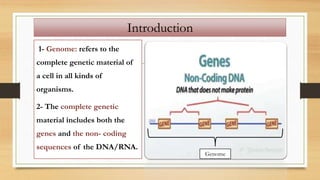
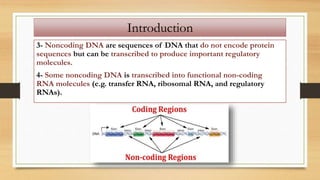
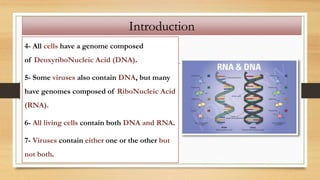
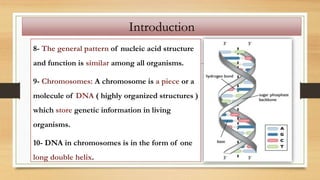
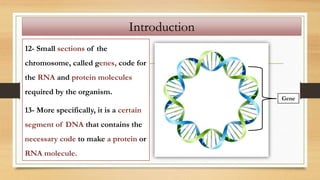
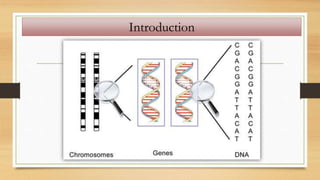
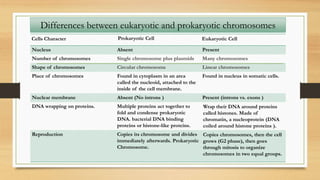
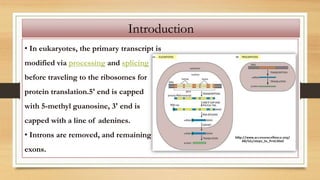
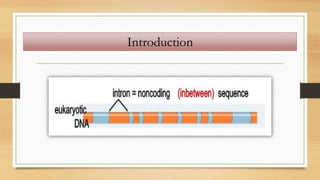
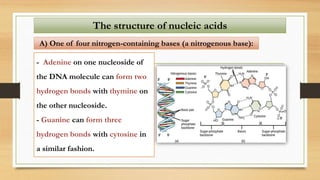
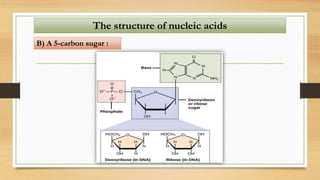
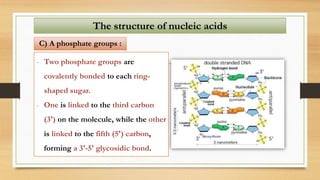
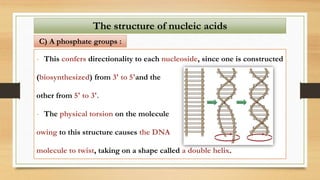
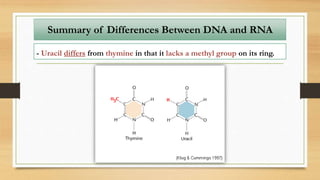
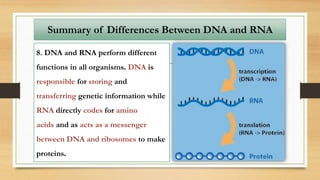
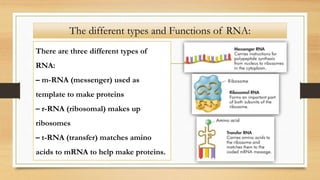
1. The document discusses the structure and function of DNA, RNA, and viral genomes. It explains that DNA contains genes which code for RNA and proteins, while RNA has different types that aid in protein production.
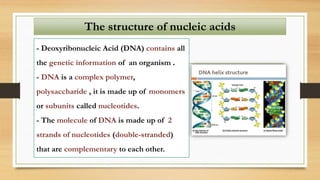
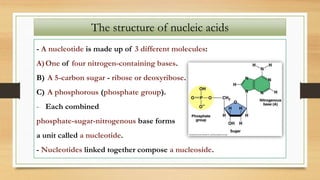
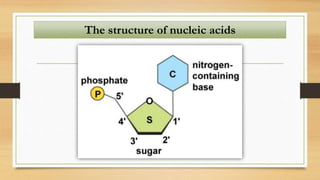
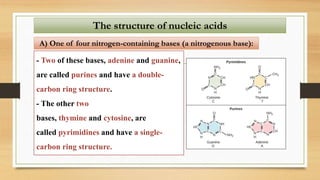
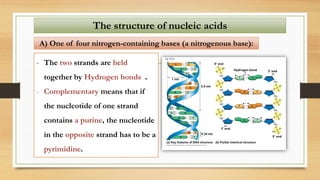
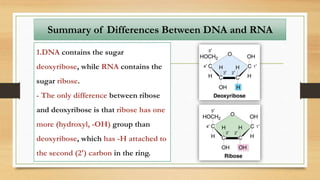
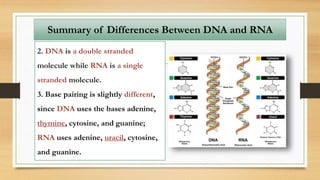
2. The key differences between DNA and RNA are that DNA is double-stranded, more stable, and stores genetic information, while RNA is single-stranded and acts as a messenger between DNA and ribosomes.
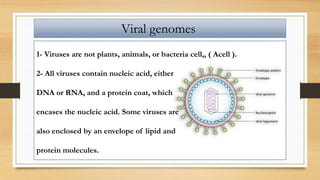
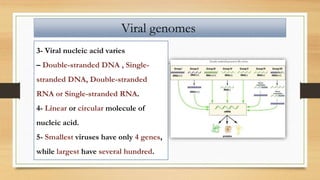
3. Viruses contain either DNA or RNA as their genetic material within a protein coat, and vary in genome size and structure between linear, circular, single-stranded and double-stranded forms.