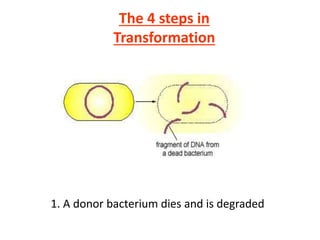
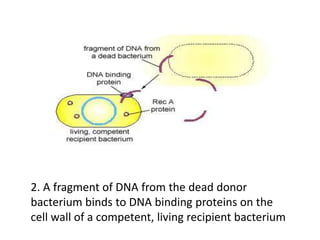
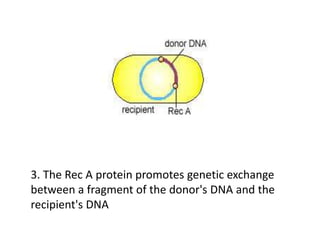
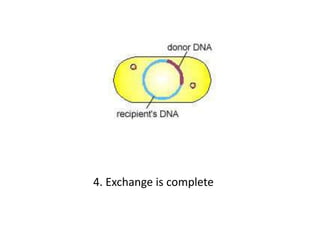
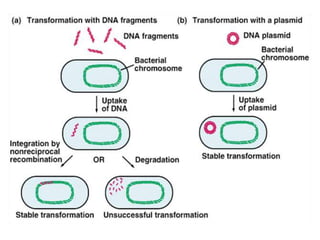
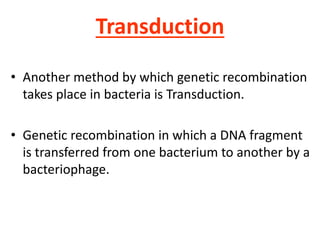
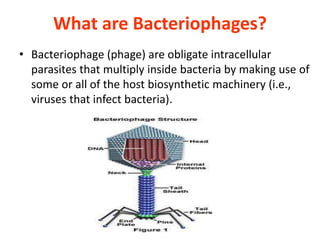
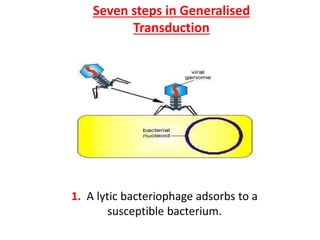
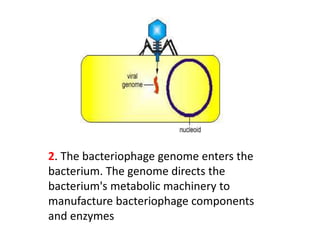
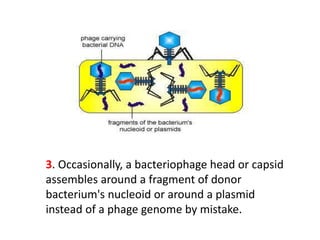
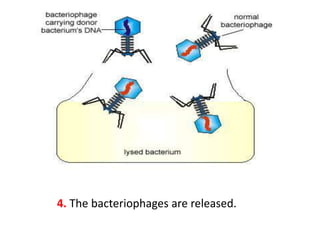
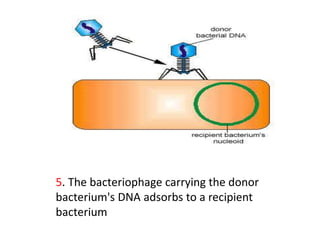
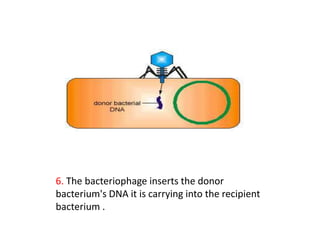
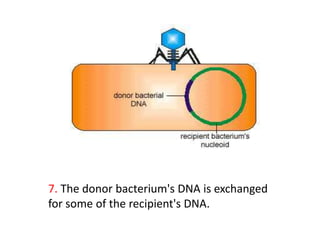
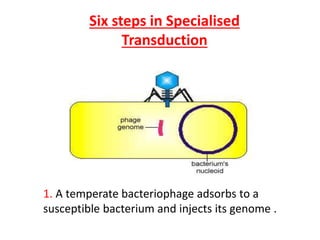
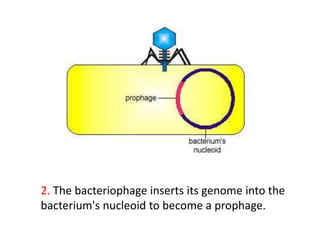
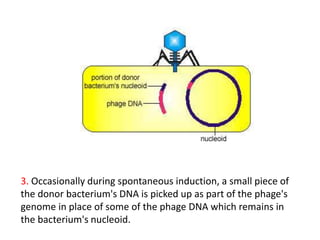
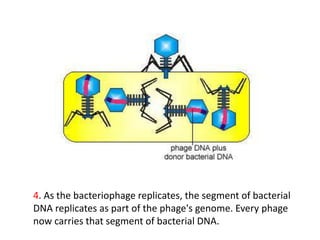
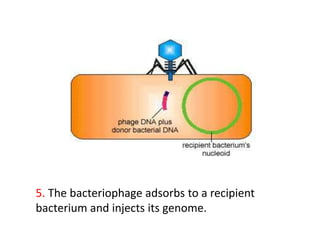
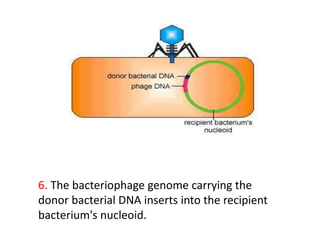
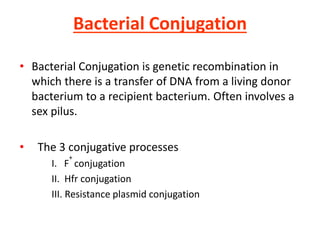
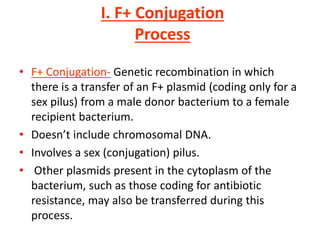
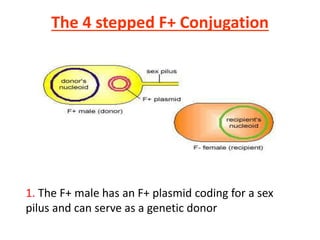
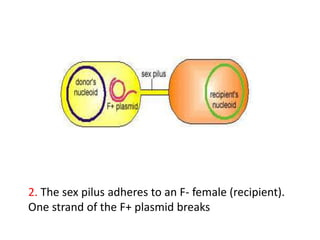
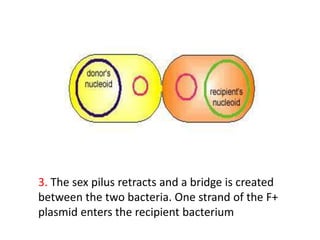
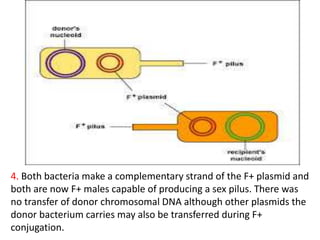
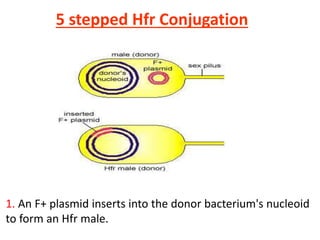
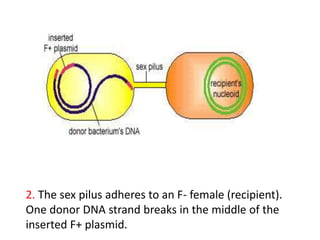
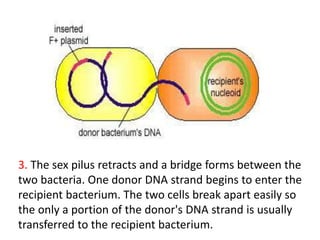
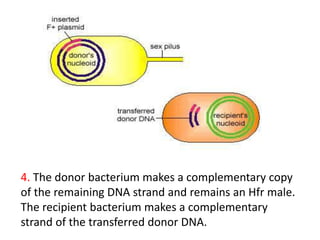
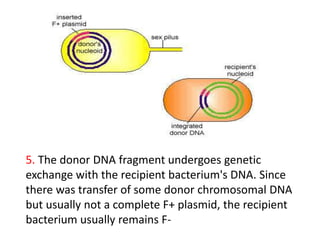
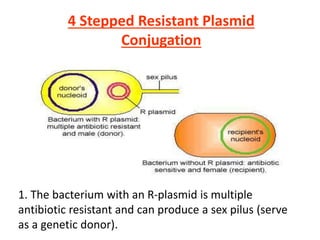
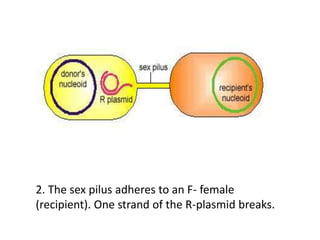
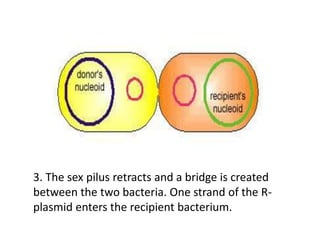
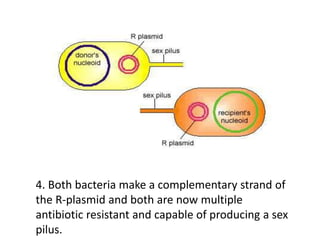
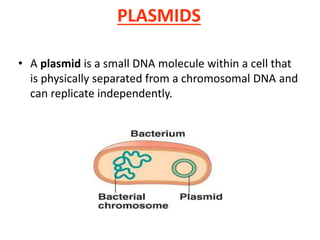
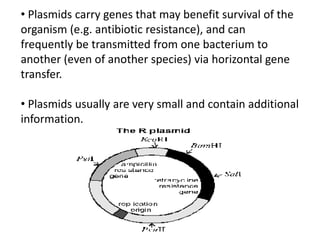
Bacterial genetic recombination can occur through transformation, transduction, or conjugation. Transformation involves DNA uptake from dead bacteria. Transduction involves DNA transfer by bacteriophages. Conjugation involves DNA transfer through cell-to-cell contact via plasmids or sex pili. Plasmids are small extrachromosomal DNA molecules that can replicate independently and be transferred between bacteria. Episomes can exist independently or integrate into chromosomes, and include plasmids, viruses, and transposons.