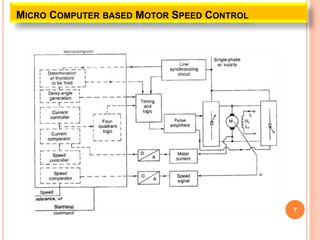
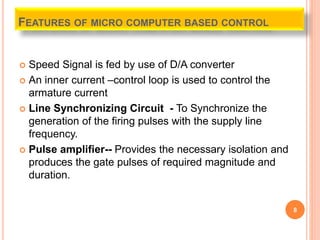
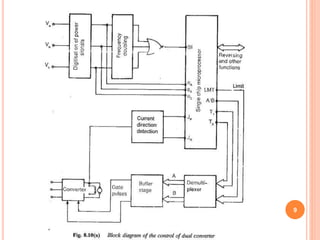
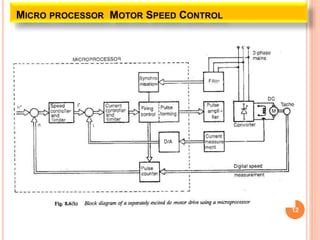
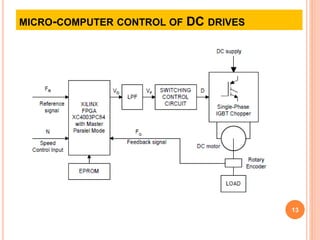
This document discusses the digital control of DC drives using microcomputers. It describes how microcomputers can be used to control the speed and current of DC motors through programs that implement constant torque and constant horsepower operations. The microcomputer provides reliable control, flexibility to change control strategies, and can incorporate additional features like diagnostics and protections. Microcomputers reduce costs and size compared to analog controls while improving control performance and reliability. Speed is detected and current sensed to provide feedback for the inner current and speed control loops implemented through the microcomputer.