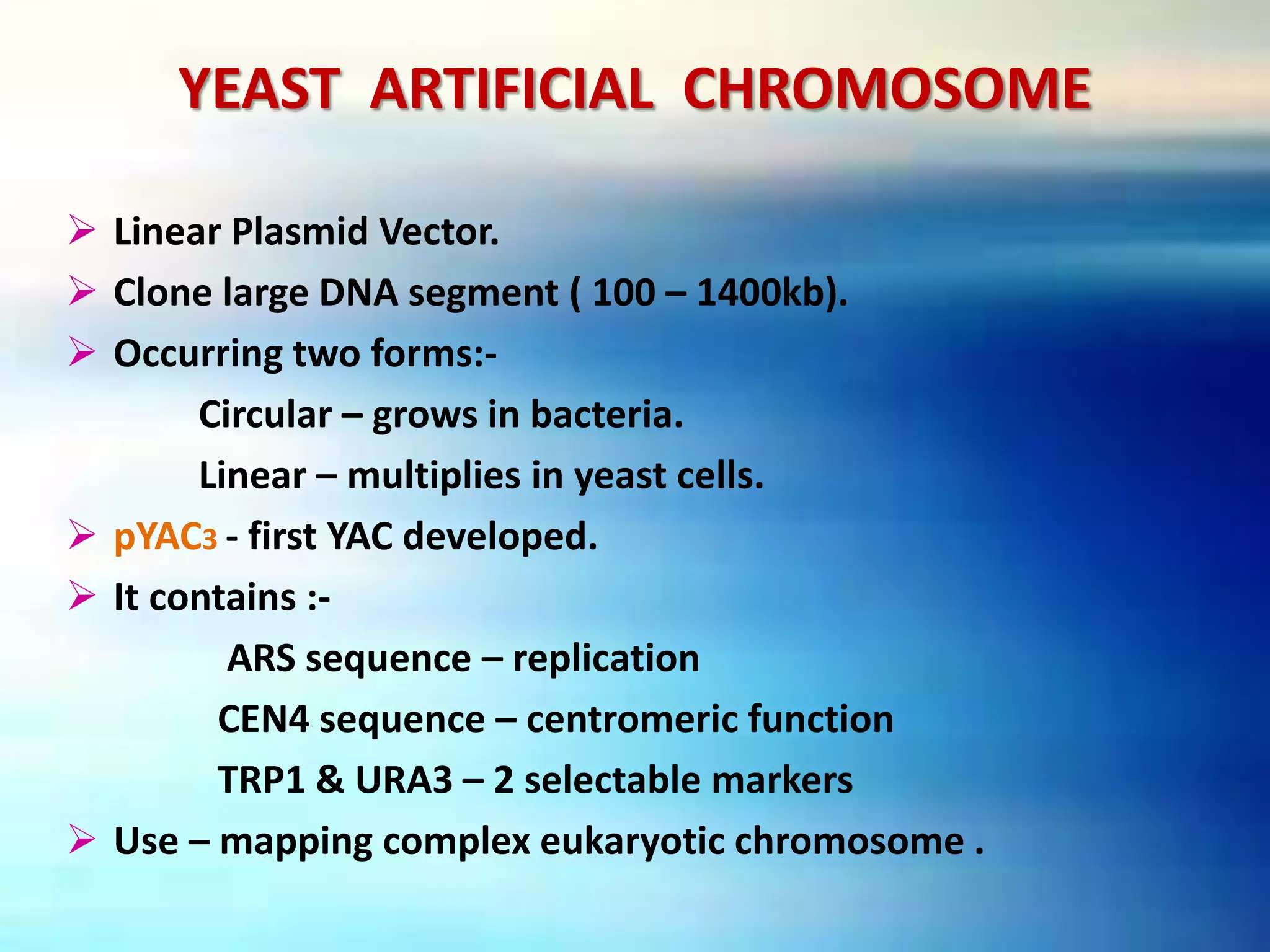
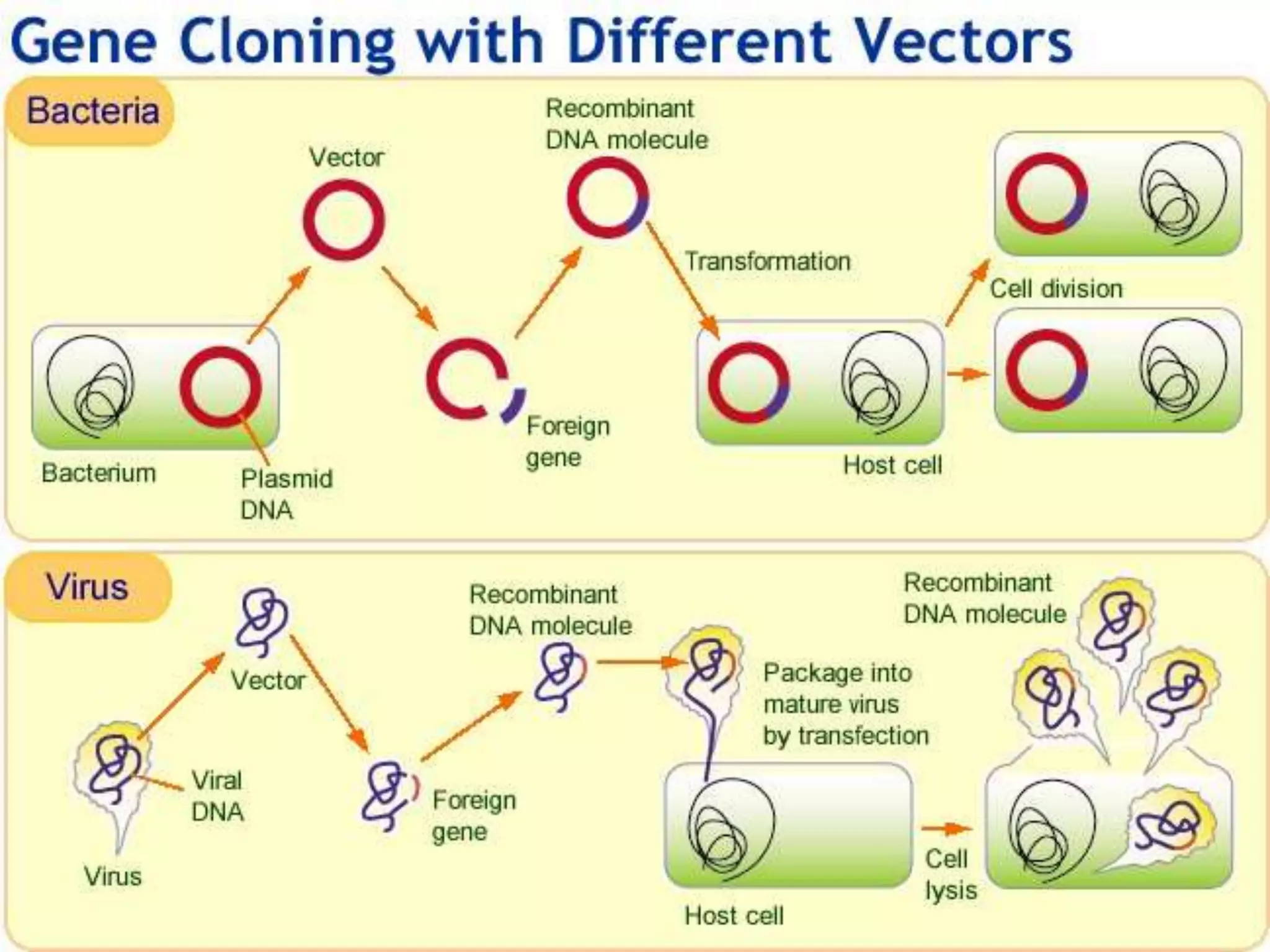
Vectors are DNA molecules that can carry foreign DNA fragments into host cells. There are two main types of vectors: cloning vectors for propagating DNA inserts and expression vectors for expressing inserted DNA. Common vector types include plasmids, bacteriophages, cosmids, and artificial chromosomes. Vectors must have key characteristics like the ability to self-replicate, selectable markers, and origins of replication to successfully clone and transfer DNA.